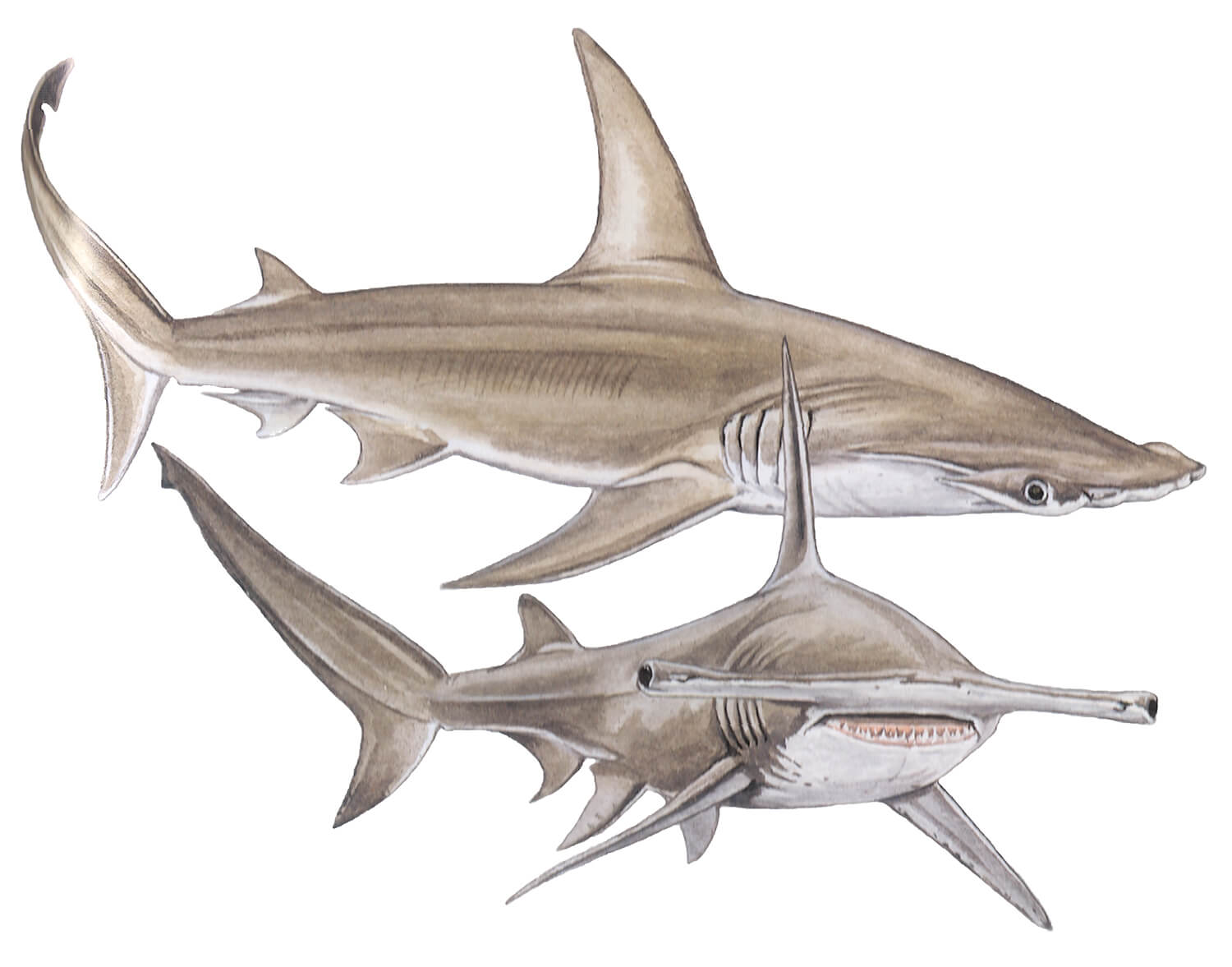
Animals Name is thrilled to delve into the fascinating world of the Great Hammerhead Shark – a creature that continues to captivate the imagination of both young and old. With its distinctively shaped head resembling a hammer, this remarkable species has an intriguing history and a wealth of intriguing facts to discover.
