The world we live in is full of fascinating creatures, both alive and long gone. Today, we dive deep into the world of extinct animals as we explore the history, facts, size, habitat, and classification of Australopithecus. This incredible creature, known as Australopithecus, has left a significant mark in the history of our planet.
Australopithecus was a genus of extinct hominins that lived millions of years ago. They were early humans that walked the Earth between 4 and 2 million years ago. These fascinating creatures were small in size, standing at around 3 to 4 feet tall. Their habitat was mainly located in Africa, specifically the areas we now know as Ethiopia, Tanzania, and South Africa.
The classification of Australopithecus is quite intriguing. They are considered a genus within the family Hominidae, which also includes the modern human species. Australopithecus played a crucial role in the evolution of our species, as they are believed to be one of our earliest ancestors. Their discovery has provided valuable insight into the origins of humankind, allowing us to better understand our own history.
Please note that our blog already features an informative article on over 155 different animal species. We welcome you to explore our diverse range of content as we continue to discover and learn about the fascinating creatures that have roamed the Earth throughout history!
History of Australopithecus
Australopithecus was an animal that lived a long time ago. Scientists believe it lived between 4 million and 2 million years ago. It was one of our earliest ancestors, which means it is related to humans. Australopithecus is special because it was the first animal to walk on two legs like humans do.
When Australopithecus first appeared, it was very different from other animals. Most animals at that time walked on four legs, but Australopithecus started to walk on two legs. This was a big change because it allowed Australopithecus to do things that other animals couldn’t do. It could see things better and use its hands more easily.
Australopithecus also had a different body shape than other animals. It had long arms and short legs. This helped it to climb trees and move around in the forests where it lived. It also had a small brain, but it was still smarter than other animals. We know this because its teeth were shaped in a way that tells us what it ate. It ate mostly plants, but also some meat.
In conclusion, Australopithecus was an animal that lived a long time ago. It was one of our earliest ancestors and is related to humans. It was special because it was the first animal to walk on two legs like humans do. This allowed it to do things that other animals couldn’t do. It had a different body shape, long arms, and short legs, which helped it in moving around its environment. It had a small brain but was smarter than other animals. Australopithecus mostly ate plants, but also some meat.
Importance of Australopithecus
Australopithecus was a type of animal that lived a long time ago. It is important because it can teach us many things about our ancestors and how we became humans.
Firstly, studying Australopithecus helps us understand the process of evolution. Scientists can use the fossils of Australopithecus to see how they changed over time and how they are related to other animals. This helps us fill in the gaps in our family tree and learn more about where we came from.
Secondly, Australopithecus gives us clues about how our early ancestors lived. By examining their teeth and bones, scientists can figure out what they ate and how they moved. This helps us imagine what life was like for them and how they survived in their environment.
Lastly, Australopithecus helps us appreciate the wonders of nature. By learning about this ancient animal, we realize that humans are just a small part of the amazing diversity of life on Earth. It is fascinating to think about all the different creatures that have come before us and how they have shaped the world we live in today.
In summary, Australopithecus is important because it helps us understand our evolution, gives us insights into our ancestors’ lives, and reminds us of the incredible variety of life on our planet.
Amazing Facts About Australopithecus
1. Australopithecus animals were a group of early hominids that lived in Africa between 4.2 and 1.7 million years ago.
2. They were bipedal, which means they walked upright on two legs, but they also had the ability to walk on all fours.
3. Australopithecus animals had a combination of ape-like and human-like features.
4. Their average height ranged from about 3 to 4 feet, making them smaller than modern humans.
5. They had a small brain size compared to contemporary humans, with an average brain volume similar to that of modern chimpanzees.
6. Australopithecus animals had a protruding jaw with large molars, indicating a diet that included tough foods like roots, nuts, and seeds.
7. They were likely omnivorous, meaning they ate both plants and small animals.
8. Australopithecus animals had long arms and curved fingers, similar to apes, which aided them in climbing trees.
9. They possessed a relatively flat face with a prominent nose and a small brow ridge.
10. Their canines were larger than those of modern humans, suggesting they may have engaged in some form of aggression or male competition.
