Gomphotherium: History, Facts, Size, Habitat, Classification
Gomphotherium, an ancient animal that roamed the Earth millions of years ago, is a fascinating creature to study. This blog post will provide you with all the information you need to know about this remarkable animal.
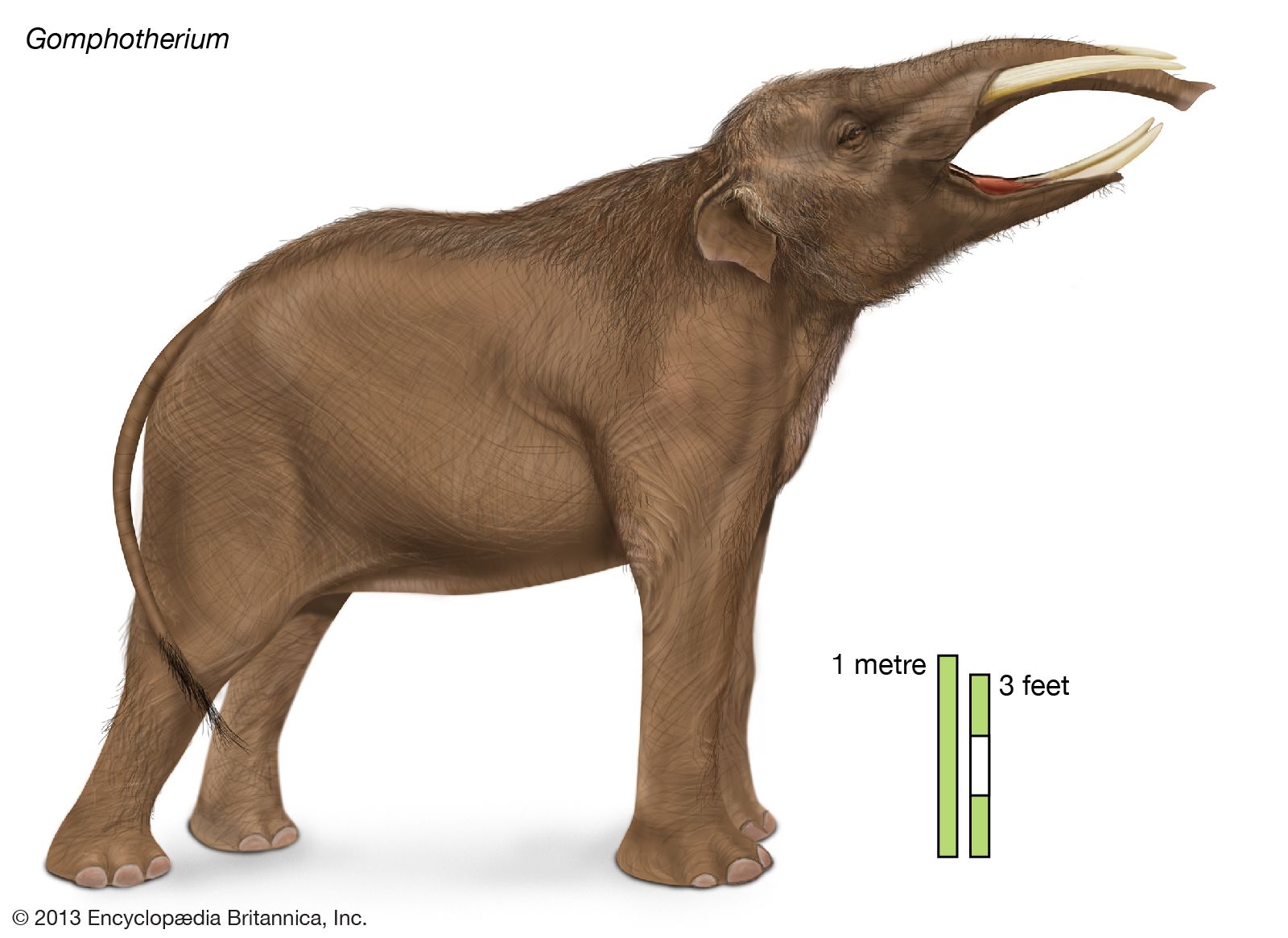
Gomphotherium was a herbivorous mammal that belonged to the same family as elephants. It lived during the Miocene and Pliocene epochs, which means it existed between 23 million and 2.6 million years ago. Similar to elephants, Gomphotherium had long, curved tusks, which it used for various purposes, such as foraging for food and self-defense.