The Great Hammerhead Shark, scientifically known as Sphyrna mokarran, can be found in oceans all around the world. These majestic creatures are known to grow to astonishing sizes, with adults reaching an average length of 13 to 20 feet, making them the largest of all hammerhead species. Their incredible size, along with their unique appearance, makes them an undeniable superstar of the animal kingdom.
Habitat-wise, these elegant sharks prefer warm tropical waters and can often be found in coastal areas, coral reefs, and even deep-sea regions. They are known for their impressive swimming abilities and are highly skilled hunters. Classification-wise, the Great Hammerhead Shark belongs to the family Sphyrnidae, which includes a total of nine species.
So, join Animals Name as we embark on a thrilling journey to explore the enthralling history, intriguing facts, astonishing size, unique habitat, and classification of the Great Hammerhead Shark. Get ready to be amazed by the wonders of the animal kingdom, as we unveil the secrets of this magnificent ocean dweller. And remember, we already have an article on 155+ Animals Name, so be sure to explore our other exciting content and expand your knowledge even further!
History of Great Hammerhead Shark
The Great Hammerhead Shark is a fascinating creature that has roamed the oceans for millions of years. It is the largest of all hammerhead shark species and can grow up to 20 feet long. These sharks are known for their unique and distinctive head, which resembles a hammer.
The history of the Great Hammerhead Shark dates back to the time when dinosaurs roamed the earth. Fossil evidence suggests that these sharks have been around for over 20 million years. They have adapted to various environments and can be found in both warm and cold waters around the world.
Great Hammerhead Sharks play an important role in maintaining the balance of the ocean ecosystem. They are skilled hunters and feed on a variety of prey, including fish, squid, and even other sharks. Due to their large size and predatory nature, they have few natural predators. However, they are currently facing threats from human activities such as overfishing and habitat destruction. Conservation efforts are being made to protect these magnificent creatures and ensure their survival for generations to come.
In conclusion, the Great Hammerhead Shark is an ancient creature that has been swimming in our oceans for millions of years. They are known for their distinctive head shape and can grow to be enormous in size. Despite their important role in the ocean ecosystem, they are facing threats from human activities. It is important to protect and conserve these incredible sharks to maintain the balance of our oceans.
Importance of Great Hammerhead Shark
The great hammerhead shark is a vital animal in our ocean ecosystem. Its importance cannot be overstated. These magnificent creatures help maintain the balance of the marine food chain, keeping our oceans healthy and thriving.
Firstly, as apex predators, great hammerhead sharks are crucial in controlling the populations of their prey. They mainly feed on a variety of fish and rays, which helps to regulate the number of these creatures in the ocean. By keeping the population of smaller fish and rays in check, the great hammerhead shark ensures that their food supply does not become too scarce, maintaining the ecosystem’s balance.
Secondly, great hammerhead sharks play a significant role in the health of coral reefs. They scavenge on dead or dying creatures, such as turtles or large fish, which prevents these carcasses from decaying on the reef. This scavenging action helps to keep coral reefs clean and free from harmful bacteria. Without the presence of great hammerhead sharks, the coral reefs would suffer from an accumulation of decomposing matter, potentially causing damage to these delicate ecosystems.
In conclusion, the role of great hammerhead sharks in our ocean ecosystem is crucial. They help control the population of their prey, maintaining balance in the marine food chain. Additionally, they play a vital role in keeping coral reefs healthy by scavenging on dead or dying animals. It is essential to protect and conserve these magnificent creatures to ensure the long-term health and vitality of our oceans.
Amazing Facts About Great Hammerhead Shark
1. The great hammerhead shark (scientific name Sphyrna mokarran) is the largest species of hammerhead shark and can grow up to 20 feet in length.
2. This shark species has a distinctive head shape that resembles a hammer, with eyes and nostrils located at the outer tips of the hammer.
3. Great hammerhead sharks are found in warm coastal waters around the world, including the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans.
