The Lamprey is a fascinating creature that belongs to the animal kingdom. In this blog post, we will explore the history, facts, size, habitat, and classification of the Lamprey. If you have an interest in learning about different animals, then you have come to the right place.
The Lamprey is an ancient species that has been around for millions of years. It is a jawless fish that can be found in both freshwater and saltwater environments. Lampreys are known for their unique feeding habits – they attach themselves to other fish and extract their blood. This might sound a bit creepy, but it’s a natural way of survival for the Lampreys.
In terms of size, Lampreys can vary greatly. They can range from a few inches to a couple of feet in length. Their bodies are long and slender, perfectly designed for their purpose in life. These incredible animals can be found in various habitats around the world, from rivers to oceans. They are known to migrate long distances in search of food and suitable breeding grounds.
In summary, Lampreys are ancient jawless fish that have a unique way of feeding. They come in different sizes and can be found in various habitats. If you want to learn more about animals, don’t forget to check out our extensive article on 155+ Animals Name. In our next blog posts, we will dive deeper into the world of different animals and explore their intriguing characteristics.
History of Lamprey
The lamprey is an ancient creature that has been around for millions of years. It belongs to a group called jawless fish, which means it does not have a proper jaw like most other fish. This unique feature sets it apart from other animals in the animal kingdom.
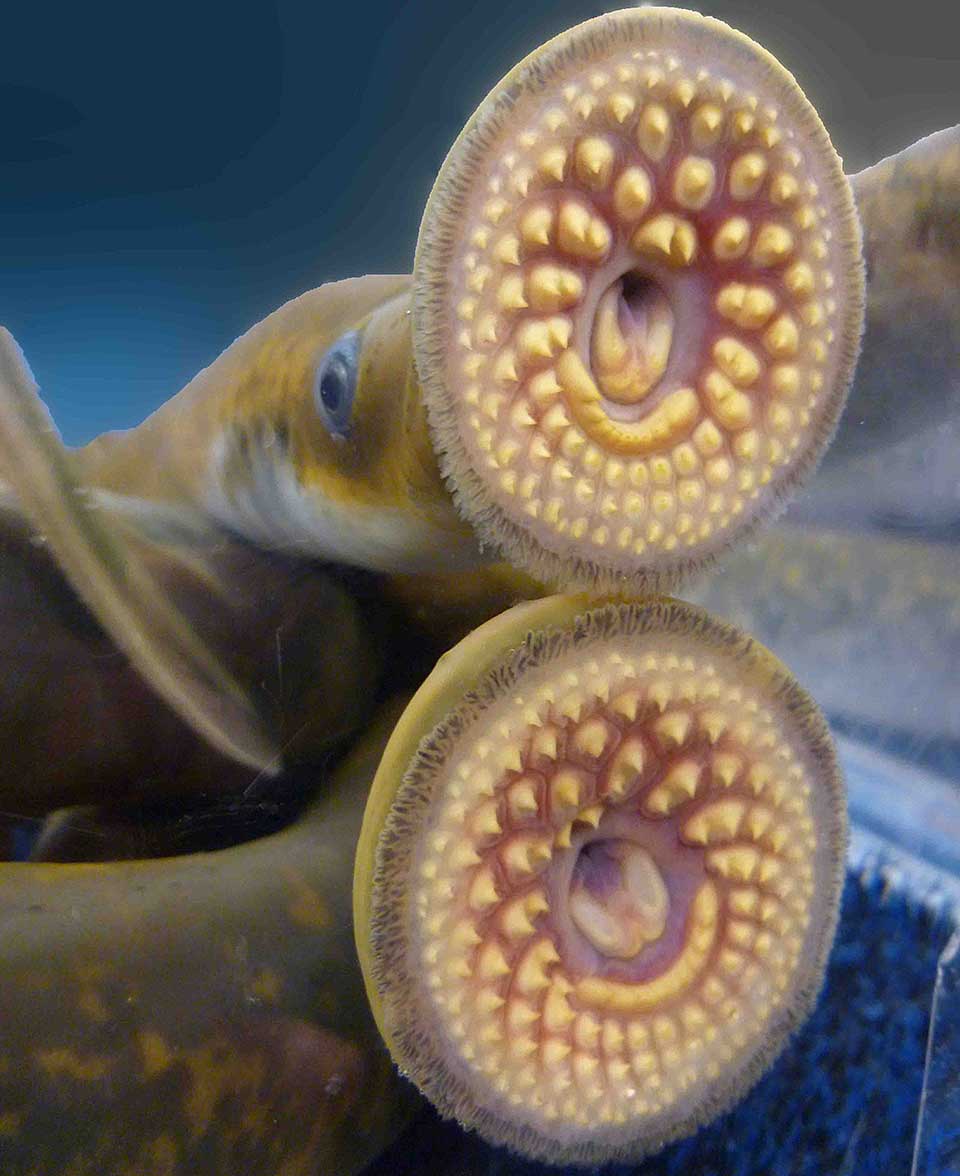
Lampreys have a long, slender body that is typically covered in smooth, slimy skin. They have a round mouth filled with rows of sharp teeth, which they use to attach themselves to other fish and suck their blood. This may sound a bit scary, but it’s how lampreys survive and get their food.