11. Australopithecus animals lived in various habitats, including woodlands, grasslands, and near water sources.
12. Fossil evidence suggests that they made and used simple stone tools for cutting and processing food.
13. They likely lived in social groups, with evidence of individuals taking care of one another.
14. Australopithecus animals may have used vocalizations and body language to communicate with each other.
15. They existed for a significant period of time in human evolution and are considered an important ancestor to our species, Homo sapiens.
Can we keep Australopithecus as our Pet?
Australopithecus is not an animal that we can keep as a pet. Firstly, Australopithecus is not even an animal anymore. It lived a very long time ago and is now extinct. This means that there are no more Australopithecus left in the world.
Australopithecus lived millions of years ago and was an early human ancestor. They looked quite similar to us, with a mixture of human-like and ape-like features. However, they were not like the animals we keep as pets today, such as dogs or cats. They had their own way of life and lived in very different environments.
It’s important to understand that we cannot keep extinct animals as pets. Extinction means that a species has completely disappeared from the Earth. This can happen for many reasons, such as changes in the environment or competition with other species. Once an animal is extinct, there is no way to bring it back or keep it as a pet.
In conclusion, Australopithecus is not an animal that we can keep as a pet because it no longer exists. Extinct animals belong to the past, and it is impossible to have them as pets. It is important to focus on protecting the animals that are still alive today and making sure they have a safe and healthy environment to live in.
Size of Australopithecus
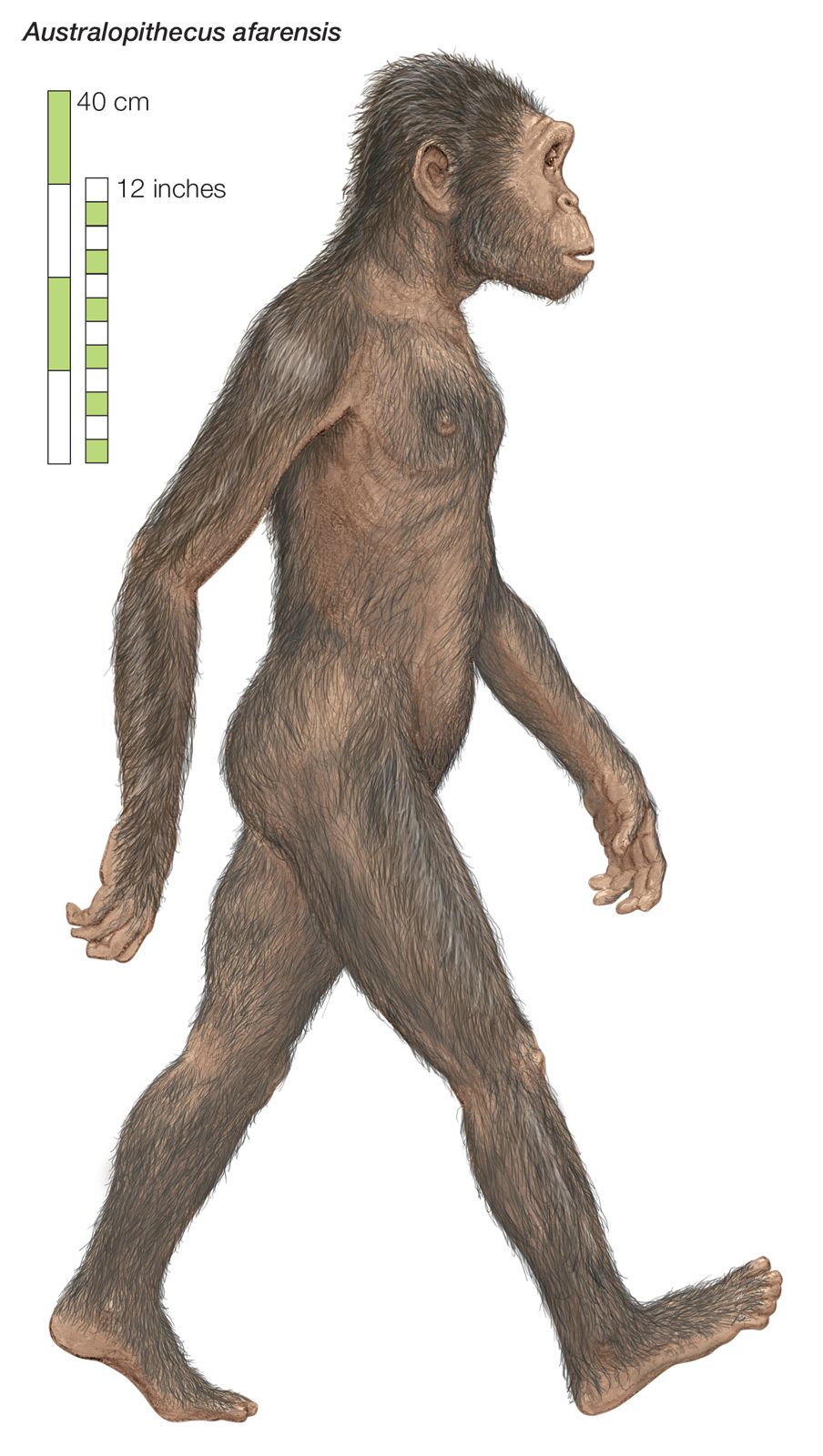
Australopithecus, an ancient human-like creature, was about the size of a chimpanzee or a small adult human today. They stood on two legs and walked upright, just like humans do, but their height was shorter, usually around 4 to 5 feet tall. Their weight varied between 70 to 120 pounds, making them quite light compared to modern adults. Australopithecus had a slim body with long arms and a small brain, which was about the size of an orange.
