Insects have always fascinated humans with their incredible diversity, interesting facts, and unique habitats. They are a crucial part of the animal kingdom, being the largest group of animals on Earth. In this blog post, we will explore the history, facts, size, habitat, and classification of insects.
Insects have been around for millions of years, with fossil records dating back to over 385 million years ago. These tiny creatures have adapted to various environments and climates, making them highly successful in their survival. From the tiniest ant to the largest beetle, insects come in all shapes and sizes, showcasing the immense diversity within this group of animals.
When it comes to their habitats, insects can be found in nearly every corner of the world, thriving in diverse ecosystems such as forests, deserts, freshwater bodies, and even within our homes. Their ability to occupy such a wide range of habitats is attributed to their incredible adaptability and wide-ranging diets.
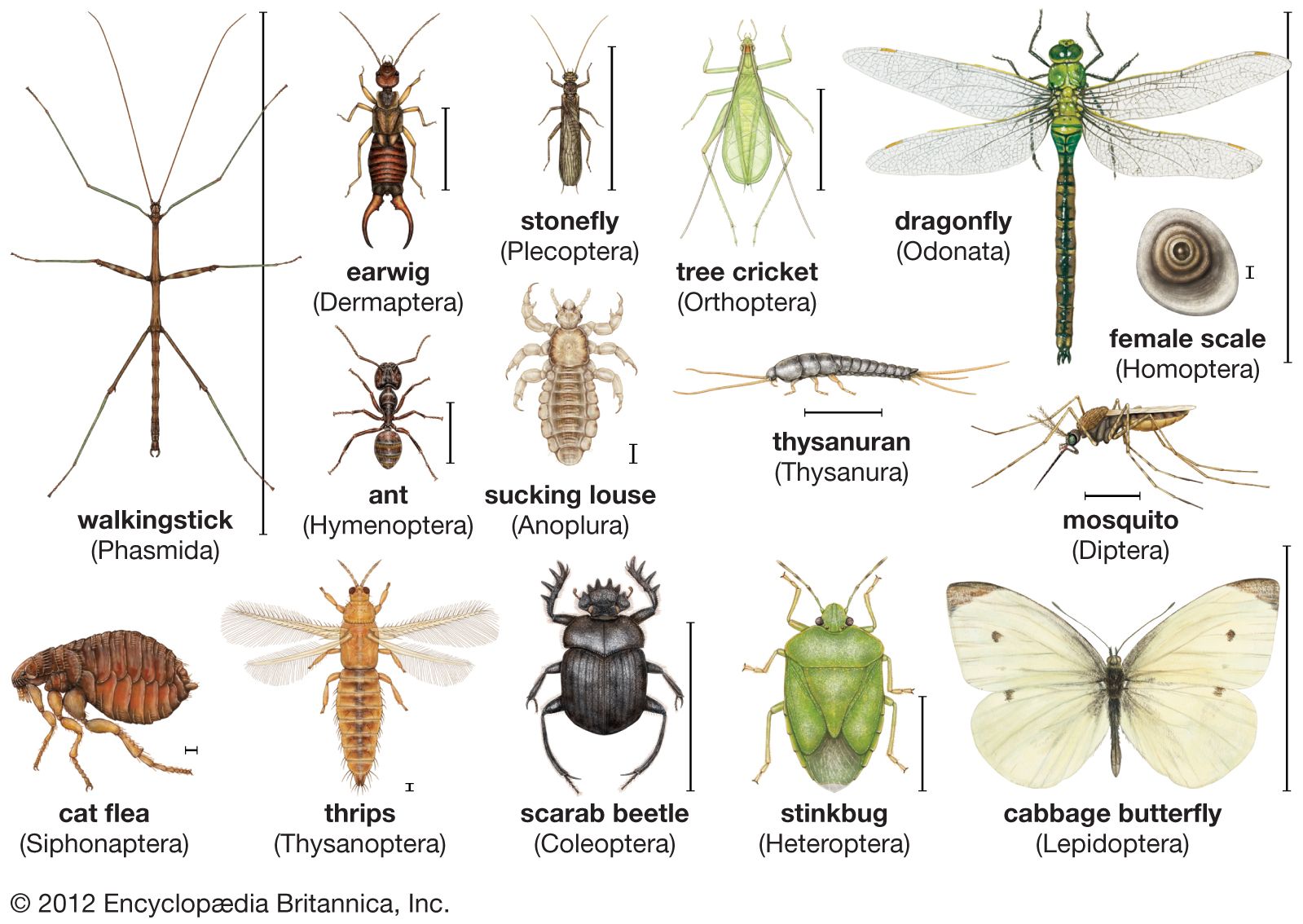
In the animal kingdom, insects belong to the phylum Arthropoda and the class Insecta. This class is further classified into numerous orders, such as Coleoptera (beetles), Hymenoptera (ants, bees), and Lepidoptera (butterflies, moths). Each order comprises several families, which in turn consist of various species.