These fascinating creatures have been around since the time of dinosaurs! Fossils of lampreys have been found that are over 360 million years old. They have survived through many changes in the Earth’s environment and have adapted to different habitats. Lampreys can be found in both freshwater and saltwater, and some of them even travel between the two for different stages of their life cycle.
In conclusion, lampreys are a unique and ancient type of fish that have been around for millions of years. They are jawless, have a long and slimy body, and are known for their blood-sucking ability. Despite their scary reputation, lampreys are an important part of the animal kingdom and have survived through many changes in the Earth’s history.
Importance of Lamprey
Lamprey is an important animal in our ecosystem. These creatures play a vital role in maintaining the balance of nature. They are an essential part of the food chain, connecting different living organisms.
Firstly, lampreys are important for their benefits in nutrient recycling. Lampreys feed on dead fish and carcasses that sink to the bottom of rivers and oceans. By consuming these decaying organisms, lampreys help break down the remains and return valuable nutrients back into the water. This process supports the growth of algae and other plants, which are the primary food source for many aquatic animals.
Secondly, lampreys are indicators of water quality. These animals are very sensitive to changes in the environment, particularly pollution. If there is a decline in lamprey population, it may indicate that there are problems in the ecosystem, such as pollution or habitat destruction. Monitoring lampreys can help scientists assess the overall health of an aquatic ecosystem and take necessary actions to protect it.
Lastly, lampreys have been studied by scientists to gain insights into human health. They possess unique characteristics that make them suitable for scientific research, especially in understanding our own nervous system and genetics. By studying lampreys, scientists can develop new treatments and medications for various human diseases and conditions.
In conclusion, lampreys are essential for maintaining a healthy environment. They contribute to nutrient recycling, act as indicators of water quality, and provide valuable insights for medical research. Protecting and understanding these creatures is crucial for the well-being of our planet and ourselves.
Amazing Facts About Lamprey
1. Lampreys are jawless fish that belong to the class of animals called cyclostomes.
2. There are around 38 known species of lampreys, found in both freshwater and marine habitats.
3. These animals have a long, cylindrical body with smooth skin and a round mouth surrounded by a disc-like sucker.
4. Lampreys have no bones, instead, their skeleton is made up of a flexible cartilage structure.
5. These creatures have a unique feeding mechanism. They attach themselves to other fish by suctioning onto their bodies with their oral disc, then use their sharp, tooth-like structures to rasp through the fish’s skin and feed on their blood and body fluids.
6. Lampreys primarily feed as parasites, but some species are non-parasitic and feed on organic debris or small invertebrates.
7. Lampreys have a complex life cycle, varying between species. Most lampreys start their life cycle as larvae, living in streams or rivers and filter-feeding on organic particles.
8. After several years as a larva, lampreys undergo a metamorphosis that transforms them into adult forms, allowing them to migrate to the ocean or stay in freshwater depending on their species.
9. Lampreys are remarkable migrators, known for their lengthy journeys. Some species can travel over 3,000 kilometers from the ocean to breed in freshwater streams and rivers.
10. Unlike most fish, lampreys do not have gills in their early stages. Instead, they have specialized structures called gill pouches, which they use to extract oxygen from the water.