In terms of size, Gomphotherium was quite impressive. It stood at about 10 to 13 feet tall, which is almost as tall as a two-story building. Its large body was supported by sturdy legs, allowing it to roam across different habitats. Speaking of habitat, Gomphotherium inhabited various regions around the world, including North America, Europe, Asia, and Africa. This indicates its adaptability to different environments.
To summarize, Gomphotherium was an extinct animal from the Miocene and Pliocene epochs. It resembled elephants with its long tusks and large size. Despite its disappearance from the earth, its interesting history and unique characteristics make it a captivating subject of study. Stay tuned for more intriguing articles on extinct animals, as we already have an article on 155+ animals’ names!
History of Gomphotherium
Gomphotherium was a prehistoric animal that lived millions of years ago. It was part of a group of animals called proboscideans, which also includes elephants and mammoths. Gomphotherium looked similar to modern elephants, but with some differences. It had four tusks, two upper ones that curved downwards, and two lower ones that pointed forwards. These tusks were used for digging and pulling up plants. Gomphotherium also had a trunk, which was not as long as an elephant’s, but still very useful for grabbing and eating food.
Gomphotherium lived during the Miocene and Pliocene epochs, which were a long time ago in Earth’s history. It inhabited different parts of the world, including Africa, Asia, Europe, and North America. Fossil remains of this animal have been found in many places, helping scientists learn more about its life and habits. Gomphotherium was a herbivorous animal, meaning it only ate plants. It likely lived in forests and grasslands, where it could find plenty of food.
Unfortunately, Gomphotherium is now extinct, which means it no longer exists. Scientists believe that changes in the environment, such as shrinking forests and changing climate, may have contributed to its disappearance. Despite its extinction, the fossils of Gomphotherium provide valuable information about Earth’s ancient past and the diversity of life that once existed. Studying these fossils helps scientists understand how animals have evolved over time and how they have adapted to different environments.
Importance of Gomphotherium
The Gomphotherium animal is very important because it helps us learn about ancient times. Scientists study these animals and their fossils to understand what life was like long ago. They can tell us things about the climate, the environment, and even how the Earth has changed.
One reason why the Gomphotherium is so important is because it helps scientists understand how different animals have evolved over time. By studying their fossils, scientists can see how the Gomphotherium and its relatives changed and adapted to their surroundings. This helps us understand the process of evolution and how different species came to be.
Another reason why the Gomphotherium is important is because it gives us clues about ancient ecosystems. By studying their fossils, scientists can learn about the plants and other animals that lived at the same time as the Gomphotherium. This helps us reconstruct what ancient environments looked like and how different species interacted with each other.
In conclusion, the Gomphotherium is an important animal because it helps us understand ancient times, the process of evolution, and ancient ecosystems. By studying its fossils, scientists can learn a lot about our planet’s history and how different species have changed over time.
Amazing Facts About Gomphotherium
1. Gomphotherium was an ancient animal that lived around 10 million to 2 million years ago during the Miocene and Pliocene periods.
2. It was a large mammal belonging to the family Gomphotheriidae, which is closely related to elephants.
3. The average size of Gomphotherium was around 9-10 feet tall at the shoulder, making it similar in size to modern elephants.
4. Unlike elephants, Gomphotherium had four tusks, two on its upper jaw and two on its lower jaw, which are more curved and twisted compared to their relatives.
5. These tusks could reach lengths of up to 10 feet, making them a prominent feature of the animal.
6. Gomphotherium had a long trunk, similar to modern elephants, which it used for grasping food, drinking water, and communication.
7. The animal had a broad and flat skull, with its eyes placed high on the skull, allowing it for better vision while browsing for food in forested areas.
8. Their diet mainly consisted of leaves, branches, fruits, and other vegetation, and their teeth were adapted for grinding plant matter.
9. Gomphotherium had a complex social structure, and it is believed they lived in herds, moving and foraging together for protection and finding food.
10. Fossils of Gomphotherium have been discovered in various parts of the world, including Europe, Africa, North America, and Asia.