With this blog post, we aim to provide our readers with a comprehensive understanding of the fascinating world of insects. From their ancient history to their incredible abilities, we will delve into the enchanting realm of these tiny creatures, shedding light on the Animals Name that make up this diverse group. Stay tuned for our upcoming articles on Animals Name, where we delve into the intriguing lives of specific insect species.
History of Insect
Insects have been part of Earth’s history for a really long time. Scientists have found fossil evidence showing that insects existed more than 400 million years ago. That’s even longer than the dinosaurs! In fact, insects are the most diverse group of animals on the planet, with over a million known species. They come in all sorts of shapes, sizes, and colors, and can be found in almost every habitat on Earth.
Throughout history, insects have played important roles in our environment. They help to pollinate plants, which allows them to reproduce and grow. Without insects like bees and butterflies, many of the fruits and vegetables we enjoy wouldn’t exist. Insects also act as decomposers, meaning they help to break down dead plants and animals. This process helps to recycle nutrients back into the ecosystem, making the soil fertile for new growth. Additionally, some insects are even considered beneficial for humans because they eat other insects that can harm our crops.
Despite their small size, insects have had a big impact on humans throughout history. They have been a source of inspiration for art, literature, and even technology. Many cultures also hold special beliefs or superstitions about insects. For example, in some cultures, ladybugs are considered a sign of good luck, while others may view certain insects as symbols of death or evil. While some insects, like ants, can be a nuisance to humans, others, like fireflies, have captivated our attention and sparked our curiosity.
In conclusion, insects have been around for a very long time and have played important roles in our planet’s history. They are incredibly diverse and can be found in almost every corner of the world. Insects are not only essential for the balance of our ecosystems, but they have also influenced human culture and have inspired us in various ways. So, next time you see an insect, take a moment to appreciate their fascinating history and the important roles they play in our lives.
Importance of Insect
Insects, little creatures that often buzz or crawl around us, might seem unimportant to some people. However, they play a significant role in our environment. Firstly, insects help in pollination, which is the process of transferring pollen from the male part of a flower to the female part. This helps plants to reproduce and grow new seeds. Without insects like bees and butterflies spreading pollen, many flowers and crops would not be able to produce seeds or fruit. This means we would have fewer flowers in gardens and less food to eat.
Secondly, insects are part of the food chain. They are a source of food for many animals such as birds, frogs, and fish. Without insects, these animals would not have enough food to survive. For example, birds rely on insects for their diet and need them to raise their chicks. If insects disappeared, these birds would struggle to find enough food and their population may decrease.
Lastly, some insects help in breaking down organic matter and recycling nutrients in the environment. Insects like beetles and flies feed on decaying plants and animals. They break them down into smaller pieces and return vital nutrients back to the soil. This helps to enrich the soil and enable new plants to grow.
In conclusion, even though insects may sometimes be seen as bothersome, they have a crucial role in our ecosystem. They help in pollination, serve as food for other animals, and aid in recycling nutrients. It’s important for us to appreciate and protect these tiny creatures, as they contribute to the balance and sustainability of our environment.
Amazing Facts About Insect
1. Insects are a type of animal that have six legs, three main body parts, and usually wings.
2. There are more than one million known species of insects, making them the most diverse group of animals on Earth.
3. Insects play a vital role in our ecosystem as pollinators. They help plants reproduce by carrying pollen from one flower to another.
4. Most insects have a hard exoskeleton on the outside of their bodies, which protects them and provides support.
5. Insects come in various sizes, ranging from tiny ones like ants to bigger ones like beetles.
6. Insects go through a process called metamorphosis, where they change from one form to another as they grow. This includes stages like eggs, larvae or nymphs, pupae, and adults.