11. These animals have a keen sense of smell, which they use to locate their prey and navigate in their environment.
12. Lampreys have a skeleton composed of cartilage, similar to sharks, making them more flexible than bony fish.
13. Most lamprey species have a distinct silver or brownish coloration, helping them blend in with their surroundings.
14. These animals have poor eyesight and rely mostly on their sense of smell and touch to detect their environment and prey.
15. Lampreys play a vital role in the ecosystem as both prey and predators. They serve as a food source for various fish, birds, and mammals, while also controlling the populations of certain fish species.
Can we keep Lamprey as our Pet?
Lampreys are not suitable pets. They are a type of primitive fish found in freshwater and saltwater habitats. Lampreys have a unique appearance with round, elongated bodies and suction cup-like mouths that they use to attach themselves to other fish and feed on their blood.
Firstly, lampreys are not commonly kept as pets because they have specific needs that are difficult to meet in a home environment. They require specific water conditions and a suitable diet, which can be challenging to provide. Lampreys are also known to be parasitic, meaning they attach themselves to other fish and feed on their blood. This behavior makes them unsuitable for keeping in a tank with other fish or as a pet in general.
Moreover, it is crucial to understand that lampreys are not extinct. However, even if they were, it would still be inappropriate to keep them as pets. When an animal goes extinct, it means that it no longer exists in the world. This can happen due to various reasons, such as changes in the environment or human activities. If a species becomes extinct, it is sad because it means that we have lost that type of animal forever. Keeping an extinct animal as a pet is not possible because there are none left.
In conclusion, lampreys are not suitable pets due to their specific needs and parasitic behavior. They are not extinct, but even if they were, it would still be inappropriate to keep them as pets. It is important to respect animals and their natural habitats, ensuring their well-being and preservation for future generations.
Size of Lamprey
The lamprey animal is a fascinating creature that often surprises people with its size. These strange fish-like animals can vary in size, but most lampreys grow to be about 12 to 20 inches long. That’s like the length of a ruler or a large-sized school binder! Some of the biggest lampreys can even reach up to three feet in length, which is about the same size as a toddler. Can you imagine a fish that long?
Even though lampreys may not seem huge compared to other animals, their size is still quite impressive considering their unique characteristics. Unlike most fish, lampreys don’t have jaws or scales. They have a round, eel-like body with a sucker-like mouth filled with rows of sharp teeth. This allows them to attach themselves to other fish and feed on their blood. So, if you were a little fish swimming in the water, you would definitely want to watch out for these lampreys!
In summary, lampreys are typically 12 to 20 inches in length, although some can grow up to a whopping three feet long. Despite their seemingly small size, lampreys are fascinating creatures due to their jawless mouths and suction-like abilities. These unusual characteristics allow them to attach themselves to other fish and survive by feeding on their blood. Isn’t nature amazing?
Habitat of Lamprey
Lamprey animals live mostly in freshwater habitats, such as lakes, rivers, and streams. These unique creatures can also be found in some coastal regions where the water is not too salty. Lampreys prefer cool and clean waters as they need a good amount of oxygen to survive.
In their natural habitat, Lampreys usually hide under rocks, logs, or inside crevices. They use their round mouths filled with sharp teeth to attach themselves to fish or other organisms. This is how they feed and obtain their food. Lampreys are parasitic animals, which means they attach themselves to other animals to get their blood or body fluids.
Lampreys are pretty adaptable and can tolerate a range of water conditions. However, changes in water quality, pollution, or destruction of their habitat can greatly affect their survival. Humans have a responsibility to protect their environment and ensure that their habitats remain healthy.
In conclusion, lampreys thrive in freshwater habitats around the world. These resilient creatures are often found in cool, clean waters and have the ability to adapt to various conditions. As parasitic animals, lampreys rely on other organisms for sustenance, attaching themselves to fish or other animals. However, their survival is at risk when their natural habitats are polluted or destroyed, emphasizing the importance of conservation efforts to safeguard their homes.
Evolution of Lamprey
Lampreys are ancient creatures that have been around for quite a long time. They can be traced back to an era even before dinosaurs roamed the Earth. These unique animals have gone through many changes over millions of years, evolving and adapting to survive in different environments.
In the beginning, lampreys were simple creatures with a basic body structure. They were jawless and had circular sucker-like mouths. These mouths helped them attach to other fish and feed on their blood. It was their main source of food, and they became quite skilled at it. However, as time passed, lampreys began to develop more advanced features.