11. Gomphotherium became extinct around 2 million years ago, possibly due to climate changes and competition with other animals, including early elephants.
12. Fossil evidence suggests that Gomphotherium had a wide distribution and lived in a variety of habitats, including grasslands, forests, and wetlands.
13. The name “Gomphotherium” means “wedge beast” in Greek, referring to the shape of their teeth, which are wedge-like in comparison to other mammals.
14. Gomphotherium’s skull was relatively small compared to its body size, with a long and flexible neck, allowing it to reach food at different heights.
15. The discovery and study of Gomphotherium fossils have helped scientists gain insight into the evolution and diversity of ancient elephant-like creatures.
Can we keep Gomphotherium as our Pet?
The Gomphotherium animal, which lived long ago, cannot be kept as a pet because it is extinct. This means that there are no more of these animals living in the world today. Gomphotherium lived millions of years ago during the Miocene and Pliocene epochs. They were large, elephant-like creatures with long curved tusks.
Sadly, Gomphotherium became extinct a very long time ago. It is believed that changes in their environment and climate played a role in their extinction. The Earth underwent drastic changes, and the habitats where Gomphotherium lived slowly disappeared. This made it difficult for them to find food and survive. Over time, their population decreased until there were none left.
Because Gomphotherium is extinct, it is impossible for us to keep them as pets. Keeping a pet means having a living animal that we can take care of, feed, and bond with. Since Gomphotherium does not exist anymore, it is not possible to have them as pets. However, we can still learn about these fascinating creatures from fossils and scientific studies. They were an important part of Earth’s history, and studying them helps us understand more about how life on our planet has evolved over time.
Size of Gomphotherium
Gomphotherium was a prehistoric animal that lived millions of years ago. It was much bigger than the animals we see today. Gomphotherium was about the size of an elephant, but it looked a bit different. While elephants have long trunks, Gomphotherium had shorter trunks with two downward-pointing tusks on their lower jaws.
The size of Gomphotherium can be hard to imagine, but think of a large elephant you may have seen at the zoo. Gomphotherium was about the same height as an elephant, reaching around 10 feet tall. It was also longer than an elephant, measuring around 20 feet from head to tail. Can you imagine an animal this huge walking around?
Gomphotherium was much bigger than other animals that lived during its time. It was part of a group called proboscideans, which included elephants and their ancestors. However, Gomphotherium had some unique features that set it apart. Apart from its short trunk and downward tusks, it also had different teeth. Its lower jaw had four tusks, with two large ones pointing down and two smaller ones pointing forward. These may have been used for digging up plants to eat.
In summary, Gomphotherium was a gigantic animal that lived long ago. It was about the same size as an elephant, but with a shorter trunk and downward-pointing tusks. It was part of a group called proboscideans and had unique teeth for digging up food. Gomphotherium was truly a fascinating creature from our planet’s past!
Habitat of Gomphotherium
The habitat of the Gomphotherium animal was mostly forests and grasslands. Gomphotherium liked to live in areas where there were lots of trees and plants. They could be found in different parts of the world, such as North America, Europe and Asia.
In the forests, Gomphotherium found shelter and protection from other animals. They liked to stay near water sources like rivers and lakes. The forests provided them with plenty of food, such as leaves, fruits, and nuts from trees.
The grasslands were also a favorable habitat for Gomphotherium. There, they could find open spaces with plenty of grass to eat. These large animals could move around more freely in the grasslands and find other plants to munch on.
Gomphotherium was well-suited for their habitat. They had long and strong trunks that helped them reach higher branches for food or pull up plants from the ground. Their large size also protected them from most predators. Gomphotherium was able to adapt to different environments within their habitat, making them successful in finding food and surviving.
Overall, Gomphotherium enjoyed living in forests and grasslands. These environments gave them access to food, water, and protection. By living in these habitats, Gomphotherium had everything they needed to thrive and grow big and strong.
Evolution of Gomphotherium
The Gomphotherium animal is a fascinating creature that lived a long time ago. Let’s take a look at how it evolved over time.
In the first paragraph, we can focus on the early ancestors of Gomphotherium. These ancient creatures lived during a time called the Eocene epoch, which was about 55 million years ago. They were small in size and had short tusks and a long trunk like modern elephants. These tusks were used for digging up roots and plants to eat. Over time, these early ancestors slowly started to change and adapt to their environment.