Although Australopithecus was smaller than modern humans, they were still bigger than some other primates. They had a sturdy and muscular build, which allowed them to move around and forage for food in their environment. Their small brain size suggests that they were not as intelligent as humans, but they were still able to use tools and communicate with each other.
The size of Australopithecus can be compared to the size of a 12-year-old child. Imagine someone around that age, standing at 4 to 5 feet tall and weighing between 70 to 120 pounds. They would be smaller and lighter than most adults. Australopithecus inhabited different parts of Africa millions of years ago, and their size helped them adapt to their surroundings and survive in the wild.
In summary, Australopithecus was around the same size as a chimpanzee or a small human today. They were about 4 to 5 feet tall and weighed between 70 to 120 pounds. While they were smaller than modern humans, they were still larger than some other primates. Their size and physical characteristics played an important role in how they lived and survived in their environments.
Habitat of Australopithecus
Australopithecus is a group of very old animals that lived around 4 to 2 million years ago. They were our distant ancestors and are important to understand human evolution. Australopithecus animals lived in Africa, which is a continent with many different types of habitats. They mainly lived in forests and grasslands but could also be found near lakes or rivers.
In the forests, Australopithecus animals found lots of trees which they climbed on to search for food. These trees provided shelter and protection from other predators. The forests were also full of fruits, nuts, and leaves which Australopithecus animals ate. They used their strong arms and hands to move easily through the trees.
When Australopithecus animals ventured outside the forests, they found themselves in grasslands. Here, they would walk on two legs, just like humans, but they were still good climbers. The grasslands had different types of vegetation, such as grasses and shrubs, which provided food for Australopithecus animals. They also found water from rivers and lakes nearby to quench their thirst.
Overall, the habitat of Australopithecus animals changed over time, just like our environments do today. They lived in forests and grasslands of Africa, using trees for shelter and finding food in the vegetation around them. Understanding their habitat helps us to learn about the early stages of humans and how our ancestors adapted and evolved to survive in different environments.