4. They prefer to inhabit areas close to the shore, such as coral reefs, seagrass beds, and shallow coastal waters.
5. Despite their large size, great hammerheads mainly feed on smaller prey, including fish, rays, squid, and crustaceans.
6. These sharks have an exceptional sense of smell, allowing them to detect prey from long distances.
7. Great hammerheads are known for their hunting technique called “hammering,” where they use their wide heads to pin down and quickly devour their prey.
8. Female great hammerheads reproduce through a process called viviparity, in which the embryos develop inside the mother’s body and are nourished by a placenta.
9. A pregnant female great hammerhead can give birth to up to 55 pups at once.
10. These sharks have a long lifespan, with some individuals living up to 30 years in the wild.
11. Great hammerheads are generally solitary creatures, only coming together during mating and certain feeding events.
12. They are known to migrate long distances, sometimes even crossing entire oceans.
13. Great hammerhead sharks are not considered a threat to humans and are generally non-aggressive, but caution should still be exercised when encountering them.
14. Unfortunately, due to overfishing and habitat destruction, the population of great hammerhead sharks is declining, and they are listed as an endangered species.
15. Conservation efforts, such as raising awareness about their importance in the ecosystem and implementing fishing regulations, are crucial to protect these magnificent sharks and their habitats.
Can we keep Great Hammerhead Shark as our Pet?
The Great Hammerhead Shark, as fascinating as it may be, is not suitable to be kept as a pet for several reasons. Firstly, these sharks are known to be quite large, often exceeding 12 feet in length and weighing over 1,000 pounds. Keeping such a massive creature in captivity would require an enormous space, a specialized tank, and a considerable amount of resources to properly care for it. These requirements make it highly impractical for most people to have them as pets.
Furthermore, the Great Hammerhead Shark is a species that roams the open ocean and has specific environmental needs. It requires constant movement and the freedom to swim vast distances in its natural habitat. Attempting to confine a creature like this would be extremely detrimental to its physical and mental health. Sharks, like many other marine animals, depend on the oceans and their ecosystems for survival. Taking them out of their natural habitat would greatly disrupt the delicate balance of marine life.
Sadly, the Great Hammerhead Shark is faced with another significant challenge – extinction. Due to overfishing, habitat destruction, and accidental capture in nets, their population numbers have drastically declined. It is important for us to make efforts to protect these magnificent creatures rather than seek to keep them as pets. Instead, we should focus on supporting conservation efforts and educating others about the importance of preserving marine life, so that future generations can appreciate the beauty and wonder of animals like the Great Hammerhead Shark in their natural environment.
Size of Great Hammerhead Shark
The Great Hammerhead Shark is a magnificent creature that can be very big in size. They are known for their unique head shape, which resembles a hammer. These amazing creatures can grow up to an impressive length of 20 feet! That’s like the size of a small truck! Imagine seeing a shark that huge swimming in the ocean, it would be an incredible sight to behold.
Not only are Great Hammerhead Sharks long, but they are also quite heavy. They can weigh up to 1,000 pounds, which is like having several grown-up humans standing on a scale together! These sharks are built with strong muscles and powerful fins that help them navigate through the water effortlessly. With their large size and mighty presence, it’s no wonder they are often considered the king of the ocean.
Despite their large size, Great Hammerhead Sharks are not harmful to humans unless they are threatened. These magnificent creatures primarily feed on smaller fish and stingrays, which they capture with their wide jaws. It’s fascinating to think about how such a big and powerful shark can coexist peacefully with other marine animals in their natural habitat. Just like in the vast ocean, there is room for all creatures to live together in harmony.
In summary, Great Hammerhead Sharks are incredibly big and strong. They can reach lengths of up to 20 feet and weigh as much as 1,000 pounds. Despite their size, they are not dangerous to humans and usually feed on smaller fish and stingrays. We should admire and respect these amazing creatures that roam the ocean and contribute to the rich biodiversity of our planet’s waters.