In the second paragraph, we can talk about how Gomphotherium evolved and changed over millions of years. As time went on, Gomphotherium started to grow larger in size. Its body became more elephant-like, with a sturdy build and long, curved tusks. These tusks continued to be used for digging, but they also became more useful for fighting off predators and attracting mates. Gomphotherium adapted to different habitats and environments, spreading across continents and evolving into various species.
In the last paragraph, we can discuss the eventual extinction of Gomphotherium. Despite its success for millions of years, Gomphotherium eventually faced challenges that it couldn’t overcome. Climate change, competition, and changes in vegetation all played a role in the decline of these magnificent creatures. Slowly, over time, Gomphotherium disappeared completely, leaving no living descendants behind.
Overall, the evolution of Gomphotherium is a reminder of how species can change and adapt to their surroundings over millions of years. It also teaches us about the fragile nature of life on Earth and how even the most successful species can face extinction.
Classification of Gomphotherium
Gomphotherium is an important animal to study because it helps us understand the evolution of elephants. It belongs to the order called Proboscidea, which includes elephants and their ancient relatives. Gomphotherium lived during the Miocene epoch around 23 million years ago to 5 million years ago.
Gomphotherium is classified under the family Gomphotheriidae. This family includes other ancient elephant-like animals such as Amebelodon and Platybelodon. These animals had long curved tusks that pointed downwards, unlike the straight tusks of modern elephants. Gomphotherium had a thick trunk and it is believed that it used it to pick up food and water just like elephants do today.
Gomphotherium was a large animal, measuring about 10 feet in height at the shoulder. It had four long legs with padded feet that helped it move around in various habitats. This herbivorous animal had long, curved upper tusks as well as smaller lower tusks. Its tusks were used for digging up plants and possibly defending against predators. Gomphotherium had four large molar teeth in each side of its jaw, which it used to grind up tough vegetation. These teeth had high ridges that enabled efficient grinding of the plant material.
In conclusion, Gomphotherium is a fascinating animal belonging to the Proboscidea order. It was a large herbivore that lived millions of years ago and is related to modern elephants. Its curved tusks and thick trunk are some of its distinguishing features. Studying Gomphotherium helps us understand the history of elephants and their evolution.
How did Gomphotherium Extinct?
Gomphotherium was a prehistoric animal that roamed the Earth millions of years ago. Sadly, this magnificent creature is now extinct. The extinction of Gomphotherium can be attributed to several factors.
Firstly, one of the main reasons for the extinction of Gomphotherium was a change in their natural habitat. These animals thrived in forests and woodlands, where they could find plenty of food and water. However, as the climate started to change, the forests turned into grasslands, which did not provide the same amount of resources for the Gomphotherium to survive. The lack of suitable habitats and food sources led to a decline in their population.
Secondly, Gomphotherium faced competition from other animals. As the environment changed and new species emerged, they had to compete for resources such as food and water. Some of their competitors, like early elephants, were better adapted to the changing conditions and had advantages that the Gomphotherium did not possess. This increased competition put further pressure on the Gomphotherium population, leading to their decline.
Lastly, human activities also played a significant role in the extinction of Gomphotherium. As humans expanded their territories and began hunting animals for food and resources, they also targeted Gomphotherium. These prehistoric creatures were large and had ivory tusks, which made them attractive targets for early humans. The combination of hunting and habitat degradation from human activities ultimately pushed the Gomphotherium to extinction.
In conclusion, the extinction of Gomphotherium can be attributed to a change in their natural habitat, increased competition from other species, and human activities such as hunting. These factors created a challenging environment for the Gomphotherium to survive, leading to their eventual extinction. The disappearance of these magnificent creatures serves as a reminder of the delicate balance of ecosystems and the importance of preserving and protecting the biodiversity of our planet.
Geographical Presence of Gomphotherium
The Gomphotherium animal is found in the regions of North America, Europe, and Asia. These regions are home to the Gomphotherium because they provide suitable habitats for them to live in. In North America, they can be found in areas such as Mexico and the southern parts of the United States. In Europe, they are found in countries like Spain, France, Germany, and the United Kingdom. In Asia, they are found in countries like China, India, and Thailand. These regions provide the Gomphotherium with the right climate, vegetation, and resources they need to survive.