Evolution of Australopithecus
The Australopithecus animal evolved over millions of years, changing in small ways to adapt and survive in the changing world. These animals first appeared in Africa around 4 million years ago. At first, they looked more like apes with long arms and walked on all fours. As time went on, they started to walk on two legs, similar to humans today.
One of the key features of Australopithecus was their teeth. They had big jaws and strong teeth, which allowed them to eat hard and tough food like fruits, nuts, and plants. However, they didn’t have the same large brain as humans. Instead, they had small brains similar to modern apes.
Over time, Australopithecus animals started to evolve and become more like humans. They began using tools to help them survive, like rocks and sticks. This showed that they had started to think and solve problems. Their brains also started to grow bigger, allowing them to become smarter and more adaptable.
Eventually, the Australopithecus animals evolved even further into what we now know as Homo habilis, the earliest human species. This transformation took place over a long period of time, with the Australopithecus animals slowly developing more human-like features. They learned to walk completely upright and started to communicate with each other through simple language. These changes set the stage for the development of even more advanced humans, like Homo erectus and Homo sapiens.
In summary, the Australopithecus animal evolved from ape-like creatures to early humans over millions of years. They walked on two legs, used tools, and developed bigger brains. These changes helped them survive and pave the way for the later human species we see today.
Classification of Australopithecus
Australopithecus is the name given to a group of animals that lived a long time ago. They were like early humans, but not exactly the same. Australopithecus animals were small and walked on two legs, just like humans do. They had long arms and strong jaws with sharp teeth.
Scientists have found different types of Australopithecus animals. One of them is called Australopithecus afarensis. They lived about 3 to 4 million years ago in East Africa. Another type is Australopithecus africanus. They lived about 2 to 3 million years ago in South Africa. There were also other types like Australopithecus sediba and Australopithecus anamensis.
Scientists think that Australopithecus animals were our ancient relatives. They were not exactly like humans, but they looked somewhat similar. They had smaller brains than humans and didn’t know how to use tools. However, they did some things like humans. They made simple tools, used fire, and lived in groups. They also walked on two legs just like us.
In summary, Australopithecus animals were early human-like creatures that lived a long time ago. There were different types of Australopithecus, such as Australopithecus afarensis and Australopithecus africanus. Although they were not exactly like humans, they had some similarities, like walking on two legs and living in groups. Scientists believe that Australopithecus animals were our ancient relatives and played an important role in our evolution.
How did Australopithecus Extinct?
A long time ago, there were creatures called Australopithecus that lived on Earth. They were not like us humans, but they were similar in some ways. They walked on two legs and had brains that were smaller than ours. They lived in Africa and were very good at climbing trees and finding food.
Unfortunately, Australopithecus could not survive forever. There were many things that caused their extinction. One reason is that the climate started to change. The weather became drier and there was not enough food for the Australopithecus to eat. This made it very hard for them to survive.
Another reason is that there were other creatures, like big cats and hyenas, that started to hunt the Australopithecus. These animals were faster and stronger, so they could catch and eat the Australopithecus. This made it even harder for them to live.
Lastly, there were changes happening in the environment where the Australopithecus lived. The forests where they used to live started to disappear and turn into grasslands. This meant that the Australopithecus had less trees to climb and hide in. They had to change their lifestyle, but they were not able to adapt quickly enough, and this led to their extinction.
In the end, the Australopithecus could not survive because of the changing climate, the threat from other animals, and the loss of their natural habitat. It is sad to think about these creatures that once lived on Earth but are no longer here. We can learn from this and try to take care of our planet so that other animals do not face the same fate.
Geographical Presence of Australopithecus
The Australopithecus animal, also known as Australopithecus, can be found in a region called Africa. This region is located in the eastern part of the world and is home to many different countries such as Kenya, Ethiopia, and South Africa. It is in these countries that scientists have discovered the remains of Australopithecus, which lived millions of years ago.
However, it is important to note that Australopithecus is not found in other regions of the world. It is exclusively found in Africa. This means that if you were to go to places like Europe, Asia, or the Americas, you would not find any Australopithecus fossils or remnants. This is because Australopithecus evolved and lived only in Africa.