One significant change in lamprey evolution was the development of a spinal cord. This allowed them to control their body movements and find new ways to navigate through the water. They also started to develop eyes, which helped them detect prey and avoid danger. These new adaptations enabled lampreys to evolve and expand into different habitats. Today, lampreys can be found in both freshwater and saltwater environments all around the world.
In conclusion, lampreys have come a long way since their early beginnings. They have evolved from simple, jawless creatures into more complex organisms with advanced features like spinal cords and eyes. Their ability to adapt to changing environments has allowed them to survive for millions of years, proving that evolution is an essential process for the survival of any species. Understanding the evolution of lampreys helps us appreciate the diversity and complexity of life on Earth.
Classification of Lamprey
The lamprey animal belongs to the class of jawless fishes called Agnatha. These unique creatures have been around for millions of years and have a very simple and primitive body structure. Lampreys are found in both freshwater and saltwater habitats all over the world.
In terms of physical characteristics, lampreys have long, snake-like bodies that are typically cylindrical in shape. They lack jaws, but instead possess a circular, disc-shaped mouth filled with sharp teeth. These teeth are used to attach themselves to other fish or marine animals, which they then feed on by boring a hole and sucking their blood. It may sound a little scary, but lampreys are harmless to humans!
Lampreys can be further classified into different species based on their specific features. For example, the sea lamprey is known for its migratory behavior, traveling from the ocean to freshwater rivers to lay their eggs. Another species, the brook lamprey, is one of the few that remains in freshwater ecosystems throughout their entire lives. While most lampreys are parasitic, attaching to other animals to feed, some species are non-parasitic and rely on different food sources.
In summary, the lamprey animal belongs to the class Agnatha and has a simple and primitive body structure. They are jawless fishes that can be found in both freshwater and saltwater habitats around the world. With their long bodies, circular mouth with sharp teeth, and blood-sucking feeding behavior, lampreys are intriguing creatures that have adapted to various environments.
Different Types of Lamprey
1. Sea Lamprey: This type of lamprey is found in the Atlantic Ocean and is known for its parasitic behavior, attaching itself to other fish with its sucker-like mouth and feeding on their blood. It can cause harm to fish populations and is considered an invasive species.
2. Japanese Lamprey: Native to Japan, this lamprey species has a unique reproductive strategy called ‘terrestrial spawning.’ After hatching in freshwater, the young lampreys migrate to the ocean and return to freshwater as adults to lay eggs on land.
3. Siberian Brook Lamprey: Found in Russia and Eastern Europe, this lamprey species is known for its ability to live in both freshwater and marine environments. It plays a crucial role in certain ecosystems by feeding on dead organic matter and aiding in nutrient cycling.
4. Chestnut Lamprey: Native to North America, this lamprey species is known for its chestnut color, hence the name. It resides in freshwater habitats and feeds by attaching itself to other fish and scraping away their skin to access blood and bodily fluids.
5. Northern Brook Lamprey: This lamprey species is found in North America and lives primarily in freshwater environments such as rivers and streams. It goes through a metamorphosis from a larval to an adult form and feeds on small organisms and detritus in the water.
6. European River Lamprey: Native to Europe, this lamprey species is the smallest of its kind and resides in freshwater habitats. It uses its sucker-like mouth to attach to and feed on the blood of fish, but it does not usually kill the host fish.
7. Australian Lamprey: Found in rivers and estuaries of Australia, this lamprey species is unique as it has a freshwater and marine life phase. As adults, they attach to other fish for feeding but generally don’t harm the host.
8. Cascade Brook Lamprey: Native to North America, this lamprey species inhabits colder streams and rivers. It lays its eggs in freshwater, and the larvae live in sediments before growing into adults and migrating to the ocean.
9. Loango Lamprey: This lamprey species is found in Africa, specifically in river systems along the West Coast. It has a complex and unique life cycle, involving prolonged larval stages and a lengthy migration to the ocean for spawning.
10. Silver Lamprey: Native to Europe and Western Asia, this lamprey species spawns in rivers and then migrates to the sea to feed as adults. They have a cylindrical body covered in mucus and are often caught for fisheries due to their high demand as food products.