However, there are regions where the Gomphotherium is not found. One such example is Australia. The Gomphotherium did not exist in Australia because they were not able to migrate or adapt to the specific conditions found there. Australia had different landscapes and climate compared to North America, Europe, and Asia, which may explain why the Gomphotherium did not inhabit this region.
Another region where the Gomphotherium is not found is Africa. Despite being home to various large mammals, such as elephants and rhinos, the Gomphotherium did not exist in Africa. This may be due to factors such as competition with other species or the inability to adapt to the specific African environment. Therefore, the Gomphotherium is not found in Africa, unlike other regions where it thrived.
In conclusion, the Gomphotherium is found in North America, Europe, and Asia, where suitable habitats provide the necessary resources for their survival. However, the Gomphotherium is not found in regions like Australia and Africa, as they were unable to migrate or adapt to the specific conditions found there. These factors contribute to the distribution patterns of the Gomphotherium in different regions around the world.
Scientific Name of Gomphotherium
The scientific name of the Gomphotherium animal is Gomphotherium. This animal lived long ago, during a time called the Miocene epoch. It was not a dinosaur, but a prehistoric relative of elephants. Gomphotherium had a long, curved trunk, large, curved tusks, and four legs with sturdy feet.
Scientists believe that Gomphotherium was about the same size as an elephant, but with some differences. It had a longer trunk, more curved tusks, and four tusks instead of two. The trunk was used to reach for food and water, just like modern elephants. The tusks were used to dig for roots and to defend themselves against predators.
Gomphotherium lived in areas with forests and grasslands. It is believed that they mainly ate vegetation such as leaves, branches, and fruits. They were herbivores, meaning they only ate plants. They may have lived in herds, similar to today’s elephants. Gomphotherium is now extinct, which means it doesn’t exist anymore, but scientists study its remains to learn more about the past and how animals have evolved over time.
Diet of Gomphotherium
Gomphotherium was an ancient animal that lived long ago. It roamed the Earth during the Miocene and Pliocene periods. But today, we will not talk about Gomphotherium. Instead, we will explore what this animal ate.
The diet of Gomphotherium was mainly made up of plants. It was a herbivore, which means it only ate vegetation and not other animals. Gomphotherium had long, curved tusks that it used to dig up roots and pull down branches. It also had molar teeth with high cusps, which helped it grind down tough plant material. This animal had a special digestive system that allowed it to break down plant fibers and extract the nutrients it needed.
Gomphotherium most likely ate a variety of plants, such as grasses, leaves, fruits, and even bark. They probably moved around in search of the best food sources, as different plants grow in different areas. Their diet would have depended on what was available in their habitat at that time.
In conclusion, Gomphotherium was a plant-eating animal with a diet consisting mainly of vegetation. It used its tusks and teeth to gather and process plant material. While we may never see Gomphotherium again, we can learn about its diet from studying its fossils and understanding its teeth and digestive system.
Locomotion of Gomphotherium
Gomphotherium was a big animal that lived long ago. When it moved around, it used a special way of walking called locomotion. Locomotion is how animals move from one place to another.
Gomphotherium had strong legs, like an elephant, but its feet were different. Instead of having a big pad like an elephant, Gomphotherium had separate toes. This helped it to walk on different types of ground. When it walked, it put its feet down one at a time in a certain order. First, the front left leg moved forward, then the back left leg, followed by the front right leg, and finally the back right leg. This made its walk very stable, so it didn’t fall easily. Gomphotherium could walk for long distances and could even run if it needed to. It used its locomotion to find food, explore new places, and escape from danger.
Social and Sexual Behaviour of Gomphotherium
Gomphotherium was a remarkable animal that lived long ago. It had unique social and sexual behaviors that helped it survive and thrive in its environment. Let’s explore these fascinating behaviors in simple terms.
Firstly, Gomphotherium was a social creature. Just like humans, Gomphotherium lived in groups called herds. These herds were made up of several individuals, including both males and females. By living together, they could protect each other from predators and find food more easily. In these herds, Gomphotherium would interact with one another, cooperating and communicating through different sounds and body language.