Habitat of Great Hammerhead Shark
The great hammerhead shark lives in the big, wide ocean. It likes warm and tropical waters. This kind of shark can be found in many different places around the world, such as the coast of Florida and Australia’s Great Barrier Reef. It prefers to swim in shallow waters close to the shore, but it can also go deeper if it needs to.
The great hammerhead shark needs a special kind of habitat to survive. It likes to hang out in places where there are lots of small fish and other sea creatures to eat. It can often be seen near coral reefs, where there is plenty of food. This shark also likes to swim in open ocean areas where there are schools of fish. It has a big, flat head that helps it find its prey under the sand in these areas.
When it is time for the great hammerhead shark to have babies, it goes to a special place called a “nursery.” This is usually a shallow area where the water is warm and safe. The baby sharks stay in the nursery until they are big and strong enough to swim out on their own. The great hammerhead shark is a fascinating creature that thrives in its unique habitat, and it plays an important role in the ocean’s ecosystem.
Evolution of Great Hammerhead Shark
The great hammerhead shark has gone through many changes over millions of years. These amazing animals have evolved over time to become better suited for their underwater environment. Let’s take a look at their evolutionary journey.
Millions of years ago, the ancient ancestors of great hammerhead sharks started out as simple fish with streamlined bodies. As time went on, these fish developed unique features that helped them survive and thrive in their ocean homes. One major change was the development of their flat, wide-shaped head. This unique hammer-like structure made hunting easier, as it allowed them to scan a wider area for prey. Over time, this head evolved to become larger and more pronounced, giving rise to the great hammerhead shark we know today.
Another significant adaptation in the evolution of great hammerhead sharks has been the development of their extraordinary sense of smell. These creatures have an incredible ability to detect even the faintest scent of blood in the water. This heightened sense, combined with their strong sense of hearing, has made them skilled hunters. Their senses have become more advanced over time, enabling them to locate prey more efficiently in their vast ocean habitat.
Furthermore, the great hammerhead shark’s body has undergone changes to help with its swimming capabilities. With their large pectoral and dorsal fins, they can glide through the water with ease. These fins act like wings and allow them to maneuver swiftly and effortlessly. This evolution has led to great hammerhead sharks being excellent swimmers, allowing them to cover large distances in search of food and mates.
In conclusion, the great hammerhead shark has evolved over millions of years to become a fearsome predator of the oceans. Through changes in their head shape, sense of smell, and swimming abilities, these incredible creatures have adapted to their marine environment. With each adaptation, they have become better equipped to navigate, hunt, and survive under the sea.
Classification of Great Hammerhead Shark
The great hammerhead shark is an amazing creature that belongs to the animal kingdom. It falls under the classification of Chondrichthyes, which means it is a type of fish with a skeleton made of cartilage instead of bones. These magnificent sharks are part of the family Sphyrnidae, making them closely related to other hammerhead shark species.
The scientific name for the great hammerhead shark is Sphyrna mokarran. The word “sphyrna” originates from Greek, referring to the shape of the shark’s head, which resembles a hammer or an axe. The specific name “mokarran” simply identifies this particular species. Great hammerhead sharks are known for their distinctive heads with wide, flattened shapes that help with their hunting and sensing prey.
Thus, the classification of the great hammerhead shark can be summarized as follows:
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Chondrichthyes
Order: Carcharhiniformes
Family: Sphyrnidae
Genus: Sphyrna
Species: mokarran
In conclusion, the great hammerhead shark is an extraordinary creature found in the animal kingdom. Belonging to the classification of Chondrichthyes and the family Sphyrnidae, it is a remarkable fish with a unique and distinctive head shape. Its scientific name is Sphyrna mokarran, and it is truly fascinating to learn about the different classifications that help us understand and appreciate this incredible species.
Different Types of Great Hammerhead Shark
1. Size: The Great Hammerhead Shark can grow up to 20 feet long and weigh over 1,000 pounds, making it one of the largest sharks in the ocean. Its immense size allows it to dominate its surrounding environment.
2. Unique Head Shape: The Great Hammerhead Shark has a distinctive T-shaped head that sets it apart from other shark species. This unusual design allows it to locate and capture prey more effectively, giving it a significant advantage in hunting.