This animal is of great importance to scientists as it is believed to be one of our early ancestors. By studying the remains of Australopithecus, scientists can learn more about how humans evolved and how we became the way we are today. It is fascinating to think that millions of years ago, our ancestors were walking the same lands that we now call home.
Scientific Name of Australopithecus
The scientific name for the animal Australopithecus is Australopithecus afarensis. These ancient creatures lived around 3 to 4 million years ago. Australopithecus afarensis is an extinct species belonging to the hominid family, which includes humans, chimpanzees, and gorillas.
One of the most famous specimens of Australopithecus afarensis is known as “Lucy.” Lucy’s skeleton was discovered in Ethiopia in 1974 and provided valuable information about our early human ancestors. These animals had a mixture of ape-like and human-like features. They had a small brain and walked upright on two legs, similar to humans today.
Australopithecus afarensis were relatively small in size, standing about three to four feet tall. They had long arms with curved fingers and strong jaws with small, sharp teeth. They mainly lived in forested areas and are believed to have been herbivorous, meaning they ate mostly fruits, leaves, and plants.
Thus, Australopithecus afarensis, or Lucy’s species, was an ancient animal that existed millions of years ago. Their discovery and study have helped scientists understand more about our early ancestors and how they lived. The scientific name Australopithecus afarensis represents an important part of the human evolutionary tree.
Diet of Australopithecus
Australopithecus, an early human ancestor that lived millions of years ago, had a diet mainly composed of plant-based foods. They were herbivores, which means they ate mostly fruits, seeds, leaves, and plants. Their strong teeth and jaws were adapted for grinding and chewing tough foods.
Fruits were a significant part of the Australopithecus diet. They would have eaten a variety of fruits, such as berries, nuts, and other similar foods that they could find in their environment. These fruits provided them with essential vitamins and nutrients, helping them to stay healthy and grow.
In addition to fruits, Australopithecus also had a taste for leaves and seeds. Leaves provided essential nutrients and fiber, while seeds like nuts could provide them with an additional source of energy. They would have spent a significant amount of time foraging for these foods, searching for trees and plants that offered the most nutritious options.
Overall, the diet of Australopithecus was mainly based on plant foods, including fruits, seeds, and leaves. This diet helped them to survive and thrive in their environment. By adapting to a plant-based diet, Australopithecus was able to find the necessary nutrients to grow and become stronger, which eventually led to the development of later human species.
Locomotion of Australopithecus
Australopithecus was an animal that lived a long time ago. It is believed that they used to walk on two legs, just like humans do today. This way of walking is called bipedal locomotion.
Walking on two legs gave Australopithecus some advantages. It allowed them to see what was happening around them more easily. It also helped them to free up their hands, which they could use for other things like carrying food or tools. However, walking on two legs was not as efficient for Australopithecus as it is for humans. They did not walk as fast or as smoothly as we do. They also had shorter legs and a different body structure, which made it a bit harder for them to walk long distances without getting tired.
In summary, Australopithecus walked on two legs, just like humans. This way of moving was helpful for them in some ways, but it was not as efficient as our way of walking.
Social and Sexual Behaviour of Australopithecus
Australopithecus were ancient animals that existed a long time ago. They were not like humans, but they were the early ancestors of humans. Australopithecus animals lived in groups and spent most of their time in the forests. They were social animals and they would communicate with each other using sounds and gestures. Being in a group helped them find food, protect themselves from predators, and take care of their young ones.
When it comes to sexual behavior, Australopithecus animals had some similarities with humans. They would form pairs or small groups to mate with each other. The males would compete with each other to attract females. They would show off their strength and skills to win the females’ attention. Once the mating was over, the females would take care of the babies. The mothers would feed and protect the young animals until they were old enough to take care of themselves.