7. Honeybees are important insects that make honey, and they live together in organized colonies with a queen bee.
8. Some insects, like mosquitoes and flies, can carry diseases through their bites or contact with humans and animals.
9. Many insects are herbivores, meaning they feed on plants, while others are carnivores and eat other animals.
10. Insects have specialized mouthparts adapted for their specific diets. For example, butterflies and moths have long proboscises for sipping nectar from flowers.
11. Ants live in large communities called colonies, where they work together to build nests, find food, and protect the colony from enemies.
12. Insects have unique ways of communicating with each other, such as through pheromones (chemical signals) or by making sounds like buzzing or chirping.
13. Some insects, like beetles, have a hard outer wing covering called elytra, which protects their delicate wings underneath.
14. Insects can be found in almost every habitat on Earth, from forests and fields to deserts and even inside our homes.
15. Insects have been around for millions of years, with some ancient species that lived during the time of dinosaurs. They have evolved and adapted to survive in various environments.
Can we keep Insect as our Pet?
Some insects can be kept as pets, but they require special care and attention. One common insect pet is the ant. Ant farms are popular, where ants live in a small container with tunnels and can be observed. However, it’s important to remember that insects have different needs compared to other pets like dogs or cats. They require specific habitats, food, and temperature conditions to thrive.
While there are many fascinating insects, some have become extinct over time. Extinction means that a certain animal species no longer exists anywhere on Earth. One example of an extinct insect is the dodo, which was a flightless bird. The dodo was a native of Mauritius, an island in the Indian Ocean. Sadly, due to human activities like hunting and the introduction of new species, the dodo became extinct in the late 17th century. This means that we can’t keep them as pets because they are no longer alive today.
Extinction is a tragic event that can happen when a species doesn’t have enough individuals to survive. It’s essential to protect and take care of animals so they don’t disappear forever. While insects can be interesting pets, we must remember to treat them with kindness and provide them with the right environment to live happily.
Size of Insect
Insect animals come in a wide range of sizes. Some insects can be really tiny, like the ants crawling around your picnic blanket. They are so small that they can easily fit onto the tip of your finger. Others are a bit bigger, like butterflies. You might have seen these colorful creatures fluttering around in your garden. They are larger than ants but still quite small compared to other animals we see.
On the other hand, there are insects that are really, really big! One example is the Atlas moth. It has the largest wingspan of any moth or butterfly in the world. Can you believe it? Its wings can be as big as 30 centimeters across! That’s almost as long as a ruler. Just imagine seeing an insect that huge flying around!
Now, you might wonder why insects vary so much in size. Well, one reason is that their size helps them survive and do their jobs. Small insects can easily hide from predators or squeeze into tiny spaces to find food. Big insects, on the other hand, can fly long distances and carry heavy loads. Each size has its advantages and plays an important role in the insect world.
In conclusion, insects can come in all sizes, from tiny ants to massive moths. Their sizes help them in different ways, whether it’s hiding from predators or transporting things around. Next time you see an insect, take a moment to appreciate its unique size and the important role it plays in our world.
Habitat of Insect
Insect animals can live in various habitats all around the world. These tiny creatures can be found in gardens, forests, fields, and even inside our homes. They are incredibly adaptable and can survive in many different environments.
One common habitat for insects is the garden. Insects are attracted to the abundant plants and flowers in gardens because they provide food and shelter. They can find nectar in flowers, leaves to munch on, and even other insects to feast on. Gardens also offer many hiding places, such as under rocks or in tree bark, where insects can lay eggs and protect themselves from predators.
Another habitat for insects is the forest. Insects make their homes among the trees and bushes. Some insects, like butterflies, rely on specific types of plants for their survival. They lay their eggs on these plants, and when the eggs hatch, the larvae feed on the leaves. Other insects, like ants, build intricate nests underground and work together to find food and protect their colony. Forests provide a wide range of food sources for insects, making them a perfect place to live.
Lastly, insects can also be found inside our homes. Although we may not always welcome them there, insects can easily find their way in through cracks, open doors, or even hitching a ride on our clothes. They can find shelter in our attics, basements, and even crawl spaces. Insects that live in our homes often feed on the same things we do, like crumbs or leftover food. However, it’s important to keep our homes clean and free from insects that could be harmful to our health.
In conclusion, insects can be found in various habitats such as gardens, forests, and even inside our homes. They are adaptable creatures that can take advantage of the resources available in each habitat. Understanding where insects live can help us appreciate their important role in the ecosystem.