3. Excellent Senses: Equipped with highly developed senses, the Great Hammerhead Shark has exceptional eyesight, hearing, and electroreception. These heightened senses enable it to detect prey from miles away, even in dark or murky waters.
4. Powerful Jaws: With a set of strong and sharp teeth, the Great Hammerhead Shark has a powerful bite force. Its jaws help it to tear through the tough skin and bones of its prey, making it an efficient predator in the sea.
5. Wide Diet: Great Hammerhead Sharks have a diverse diet that includes a variety of prey such as stingrays, fish, squid, and crustaceans. This adaptability allows them to thrive in different marine habitats and ensures their survival in various environments.
6. Sea Migration: These sharks are known for their long-distance migrations, traveling great distances in search of food, mates, or suitable habitats. Their ability to navigate vast oceanic spaces is a remarkable feat of nature.
7. Maternal Care: Female Great Hammerhead Sharks are attentive mothers, protecting their young until they are ready to survive on their own. The females give live birth and provide nutrition and protection for their offspring, ensuring the survival of the species.
8. Threatened Species: Unfortunately, Great Hammerhead Sharks face significant threats due to overfishing and habitat destruction. They are classified as an endangered species, and conservation efforts are necessary to safeguard their population for future generations.
9. Importance in Ecosystems: As apex predators, Great Hammerhead Sharks play a crucial role in balancing marine ecosystems. They help control the populations of smaller marine species, preventing imbalances in the food chain and maintaining a healthy underwater environment.
10. Fascination and Research: These amazing creatures have captivated the interest of scientists and shark enthusiasts worldwide. Studying Great Hammerhead Sharks provides valuable insights into the behavior, adaptations, and ecological importance of sharks, helping us better understand and protect these incredible animals.
Geographical Presence of Great Hammerhead Shark
The Great Hammerhead Shark can be found in the coastal regions of tropical and subtropical waters around the world. They are commonly seen in the Atlantic Ocean, from the eastern coast of the United States to South America, as well as in the western Indian Ocean and the western Pacific Ocean. These regions provide the hammerheads with a suitable habitat where they can thrive.
However, there are certain areas where the Great Hammerhead Shark is not found. They are not typically seen in very cold waters, such as those found in the Arctic or Antarctic regions. Additionally, they are rarely spotted in the eastern Pacific Ocean, particularly along the coast of California. The reasons for their absence in these regions may be related to temperature preferences and availability of prey.
In conclusion, the Great Hammerhead Shark can be found in the coastal regions of tropical and subtropical waters worldwide, including the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Oceans. They prefer warmer waters, which provide them with the necessary conditions to survive and hunt for food. However, they are not commonly found in very cold waters or along the eastern coast of the Pacific Ocean.
Scientific Name of Great Hammerhead Shark
The scientific name of the Great Hammerhead Shark is Sphyrna mokarran. This stunning creature is a type of shark that can be found in oceans all around the world. It is named after its unique hammer-like head, which is shaped like a big “T” or hammer. The Great Hammerhead Shark is the largest species of hammerhead shark, with some individuals growing up to 20 feet long!
These incredible sharks have a distinct and powerful body shape, enabling them to be agile swimmers. They have a broad head with eyes placed on either end, giving them excellent all-round vision. Additionally, their mouths are located on the undersides of their heads, allowing them to explore the ocean floor more easily in search of food, such as fish, rays, squid, and even other small sharks!
Despite their size and strength, Great Hammerhead Sharks are generally not considered dangerous to humans. They are typically shy and prefer to avoid human contact. However, as with any wild animal, it is important to treat them with respect and admire them from a safe distance. These sharks play an important role in maintaining the balance of the marine ecosystem and are a marvel to behold in their natural habitats.
Diet of Great Hammerhead Shark
The Great Hammerhead Shark is a fascinating creature with a unique diet. Unlike other sharks that mainly eat fish and marine mammals, the Great Hammerhead Shark enjoys a wider range of food options. Its diet consists of a variety of marine creatures such as fish, squid, stingrays, and even other smaller sharks.