Geographical Presence of Lamprey
Lampreys are found in various regions around the world, primarily in freshwater and marine environments. They are commonly found in North America, Europe, and Asia. In North America, lampreys can be found in the Great Lakes, Mississippi River basin, and various rivers along the Eastern and Western coasts. In Europe, they can be found in rivers such as the Danube and Rhine, and in Asia, they are found in rivers like the Amur and Yangtze.
However, there are regions where lampreys are not found. Lampreys are not found in regions with extreme temperatures, such as the Arctic or Antarctic. These areas are too cold for them to survive. Additionally, lampreys are not found in regions with limited water resources, such as deserts or arid environments. They rely on water for their survival and reproduction, so they need habitats that can provide suitable conditions.
Overall, lampreys are widely distributed in many regions across the globe, particularly in freshwater and marine environments. They can be found in North America, Europe, and Asia, but are absent in extremely cold regions and areas with limited water resources. Their distribution is determined by their specific habitat requirements, as lampreys need water and suitable environmental conditions to thrive.
Scientific Name of Lamprey
Lamprey is a type of animal with a scientific name called Petromyzontida. It is a unique creature that belongs to a group of jawless fish. Lampreys are ancient and have been around for millions of years. They have a long, slender body and a round mouth filled with sharp teeth.
These fascinating animals are known for their parasite-like behavior. They attach themselves to other fish by using their mouth to create a suction and feed on their blood and body fluids. Lampreys can be found in both saltwater and freshwater environments, including lakes, rivers, and even oceans.
Lampreys play an important role in the ecosystem as they help regulate the population of certain fish species. They also serve as prey for other animals like birds and larger fish. Despite their peculiar feeding habits, lampreys are interesting creatures to study and understand more about their biology and behavior.
Diet of Lamprey
Lampreys are unique creatures that have a special kind of diet. They feed on the blood and body fluids of other fish. Lampreys use their strong suction cup-like mouth to attach to the fish they prey upon. Once attached, they use their sharp teeth to pierce the fish’s skin and suck out its blood and fluids.
The diet of lampreys varies depending on their life stage. As larvae, they are filter feeders, meaning they eat tiny aquatic plants and animals that float in the water. This helps them grow and develop into their next stage of life. As adults, lampreys switch to a parasitic diet, preying mostly on fish such as salmon and trout. They attach themselves to their host fish and feed on their blood and body fluids, sometimes causing harm or even death to the fish they latch onto.
Lampreys are an important part of the ecosystem, despite their parasitic diet. They help control fish populations by feeding on weak or diseased individuals. Additionally, they provide a food source for other animals such as birds and larger fish. While lampreys may seem strange or scary, they play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of aquatic ecosystems.
Locomotion of Lamprey
The lamprey is a unique and fascinating animal known for its unusual way of moving, called locomotion. Unlike most fish, the lamprey does not have any fins to help it swim in the water. Instead, it uses its long and flexible body to wiggle and undulate through the water. This movement is similar to how a snake slithers on land.
By contracting and relaxing its muscular body, the lamprey creates waves that travel from its head to its tail. These waves push against the water, propelling the lamprey forward in a snake-like motion. It can control the intensity and speed of these waves to maneuver through the water with great agility.
To help it navigate, the lamprey also has a sucker-like mouth that it uses to attach to surfaces and hold its position. This mouth has many small teeth that it uses to latch onto its prey or to hold onto the rocks in the water. By combining its flexible body movement and sticky mouth, the lamprey is able to move and stay in place in the water without the need for fins like other fish.
In summary, the lamprey is a strange and interesting animal that has its unique way of getting around in the water. It wiggles and undulates its body to create waves that propel it forward, kind of like how a snake moves on land. Additionally, its sucker-like mouth helps it attach to surfaces and hold its position. The lamprey’s locomotion is a great example of how animals have adapted to their environment in creative and efficient ways.
Social and Sexual Behaviour of Lamprey
Lampreys are unique creatures that show interesting social and sexual behaviors. These animals live in freshwater and are known for their unusual appearance and behavior. When it comes to social behavior, lampreys often engage in shoaling, which means they like to gather together in groups. This helps them protect themselves and increase their chances of survival. Lampreys also communicate with each other through chemical signals released from their bodies.