Evolution of Insect
Animal evolution is a fascinating process that has taken place over millions of years. One particular group of animals, known as insects, has undergone a remarkable transformation. They have evolved in several key ways to become the diverse and successful creatures we see today.
Insect evolution began around 385 million years ago, during the Devonian period. At that time, insects were much larger than they are now, with some reaching sizes up to 1 meter long! Over time, they adapted to changing environments and developed a protective exoskeleton. This outer covering not only provided support but also prevented water loss, enabling them to live in a wider range of habitats.
As the ages passed, insects continued to evolve and diversify. One of the most significant developments was the evolution of wings. Around 320 million years ago, insects developed flight, allowing them to explore new territories, escape predators, and find food more easily. Flying insects became incredibly successful and began to dominate many ecosystems, filling various ecological niches.
Another remarkable evolution among insects is metamorphosis. Earlier insects had direct development, meaning they hatched from eggs and resembled miniature versions of their parents. But about 300 million years ago, some insects started to undergo complete metamorphosis. This means they undergo dramatic changes during their life cycle, transforming from larva to pupa, and finally into adults. Metamorphosis provided insects with distinct advantages such as specialized body structures for specific tasks and reduced competition between different stages of the life cycle.
In summary, insects have evolved in incredible ways throughout history. They developed exoskeletons, gained the ability to fly, and underwent metamorphosis. These adaptations allowed them to survive and thrive in various environments, becoming one of the most diverse and successful groups of animals on Earth.
Classification of Insect
Insects are a diverse group of animals that belong to the phylum Arthropoda. They have a unique body structure with three main parts: head, thorax, and abdomen. Insects are also known for their six legs, two pairs of wings, and antennas. This amazing group of animals is further classified into different orders based on their physical characteristics and habits.
The first order of insects is called Coleoptera, which includes beetles. Beetles are characterized by their hard outer wings that protect their delicate wings underneath. They have a tough exoskeleton that helps them survive in different environments. Another order is Lepidoptera, which consists of butterflies and moths. These insects have scaly wings and undergo a remarkable transformation from caterpillars to beautiful flying creatures.
Another important order is Hymenoptera, which includes bees, wasps, and ants. These insects have four membranous wings and a narrow waist connecting the thorax and abdomen. Hymenoptera play essential roles in pollination and also exhibit complex social behaviors. One of the largest insect orders is Diptera, comprising flies and mosquitoes. These insects have only one pair of wings and are known for their ability to transmit diseases.
Insects are not only fascinating creatures but also have a great impact on our ecosystem. Understanding their classification helps us appreciate their diversity and important roles in various ecosystems. From beetles to butterflies, bees to flies, each order of insects has its unique features and contributions to the natural world. So next time you come across an insect, take a moment to observe its characteristics and marvel at the wonders of insect animal classification.
Types of Insect
1. Butterflies: These delicate insects are known for their gorgeous, colorful wings. They undergo a process called metamorphosis, where they transform from caterpillars into butterflies. Butterflies play a crucial role in pollination, helping plants reproduce.
2. Ants: Ants are social insects that live in colonies. They work together to build intricate underground nests and have a highly organized division of labor. Ants communicate through pheromones and are known for their strength, teamwork, and resilience.
3. Bees: Bees are known for their vital role as pollinators. They collect nectar from flowers to make honey and also play a significant role in the production of fruits and vegetables. Bees live in hives and have a complex social structure.
4. Ladybugs: Ladybugs are small beetles known for their colorful appearance and distinct markings. They are beneficial insects as they help control pests like aphids by feeding on them. Ladybugs are considered a symbol of good luck in many cultures.
5. Dragonflies: Dragonflies are ancient and fascinating insects found near water bodies. They have large eyes, slender bodies, and powerful wings. Dragonflies are excellent hunters; they catch prey, such as mosquitoes, mid-flight, and are known for their aerial acrobatics.
6. Grasshoppers: Grasshoppers are known for their ability to jump high distances. They are herbivorous insects and play a role in plant pollination and seed dispersal. Grasshoppers produce a unique sound by rubbing their hind legs against their wings.
7. Fireflies: Fireflies, also known as lightning bugs, are insects capable of producing light through a biochemical process called bioluminescence. They use this ability to communicate and attract mates. Fireflies are commonly found in forests and fields during summer evenings.
8. Beetles: Beetles are the largest order of insects, with over 400,000 different species. They have a hard exoskeleton and are known for their remarkable diversity in size, shape, and coloration. Beetles can be found in almost every type of habitat, from deserts to rainforests.