Secondly, Gomphotherium also had interesting sexual behavior. During certain times, males would compete for the attention of females. This is called sexual competition. They would use their tusks, which were long and curved teeth, to fight against each other. The winner would then get the chance to mate with the females, ensuring the survival of their genes.
In summary, Gomphotherium was a social animal that lived in herds and had unique ways of interacting with each other. They also had interesting sexual behavior, where males competed for females through tusk fights. By understanding these behaviors, we can learn more about the lives of ancient creatures and how they adapted to their surroundings.
Reproduction and Lifecycle of Gomphotherium
Gomphotherium is an ancient animal that lived long ago. It had a unique way of reproducing and going through its life cycle. In the animal kingdom, reproduction is how new living beings are created.
The life cycle of Gomphotherium started with a female Gomphotherium giving birth to a baby. This process is called birth. The mother Gomphotherium took care of her baby and provided it with food and protection. As the baby grew, it learned how to walk, eat, and survive. This is called growing up.
Once the baby Gomphotherium was fully grown, it was able to find a mate and have babies of its own. This is called reproduction. The cycle would then start all over again, with the new Gomphotherium parent taking care of their baby and helping it grow. This continued for many generations, ensuring the survival of the Gomphotherium species.
In summary, the reproduction and life cycle of Gomphotherium involved a female giving birth to a baby, the baby growing up with the help of its parent, and eventually having its own babies. This cycle repeated over many generations, allowing the Gomphotherium species to thrive.
Threats to Gomphotherium
Gomphotherium, an ancient animal, faced various threats during its time on Earth. One major threat it encountered was climate change. The Earth’s climate during Gomphotherium’s existence went through significant fluctuations, leading to changes in temperature, rainfall patterns, and vegetation. These alterations in the environment could have affected the availability of food and water sources for the Gomphotherium, making it difficult for them to survive.
Another threat to Gomphotherium was hunting by other animals. As a large animal, Gomphotherium may have been targeted by predators looking for a meal. Animals such as saber-toothed cats and large hyenas could have posed a risk to Gomphotherium, especially if they hunted in groups. The smaller and weaker Gomphotherium may have struggled to defend itself against these predators, which would have posed a serious threat to its survival.
Lastly, the loss of habitat could have been a significant threat to Gomphotherium. Due to natural events like volcanic eruptions or changes in rivers, the Gomphotherium’s habitat could have been destroyed or altered. Additionally, human activities, such as clearing land for agriculture or settlement, could have led to habitat destruction for Gomphotherium. The loss of suitable places to live and find food would have negatively impacted the Gomphotherium population.
In conclusion, Gomphotherium faced threats such as climate change, predation by other animals, and habitat loss. These challenges played a significant role in shaping the fate of this ancient animal. By understanding the threats they faced, scientists can gain valuable insights into the factors that contribute to the extinction or survival of different species.
Population of Gomphotherium
The population of Gomphotherium, a prehistoric animal, is believed to have been quite large during its time. Although there are no exact numbers available, scientists estimate that there could have been thousands or even millions of these creatures living on Earth. Gomphotherium was a relative of modern elephants and had long tusks and a trunk, which helped it eat plants and find water. It roamed the Earth about 11 million years ago, and its population was spread across different parts of the world.
Unfortunately, Gomphotherium is now extinct. This means that there are no more living individuals of this animal. Extinction happens when a species disappears entirely. It is often caused by various factors like changes in the environment, lack of food, or competition with other animals. For Gomphotherium, it is believed that a combination of climate change and competition with other animals led to its extinction. It is sad to think that such fascinating creatures once lived on Earth and are no longer here.
Today, we can only learn about Gomphotherium through fossils and scientific studies. These ancient animals provide valuable insights into our planet’s past and help us understand the importance of preserving biodiversity. While there may not be any Gomphotherium around anymore, we have the responsibility to protect and care for the living animals that still share our world.
Conclusion
To sum it up, Gomphotherium is a fascinating animal that roamed the Earth millions of years ago. Despite its unusual name, it was a distant relative of today’s elephants and had some distinct characteristics that set it apart. This blog post shed light on the history, facts, size, habitat, and classification of this prehistoric creature, giving us a glimpse into its mysterious world.