Now, let’s talk about their sexual behavior. Lampreys have separate genders, with males and females existing within the same population. During the breeding season, male lampreys compete with each other to attract females. They do this by constructing nests composed of small stones and debris. The male lamprey will then try to entice a female to enter the nest and lay her eggs. Once she does, the male will fertilize the eggs by releasing his sperm.
In conclusion, lampreys exhibit interesting social and sexual behaviors. They gather in groups for protection and communicate through chemical signals. During the breeding season, males construct nests to attract females and fertilize their eggs. These behaviors are essential for lampreys to survive and reproduce in their freshwater environments.
Reproduction and Lifecycle of Lamprey
The life cycle of lamprey animals is quite unique and interesting. These creatures go through a series of stages before they become adults and reproduce. One important thing to know is that lampreys are primitive fish and they do not have any jaws or scales.
The first stage of the lamprey life cycle is the egg stage. Female lampreys lay their eggs in freshwater rivers or streams. The eggs are usually attached to stones or other underwater materials. Lamprey eggs are small and transparent, making them hard to spot. These eggs take around two to three weeks to hatch.
Once hatched, the lampreys enter the larval stage. During this stage, they are called ammocoetes. Ammocoetes are tiny and have a long, slender body. They live in freshwater and use their mouths to filter tiny food particles from the water. During this stage, ammocoetes grow and develop for several years.
After spending several years as ammocoetes, lampreys undergo a transformation and enter the adult stage. This is when they become true lamprey animals that we are familiar with. Adult lampreys have a cylindrical body and a circular mouth surrounded by teeth. They are known for attaching themselves to other fish and sucking their blood. In this adult stage, lampreys are ready to reproduce and continue the life cycle once again.
In summary, lamprey animals start their life as tiny eggs. Once hatched, they become ammocoetes and spend their time filtering food from the water. After several years, they transform into adult lampreys and are ready to reproduce.
Threats to Lamprey
Lampreys, a type of fish, are facing a number of threats that are putting their very existence at risk. One major threat to lampreys is habitat destruction. With the expansion of human activities such as dam building, pollution, and deforestation, lampreys are losing their homes. These fish need clean and healthy rivers and streams to survive, but when their habitats are destroyed or polluted, they struggle to find suitable places to reproduce and feed.
Another threat to lampreys is overfishing. Some people catch lampreys for food or for use as bait, and this can lead to a decline in their populations. Overfishing can disrupt the delicate balance in ecosystems, affecting not only lampreys but also other species that rely on them for food or ecological functions.
Lastly, the introduction of non-native species is also a threat to lampreys. Sometimes, species from one place are intentionally or accidentally brought to another location. If these non-native species have no natural predators in their new home, they can multiply rapidly and outcompete the native lampreys for resources. This can disrupt the food chain and negatively impact the lampreys’ survival.
In conclusion, lampreys face several threats to their survival, including habitat destruction, overfishing, and the introduction of non-native species. It is important for humans to recognize these threats and take action to protect lampreys and their habitats. By preserving and restoring their natural environments, limiting overfishing, and preventing the introduction of non-native species, we can ensure the survival of these unique and important fish species.
Population of Lamprey
The population of Lamprey animal is not very well known. However, it is estimated that there are around 40 species of lampreys currently existing in the world. These fascinating creatures can be found in both freshwater and saltwater habitats, such as rivers, lakes, and oceans. Lampreys have a unique appearance with a long, snake-like body and a circular mouth filled with sharp teeth.
Sadly, some lamprey species have gone extinct over time. One example is the Great Lakes sea lamprey, which used to be abundant in the Great Lakes region of North America. Due to human activities, such as the construction of dams and pollution, their population declined rapidly. Invasive species, like the sea lamprey, have also had a negative impact on other lamprey species and native fish populations, further contributing to their decline.
The extinction of lamprey species is a great loss to the natural world. They play a vital role in ecosystems as they are both predators and scavengers. Lampreys help maintain a balance in underwater communities by feeding on dead fish, controlling parasites, and providing food for other animals. Efforts are being made to protect and conserve the remaining lamprey populations and their habitats to ensure their survival for future generations.
Conclusion
In the vast world of the animal kingdom, few creatures capture our curiosity as much as the lamprey. These remarkable animals have a long and fascinating history that can be traced back millions of years. Lampreys are jawless fish that have a unique cylindrical body shape and can be found in both freshwater and marine habitats. Let’s delve deeper into the history, facts, size, habitat, and classification of this intriguing animal.