9. Mosquitoes: Mosquitoes are small, flying insects that feed on the blood of humans and animals. While they may be annoying, mosquitoes also serve as a food source for other animals. However, they can also transmit diseases like malaria and dengue fever.
10. Termites: Termites are social insects known for their ability to break down cellulose present in wood and plant matter. While they can cause damage to buildings and wooden structures, termites are also important in nutrient recycling in ecosystems. They live in large colonies structured with queens, workers, and soldiers.
Geographical Presence of Insect
The insect animal can be found all around the world in many different regions. These regions can include places like forests, meadows, deserts, and even some cities. Insects are very adaptable creatures, which means they can live in many different environments. They play an important role in our ecosystems by pollinating plants, decomposing organic matter, and even being a food source for other animals.
However, there are some places where insects are not commonly found. One such place is the Arctic region, which is very cold and covered in ice and snow for much of the year. Insects cannot survive in such extreme temperatures, and so they are not found in this part of the world. They also tend to avoid very dry and barren places, like some deserts, where there is not enough water or food for them to survive.
Insects are incredibly diverse and can be found in almost every imaginable habitat on Earth. From tropical rainforests to grasslands to wetlands, insects thrive in these regions. They have adapted to different climates and conditions, allowing them to inhabit a wide range of environments. Whether it’s a tiny ant on the forest floor or a colorful butterfly in a garden, insects are an important part of our natural world.
Scientific Name of Insect
The scientific name of an insect animal is composed of two parts: the genus and species. These names are used by scientists to accurately identify different types of insects. For example, the scientific name of a common housefly is Musca domestica.
The first part of the scientific name, the genus, represents a group of closely related organisms. In the case of the housefly, the genus is Musca. The second part, the species, represents a particular type of organism within that genus. In this case, the species is domestica.
Scientists give insects these scientific names to ensure accurate communication and to avoid confusion. Just like a person’s name, the scientific name of an insect helps scientists refer to specific individuals or groups. This way, researchers can easily distinguish between different species and can study their characteristics, behaviors, and habitats.
By using scientific names, scientists all around the world can understand and communicate about insects more effectively. It allows them to share knowledge, discoveries, and conduct research to further our understanding of these fascinating creatures. Understanding the scientific names of insects helps scientists and researchers better appreciate the diversity and complexity of the insect world.
Diet of Insect
Animals that eat insects have a special diet. These animals survive by hunting and eating other smaller creatures. They have sharp teeth or beaks to catch and kill their insect prey. They can be found in different habitats such as forests, grasslands, or even in our own backyards.
The diet of insect-eating animals consists mainly of insects like flies, beetles, and ants. Some animals, like birds, swoop down from the sky to catch flying insects. Others, such as frogs and lizards, use their long tongues to snatch bugs off plants or from the ground. Some animals, like spiders, build intricate webs to trap insects for their meal.
These animals are important because they help control insect populations. By feeding on insects, they prevent them from becoming a nuisance or damaging crops. Insect-eating animals are also a vital part of the food chain, as larger predators like snakes and birds rely on them for their own survival.
In conclusion, the diet of insect-eating animals consists mainly of small crawling or flying creatures like insects. These animals play an essential role in maintaining the balance of nature by controlling insect populations and serving as food for larger predators. So, the next time you spot a bird or a frog, remember that they are not just cute but also crucial for maintaining the ecosystem.
Locomotion of Insect
Insects have a unique way of moving around called locomotion. They use their six legs to walk, run, crawl, jump, and even fly. With their lightweight bodies, insects can move very fast and easily navigate through different terrains.
When insects walk or run, they coordinate their legs in a rhythmic pattern. They move their legs in two phases: the swing phase and the support phase. During the swing phase, the leg is lifted off the ground, while in the support phase, it touches and pushes against the surface to move forward. This cycle repeats for each leg, allowing the insect to move forward smoothly.
Some insects, like grasshoppers and fleas, have powerful legs that enable them to jump long distances. They store energy in a special body part called a tendon, which acts like a spring. When released, the energy is swiftly transferred to their legs, launching them into the air. Other insects, such as bees and butterflies, have wings that flap in the air, allowing them to fly from one place to another.
Insect locomotion is fascinating because it showcases the incredible diversity and adaptability found in the animal kingdom.