The Great Hammerhead Shark’s most preferred meal is stingrays. With its wide head and hammer-shaped structure, the Great Hammerhead Shark is perfectly equipped to locate and capture stingrays. It uses its sensory organs called ampullae of Lorenzini to detect the electrical signals produced by the buried stingrays. Once it finds its prey, it swiftly attacks, immobilizes it with its teeth, and devours it. Stingrays normally make up a significant portion of the Great Hammerhead Shark’s diet.
Apart from stingrays, the Great Hammerhead Shark also preys on different fish species. It uses its sharp teeth to catch and consume various types of fish, such as tuna, groupers, and smaller sharks. By eating a diverse range of prey, the Great Hammerhead Shark ensures it gets all the necessary nutrients and energy it needs to survive and thrive in its marine habitat.
In summary, the Great Hammerhead Shark has an interesting diet that includes stingrays, fish, squid, and smaller sharks. It is well-adapted to detect and capture its favorite prey, the stingrays, using its unique head shape and specialized sensory organs. By consuming different types of animals, the Great Hammerhead Shark maintains a balanced diet and remains a top predator in the ocean ecosystem.
Locomotion of Great Hammerhead Shark
The great hammerhead shark is a powerful and majestic creature that moves through the water with grace and strength. It uses its long, crescent-shaped body and large pectoral fins to propel itself forward in a method called locomotion.
When swimming, the great hammerhead shark uses a unique technique known as “undulatory locomotion.” It swims by flexing its long body from side to side, creating a wave-like motion that pushes it forward. This allows the shark to move quickly and efficiently through the water, using its powerful muscles to generate enough force to swim against the currents.
In addition to undulatory locomotion, the great hammerhead shark also relies on its large pectoral fins for steering and stability. These fins, located on each side of its body, act like wings and help the shark change direction or maintain its balance while swimming. By adjusting the angle and position of its pectoral fins, the great hammerhead shark can make precise movements and navigate through the waters with ease.
Overall, the locomotion of the great hammerhead shark is a remarkable sight. It uses its long body and powerful fins to swim with grace and strength, allowing it to move swiftly through the water and survive in its ocean home.
Social and Sexual Behaviour of Great Hammerhead Shark
The great hammerhead shark is a fascinating creature with unique social and sexual behavior. These sharks are often seen swimming alone, but they also gather in groups called schools. Within these schools, they engage in social interactions such as circling and bumping into each other. These behaviors help them establish dominance and hierarchy within the group.
During mating season, male great hammerhead sharks often compete for the attention of females. They do this by using their sensory organs to detect the pheromones released by females. Once a male has found a receptive female, he will bite her pectoral fins to hold her in place while he mates with her. This behavior is known as “mating bite,” and it ensures successful reproduction.
Apart from mating, great hammerhead sharks have solitary lives, preferring to be on their own most of the time. However, when it comes to reproduction, they engage in complex social and mating behaviors. These behaviors help them find suitable mates and ensure the survival of their species. Understanding these behaviors is crucial for the conservation of these magnificent creatures and maintaining the balance of our oceans.
Reproduction and Lifecycle of Great Hammerhead Shark
The Great Hammerhead Shark is a fascinating creature that goes through a unique life cycle. Reproduction is an important part of the shark’s life, as it ensures the survival of the species. Female hammerhead sharks give birth to live young ones, a process called viviparity. This means that the embryos grow inside the mother’s womb and receive nutrients through a placenta-like structure. Once fully developed, the mother gives birth to several pups.
The life cycle of a Great Hammerhead Shark begins with reproduction. Mating usually occurs during the warmer months, when the sharks migrate to shallower waters. The male shark uses specialized claspers, which are located on the pelvic fins, to transfer sperm into the female. After mating, the female shark carries the embryos for several months, ranging from 9 to 11 months, depending on the species.