Australopithecus animals had a social and sexual behavior that helped them survive. They lived in groups, communicated with each other, and took care of their young ones. Their mating behavior was similar to humans, with males competing to attract females. These early animals played an important role in our evolutionary history by laying the groundwork for the development of social and sexual behaviors seen in modern humans.
Reproduction and Lifecycle of Australopithecus
Australopithecus were animals from a long, long time ago. They had a special way of making babies called reproduction. Just like humans, Australopithecus had males and females. When a male Australopithecus met a female, they would dance and play together. While they were having fun, they would also mate. This means the male’s sperm would meet with the female’s egg, and this is how a baby Australopithecus would start to grow inside the female’s body.
The life cycle of Australopithecus had different stages, just like how humans grow up. The baby Australopithecus would be born from the mother after some time, just like human babies. Then, the baby would start growing into a child Australopithecus. This child would learn from their parents and the other members of their group. They would learn how to find food, use tools, and communicate with each other. As the child Australopithecus grew older, they would become an adult. At this stage, they would be able to find their own food and have babies. The adults would take care of their little ones and teach them everything they knew, just like human parents do.
The life cycle of Australopithecus was fascinating and similar to humans in many ways. They would reproduce, or make babies, by mating. The babies would grow into children, learn from their parents, and become adults to have their own babies. The way Australopithecus lived and had babies helped them survive and adapt to their environment. These interesting creatures are a part of our ancient history and have left a mark in our understanding of human evolution.
Threats to Australopithecus
Australopithecus animals faced many threats during their time on Earth. One major threat was predators. These animals had to be wary of large predators such as lions, leopards, and hyenas, who saw them as potential prey. Australopithecus had to be constantly aware of their surroundings and live in groups to protect themselves from becoming dinner.
Another threat to Australopithecus was the scarcity of food. They lived in a time when the Earth’s climate was changing, and this affected the availability of food sources. They had to compete with other animals for limited resources, which made it difficult for them to find enough food to survive. This led to their need to evolve and develop new strategies for finding food.
Lastly, a threat to Australopithecus was disease and illness. Just like humans today, Australopithecus was susceptible to various diseases and infections. Without access to modern medicine and healthcare, they had to rely on their own immune systems to fight off illnesses. Unfortunately, this meant that many individuals did not survive when faced with serious diseases.
In conclusion, Australopithecus animals faced threats from predators, limited food sources, and diseases during their time. These challenges required them to adapt and find ways to survive in a constantly changing environment. While they may have faced many dangers, their ability to respond to these threats played a crucial role in their evolution and eventual development into the species we know today.
Population of Australopithecus
The population of Australopithecus, an ancient animal, is not easy to determine accurately since they lived a long time ago. However, scientists estimate that there may have been several thousand Australopithecus individuals living at any given time. These creatures roamed the Earth around 2 to 4 million years ago. They were small and walked on two legs, similar to humans.
Sadly, Australopithecus is now extinct, which means they no longer exist. They gradually disappeared from the Earth around 2 million years ago, possibly due to changes in their environment. Extinction is a natural process that happens when a species cannot adapt or survive in a changing world. Although we cannot see Australopithecus today, their remains have been found by scientists, helping us learn about our past and how humans evolved.
In conclusion, Australopithecus, a small ancient creature that walked on two legs, lived millions of years ago. Scientists estimate that there may have been several thousand Australopithecus individuals at a time. Unfortunately, Australopithecus is now extinct and disappeared around 2 million years ago. Their remains help scientists understand the story of human evolution.
Conclusion
In summary, Australopithecus was a fascinating creature that lived a long, long time ago. This animal, whose name means “southern ape,” provides us with valuable information about our ancient history. With its small size and unique features, it helps scientists understand how humans have evolved over millions of years.
Australopithecus was a small animal that generally stood about 3 to 4 feet tall. They had a mix of human-like and ape-like characteristics, such as a curved spine and long arms. This suggests that they were able to walk upright on two legs, but they were also good at climbing trees. They lived in forests and savannas, which offered them a variety of habitats to explore and survive in.