Social and Sexual Behaviour of Insect
Insect animals have very interesting social and sexual behavior. They live together in groups called colonies and work together to survive. Each insect has a different role to play within the colony. Some insects are workers and collect food, build nests or take care of the young ones. Other insects are the leaders, called queens or kings, who make important decisions for the colony. They communicate with each other using pheromones, which are special chemicals that let them know what they should do and where they should go.
When it comes to sex, insects have some unique ways of doing things! Most insects have separate sexes, with males and females looking different from each other. The males usually have bigger eyes and fancier bodies to attract the females. Some insects even have special dances or songs to impress their mates. Once the female lays her eggs, the males usually have no more role to play in parenting. In some cases, the female can even store the male’s sperm for a long time and use it to fertilize her eggs whenever she wants.
In conclusion, insects have fascinating social and sexual behavior. They live together in colonies, with each insect having a different job. They use chemicals to communicate and work as a team. When it comes to sex, insects have special ways to attract and reproduce. Males use their appearance and behaviors to impress females, and once the eggs are laid, they may have no further involvement.
Reproduction and Lifecycle of Insect
Insects have a unique way of reproducing and going through their life cycle. Let’s explore how they bring new life into the world and grow into adult insects.
The life cycle of an insect begins with the female insect laying eggs. These eggs can be found in different places, depending on the species of insect. Some lay their eggs on plants, while others lay them in water or even on other insects! After a period of time, the eggs hatch into larva, also known as caterpillars or maggots. These young insects look quite different from their adult forms and have to eat a lot to grow. They go through different stages of growth called instars, shedding their skin as they get bigger.
Once the larva have grown enough, they enter the next stage of their life cycle called the pupa. During this stage, the insect is enclosed in a protective case called a cocoon or chrysalis. Inside the cocoon, the insect undergoes a remarkable transformation called metamorphosis. This process changes the insect’s body structure and appearance until it finally emerges as an adult insect.
The last stage of the life cycle is the adult stage. Adult insects have wings and are able to reproduce. They find a mate, and the female may lay more eggs to start the cycle all over again. Some insects, like butterflies, moths, and beetles, have a relatively short adult life span, while others, like ants and bees, can live for many years. And so, the life cycle of an insect continues, as new generations are born and the cycle repeats itself, ensuring the survival of these amazing creatures.
Threats to Insect
Insects, like many other animals, face various threats that can harm their survival. One significant threat to insect animals is habitat loss. Due to deforestation or the destruction of natural habitats, many insects lose their homes. Without a place to live and find food, their populations can decrease, and some insects may even face the risk of extinction.
Another major threat to insect animals is the use of pesticides. Pesticides are chemicals used to kill insects that harm crops. However, when these pesticides are sprayed on plants, they can also harm beneficial insects like bees and butterflies. Without these important pollinators, many plants and crops would struggle to produce fruits and seeds. It is therefore crucial to find ways to protect insect animals while still supporting agriculture and food production.
Climate change is also becoming a significant threat to insect animals. As temperatures rise and weather patterns change, it can disrupt the life cycles and behaviors of many insects. Some insects may struggle to adapt to these changes, while others may face challenges in finding suitable food sources or mating partners. Climate change can also lead to extreme weather events such as hurricanes or droughts that can directly harm insect populations.
In conclusion, habitat loss, pesticide use, and climate change are all threats that significantly impact insect animals. It is important for us to take action to protect their habitats, find alternative ways to control pests without harming beneficial insects, and reduce our impact on the climate. By doing so, we can help ensure the survival and well-being of these vital creatures in our ecosystems.
Population of Insect
The population of insect animals is massive, with an estimated 10 quintillion (that’s 10 with 18 zeros!) insects living on Earth. These tiny creatures can be found in almost every environment, from forests to deserts and even in our homes. Insects play an essential role in our ecosystems, pollinating plants, decomposing organic matter, and serving as a vital food source for other animals.
However, sadly, some insect animals have gone extinct over the years. One example is the passenger pigeon, a bird-like animal that once lived in North America. In the past, their population was in the billions. However, due to hunting and habitat destruction, the last passenger pigeon died in captivity in 1914. This extinction serves as a reminder of the importance of protecting and conserving our animal species.
It is crucial to recognize the significance of insect animals within our world. Their enormous population and ecological role make them a fundamental part of maintaining a healthy environment. While some species have faced extinction, it is up to us to understand and preserve the biodiversity of insect animals to ensure their continued presence for future generations.