Gomphotherium lived during the Miocene and Pliocene epochs, around 15 to 5 million years ago. It was a large mammal, about the size of a modern-day elephant, but with some notable differences. Unlike elephants, Gomphotherium had long, curved tusks in its upper jaw, which it likely used for digging and stripping bark off trees. It also had four tusks, two in the upper jaw and two in the lower, further setting it apart from its modern relatives.
This ancient animal thrived in various habitats, including woodlands and forests. It was an herbivore, meaning it only ate plants. By studying its fossil remains, scientists have been able to piece together its classification and understand its place in the animal kingdom. Gomphotherium belonged to a group called Gomphotheriidae, which are now extinct but were once abundant across the globe.
In conclusion, learning about prehistoric animals like Gomphotherium allows us to appreciate the rich diversity of life that existed in the past, alongside the creatures we know today. Understanding the history, facts, size, habitat, and classification of these ancient beings gives us valuable insights into the natural world and the evolution of species. While Gomphotherium may no longer roam the Earth, its story serves as a reminder of the incredible animals that once called this planet home.
Frequently Asked Questions about Gomphotherium (FAQ’s)
Q1: What is a Gomphotherium animal?
A1: Gomphotherium is an extinct genus of proboscidean mammals that resembled elephants.
Q2: When did the Gomphotherium animal exist?
A2: Gomphotherium existed during the Miocene and Pliocene epochs, approximately 15 to 2 million years ago.
Q3: What was the size of a Gomphotherium?
A3: Gomphotherium species ranged in size from small to quite large, with some individuals reaching sizes similar to modern elephants.
Q4: Did Gomphotherium have tusks?
A4: Yes, Gomphotherium had long, curved tusks on both the upper and lower jaws.
Q5: How did Gomphotherium use its tusks?
A5: It is believed that Gomphotherium used its tusks for defense, digging, stripping bark from trees, and possibly for fighting amongst themselves.
Q6: What did Gomphotherium eat?
A6: Gomphotherium was primarily a browser, feeding on leaves, twigs, and other vegetation.
Q7: Where have Gomphotherium fossils been found?
A7: Gomphotherium fossils have been found in various parts of the world, including North America, Europe, Africa, and Asia.
Q8: What were the closest living relatives of Gomphotherium?
A8: The closest living relatives of Gomphotherium are the elephants and mammoths.
Q9: Why did Gomphotherium go extinct?
A9: The exact reason for Gomphotherium’s extinction is not known, but it is believed to be primarily due to environmental changes and competition with other herbivorous mammals.
Q10: Was Gomphotherium a social animal?
A10: It is thought that Gomphotherium lived in small family groups, similar to modern elephants.
Q11: How did Gomphotherium move around?
A11: Gomphotherium moved on all fours, using its sturdy legs and padded feet.
Q12: Did Gomphotherium have a trunk?
A12: Yes, Gomphotherium had a trunk-like appendage, although it was not as elongated and flexible as the trunks of modern elephants.
Q13: Was Gomphotherium sexually dimorphic?
A13: Some Gomphotherium species showed sexual dimorphism, with males being larger and having larger tusks than females.
Q14: What other prehistoric animals coexisted with Gomphotherium?
A14: Gomphotherium shared its environment with other extinct mammals such as sabertooth cats, giant ground sloths, and early rhinoceroses.
Q15: What can we learn from studying Gomphotherium fossils?
A15: Studying Gomphotherium fossils provides valuable insights into the evolution and diversity of prehistoric mammals, as well as their ecological roles and interactions with their environment.

Hi there! I’m Morgan Gutierrez, and I love animals! I work as a Seasonal Animal Care Specialist at Brookfield Zoo and also teach people about animals, which is super fun. I studied at Valparaiso University in Lockport, Illinois, where I learned even more about these amazing creatures.
I’m not just about taking care of animals; I write articles about them, too! I explore and share many interesting animal stories, from cute kittens to giant elephants.
In the past, I’ve worked with veterinarians, helped with research, and even been an Animal Ambassador, bringing animals closer to people. Animals are my passion, and I enjoy helping others learn about them. So, if you ever want to know about animals, feel free to ask. I’ll explain it in a way that’s easy to understand, just like talking to a friend!