Classification-wise, Australopithecus belongs to the family of hominids, which includes the great apes and humans. They were our distant relatives, but not direct ancestors. Instead, they were more like cousins to our early human ancestors. By studying Australopithecus, scientists can piece together the puzzle of human evolution and learn more about our ancestors’ behavior, diet, and habitat.
In conclusion, Australopithecus was an important creature in our evolutionary history. This ancient animal helps us understand the beginnings of human life and how we evolved over time. By examining Australopithecus, scientists can uncover more details about our ancestors and the environments they lived in. Learning about Australopithecus gives us a glimpse into our past and helps us appreciate the journey that has brought us to where we are today.
Frequently Asked Questions about Australopithecus (FAQ’s)
Q1: What is Australopithecus animal?
A1: Australopithecus refers to a genus of extinct hominins believed to have been the ancestors of modern humans.
Q2: In what time period did Australopithecus exist?
A2: Australopithecus existed around 4 to 2 million years ago during the Pliocene and early Pleistocene epoch.
Q3: Are there different species of Australopithecus?
A3: Yes, there are several known species within the Australopithecus genus, such as Australopithecus afarensis and Australopithecus africanus.
Q4: What is the average size of Australopithecus?
A4: Australopithecus individuals typically ranged from about 3 to 5 feet tall, and their weight varied between 70 to 110 pounds.
Q5: What is the significance of Australopithecus?
A5: Australopithecus plays an important role in our understanding of human evolution as they are considered one of our earliest ancestors.
Q6: Did Australopithecus walk on two legs?
A6: Yes, Australopithecus is known for its bipedal locomotion, which is the ability to walk upright on two legs.
Q7: What did Australopithecus eat?
A7: Australopithecus had a diet consisting of mostly plant-based foods, such as fruits, leaves, and seeds. They were primarily herbivorous.
Q8: Did Australopithecus use tools?
A8: While they did not use sophisticated tools like later hominins, some evidence suggests that Australopithecus may have used simple stone tools for specific tasks.
Q9: Where have Australopithecus fossils been found?
A9: Fossils of Australopithecus have been found mainly in eastern and southern Africa, particularly in countries like Ethiopia, Tanzania, and South Africa.
Q10: Did Australopithecus have a larger brain than chimpanzees?
A10: Generally, Australopithecus had a slightly larger brain than modern chimpanzees, but significantly smaller than that of modern humans.
Q11: How do scientists estimate the age of Australopithecus fossils?
A11: Scientists use various dating methods, including radiometric dating of volcanic ash layers and analyzing the fossil’s position in relation to other dated fossils or geological events.
Q12: Did Australopithecus live in groups?
A12: Yes, it is believed that Australopithecus individuals lived in small social groups, which provided protection and facilitated cooperative activities like food gathering.
Q13: How long did Australopithecus live?
A13: The lifespan of Australopithecus is estimated to have been around 30 to 40 years, similar to modern humans.
Q14: Were there any predators of Australopithecus?
A14: While there is limited evidence, it is possible that large carnivores such as big cats may have posed a threat to Australopithecus individuals.
Q15: Was Australopithecus the direct ancestor of Homo sapiens?
A15: While Australopithecus is considered an important ancestor in our evolutionary lineage, it is not a direct ancestor of Homo sapiens. Instead, it represents a side branch that eventually went extinct.

Hi there! I’m Morgan Gutierrez, and I love animals! I work as a Seasonal Animal Care Specialist at Brookfield Zoo and also teach people about animals, which is super fun. I studied at Valparaiso University in Lockport, Illinois, where I learned even more about these amazing creatures.
I’m not just about taking care of animals; I write articles about them, too! I explore and share many interesting animal stories, from cute kittens to giant elephants.
In the past, I’ve worked with veterinarians, helped with research, and even been an Animal Ambassador, bringing animals closer to people. Animals are my passion, and I enjoy helping others learn about them. So, if you ever want to know about animals, feel free to ask. I’ll explain it in a way that’s easy to understand, just like talking to a friend!