Conclusion
Insects, as we have learned, are fascinating creatures that have been around for millions of years. They are a diverse group of animals that come in various shapes, sizes, and colors. From the fluttering butterfly to the buzzing bee, insects capture our attention with their unique features and behaviors. By exploring their history, facts, size, habitat, and classification, we have gained a deeper understanding of these remarkable creatures.
One thing we can take away from our exploration is the incredible variety of insects in the animal kingdom. With over a million known species, they are the largest group of animals on Earth. These tiny beings play important roles in our ecosystems as pollinators, decomposers, and even as a food source for other animals. Their ability to adapt and thrive in different environments showcases their resilience and evolutionary success.
From minuscule ants to the magnificent dragonflies, insects have adapted to diverse habitats all over the world. Whether they dwell in forests, deserts, or even our own backyards, insects have found ways to survive and reproduce in their specific environments. This adaptability is what has allowed them to inhabit nearly every corner of our planet, making them one of the most successful groups of animals.
In conclusion, our exploration of insects has revealed a world full of wonder and beauty. We have discovered that these small creatures play a vital role in our ecosystems and have managed to thrive in various habitats. By understanding and appreciating insects, we can learn to respect and protect the remarkable diversity of life on our planet. So, the next time you spot a little insect crawling or flying by, take a moment to appreciate the incredible world of animals they represent.
Frequently Asked Questions about Insect (FAQ’s)
Q1: What is an insect?
A1: An insect is a type of animal that belongs to the class Insecta and is characterized by a body divided into three parts (head, thorax, and abdomen), six legs, and often wings.
Q2: How many species of insects exist?
A2: It is estimated that there are over 1 million known species of insects, with potentially millions more yet to be discovered.
Q3: What is the largest insect in the world?
A3: The largest insect in the world is the Giant Weta, native to New Zealand, which can measure up to four inches in length.
Q4: Do all insects have wings?
A4: No, not all insects have wings. Some species have evolved to be wingless, such as ants and fleas.
Q5: What is an exoskeleton?
A5: An exoskeleton is a hard and protective outer covering that insects have. It serves as their skeleton, providing support and protection.
Q6: Can insects see colors?
A6: Yes, most insects have color vision and can perceive a wide range of colors.
Q7: How do insects communicate with each other?
A7: Insects communicate through various means, such as chemical signals (pheromones), sounds, and visual displays.
Q8: Why are insects important to ecosystems?
A8: Insects play a crucial role in ecosystems as pollinators, decomposers, and as a food source for other animals.
Q9: How long do insects live?
A9: The lifespan of insects varies greatly depending on the species. Some live only a few days, while others can live for several months or even years.
Q10: Can insects feel pain?
A10: Insects do not possess the same neural pathways as mammals for experiencing pain. However, they may exhibit certain behaviors indicating discomfort or stress.
Q11: What do insects eat?
A11: Insects have diverse diets; they can be herbivorous (feeding on plants), carnivorous (feeding on other insects or small animals), or omnivorous (feeding on both plants and animals).
Q12: Are all insects harmful to humans?
A12: No, the majority of insects are not harmful to humans. In fact, many insects are beneficial for agriculture, as they help in pollination and pest control.
Q13: Can insects transmit diseases to humans?
A13: Yes, certain insects, such as mosquitoes and ticks, can transmit diseases to humans, including malaria, dengue fever, Lyme disease, and Zika virus.
Q14: How do insects reproduce?
A14: Insects reproduce through a process called metamorphosis, which involves stages of egg, larva, pupa, and adult. There are also some insects that undergo incomplete metamorphosis.
Q15: What is the economic importance of insects?
A15: Insects have significant economic importance. They are used in industries such as agriculture, medicine (e.g., silk production), and food (e.g., honey and edible insects).

Hi there! I’m Morgan Gutierrez, and I love animals! I work as a Seasonal Animal Care Specialist at Brookfield Zoo and also teach people about animals, which is super fun. I studied at Valparaiso University in Lockport, Illinois, where I learned even more about these amazing creatures.
I’m not just about taking care of animals; I write articles about them, too! I explore and share many interesting animal stories, from cute kittens to giant elephants.
In the past, I’ve worked with veterinarians, helped with research, and even been an Animal Ambassador, bringing animals closer to people. Animals are my passion, and I enjoy helping others learn about them. So, if you ever want to know about animals, feel free to ask. I’ll explain it in a way that’s easy to understand, just like talking to a friend!