Lampreys have been around for over 360 million years, making them one of the oldest vertebrate species on Earth. These ancient creatures have witnessed the rise and fall of numerous other animals, including the dinosaurs! Lampreys are known for their parasitic habits, attaching themselves to other fish and using their rasping tongue to feed on their host’s blood and bodily fluids. However, not all lampreys are parasitic – some are non-parasitic and have a less damaging impact on their hosts.
Despite their tiny size, lampreys play a significant role in their ecosystems. They contribute to the balance of aquatic food chains, serving as both prey and predator. Lampreys are classified under the class “Petromyzontida” and are further divided into multiple species. While some lampreys live exclusively in freshwater rivers and lakes, others spend their entire lives in the ocean, migrating up rivers to spawn.
In conclusion, the lamprey is a unique and ancient animal that has managed to survive for millions of years. With their intriguing history, parasitic habits, and important role in various ecosystems, they prove that even small creatures can have a big impact. The lamprey’s ability to adapt and thrive in diverse environments showcases the resilience and diversity of the animal kingdom.
Frequently Asked Questions about Lamprey (FAQ’s)
Q: What is a lamprey animal?
A: A lamprey animal is a type of jawless fish belonging to the class Petromyzontidae.
Q: How do lamprey animals differ from other fish?
A: Lamprey animals lack true jaws and have a distinctive sucker-like mouth.
Q: Where can lamprey animals be found?
A: Lamprey animals can be found in freshwater and saltwater environments worldwide.
Q: What do lamprey animals feed on?
A: Lamprey animals are parasitic creatures that feed on the blood and bodily fluids of other fish.
Q: How do lamprey animals attach themselves to their hosts?
A: Lamprey animals use their sucker-like mouth filled with sharp teeth to attach themselves to their hosts.
Q: Are lamprey animals harmful to humans?
A: While lamprey animals can latch onto humans, they generally do not cause harm and are more of a nuisance.
Q: Can lamprey animals survive out of water?
A: Lamprey animals need to be in water to survive as they rely on it for oxygen absorption through their skin.
Q: How long do lamprey animals live?
A: The lifespan of lamprey animals can vary depending on the species, but most live for around 2 to 3 years.
Q: Do lamprey animals have a skeleton?
A: Yes, lamprey animals have a cartilaginous skeleton like other fish.
Q: Can lamprey animals regenerate body parts?
A: Although lamprey animals can regenerate certain body parts, such as their fins, they cannot regrow their whole body if severed.
Q: How do lamprey animals reproduce?
A: Lamprey animals are semelparous, meaning they reproduce only once in their lifetime. They lay eggs in freshwater streams.
Q: Are lamprey animals endangered?
A: Some species of lamprey animals are considered endangered due to habitat loss, pollution, and human activity.
Q: Do lamprey animals have any predators?
A: Lamprey animals have several natural predators, including birds, larger fish, and some mammals.
Q: Can lamprey animals inflict harm on their hosts?
A: Lamprey animals are known to weaken and potentially kill their hosts, especially in larger numbers or when feeding on smaller fish.
Q: Are lamprey animals important for the ecosystem?
A: Lamprey animals play a crucial role in the ecosystem as both predators and prey, contributing to the balance of aquatic food webs.
Q: Are lamprey animals widely studied?
A: Yes, lamprey animals have been the subject of extensive scientific research due to their unique physiology and evolutionary significance.

Hi there, I’m Emily Buono, and I’m thrilled to introduce myself! Currently, I’m part of two fantastic places: I work as a VisEx at the New England Aquarium and as an RAS at MGH CCM.
I completed my education at the Mass General Research Institute and Stonehill College, which is located in Valatie Colony, New York, in the United States.
Now, here’s the exciting part: I absolutely adore animals! They captivate me, and I’m always eager to learn more about them. In fact, I write articles all about these incredible creatures.
In the past, I’ve worn many hats, such as being a biologist at the Maria Mitchell Association, a cashier, a floor organizer, and a visitor experience and research animal specialist.
My passion lies in exploring the world of animals and helping others understand them better. So, if you ever have questions about animals, feel free to reach out. I’m here to make animal info easy and fun to grasp!