Once born, the young hammerhead sharks are fully independent and must fend for themselves. However, they are more vulnerable to predators at this stage. The pups spend their early days close to coastal areas, where they can find plenty of food and shelter. As they grow older, they gradually move away from the shore and begin their life as solitary predators, hunting for prey in the open ocean.
In conclusion, the Great Hammerhead Shark’s reproductive process is viviparous, with the mother giving birth to live young ones. The life cycle includes mating, gestation, and the independent life of the newborns. It is fascinating to observe how these magnificent creatures reproduce and continue to thrive in our oceans.
Threats to Great Hammerhead Shark
The Great Hammerhead Shark faces many threats in its ocean home. One major problem is overfishing. People catch too many sharks for their fins, which are used in a popular dish called shark fin soup. This makes it hard for the shark population to grow and survive. The demand for shark fins needs to decrease in order to protect these amazing creatures.
Another threat to the Great Hammerhead Shark is habitat loss. Activities like fishing and pollution are damaging their homes, such as coral reefs and mangroves. When these habitats are destroyed, the sharks lose their sources of food and shelter. They are left vulnerable and struggle to find new habitats to live in. It’s important to protect and preserve their habitats so that they can continue to thrive.
Lastly, climate change is also a big threat to the Great Hammerhead Shark. Rising ocean temperatures affect the sharks’ food sources, migration patterns, and reproductive cycles. In addition, the increasing acidity of the water makes it harder for them to survive. We need to take action to reduce our carbon footprint and slow down climate change in order to safeguard the future of these magnificent creatures.
In conclusion, the Great Hammerhead Shark faces several threats including overfishing, habitat loss, and climate change. It is our responsibility to take action and protect these amazing creatures. By reducing our demand for shark fins, preserving their habitats, and combatting climate change, we can ensure a brighter future for the Great Hammerhead Shark. Let us work together to protect and conserve this magnificent species for generations to come.
Population of Great Hammerhead Shark
The population of the Great Hammerhead Shark is estimated to be decreasing. Scientists assume that there are fewer than 10,000 left in the wild. One reason for their decline is overfishing. Many people catch these sharks for their fins, which are used in making soup. This is a big problem because sharks play an important role in maintaining balance in the ocean ecosystem.
Another reason for the decline in population is habitat loss. Hammerhead sharks need healthy coral reefs and seagrass beds to survive. However, these habitats are being destroyed due to pollution, climate change, and human activities like coastal development. As a result, the Great Hammerhead Shark is losing its homes and struggling to find suitable places to live and reproduce.
If the population of the Great Hammerhead Shark continues to decrease at this rate, there is a chance that they could become extinct in the future. Extinction means that the animal no longer exists anywhere in the world. It would be a sad day if we lose these amazing creatures forever. That’s why it’s crucial for us to protect their habitats, limit fishing activities, and raise awareness about the importance of conserving marine life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Great Hammerhead Shark is an incredible creature that has fascinated people around the world. With a unique hammer-shaped head, these sharks have a rich history that dates back millions of years. Found in various oceans across the globe, they are known for their impressive size and habitat preferences.
One interesting fact about the Great Hammerhead Shark is its classification as a cartilaginous fish. This means that its skeleton is made of cartilage instead of bone, making it more flexible and lighter. Despite their intimidating appearance, these sharks are generally not a threat to humans unless provoked.
The Great Hammerhead Shark’s habitat includes both shallow and deep waters, and they can be found in a range of environments such as coral reefs, seagrass beds, and even open ocean areas. They are skilled hunters, using their unique head shape to sense electrical impulses from prey hidden in the sand. Their diet consists mainly of fish, squid, and other smaller marine animals.
In conclusion, the Great Hammerhead Shark is a captivating animal with a long history and interesting characteristics. Its classification as a cartilaginous fish and its impressive hunting abilities make it a truly fascinating species. Understanding and respecting these creatures is crucial for protecting their natural habitats and ensuring their survival in the future.
Frequently Asked Questions about Great Hammerhead Shark (FAQ’s)
Q: What is the scientific name of the Great Hammerhead Shark?
A: The scientific name of the Great Hammerhead Shark is Sphyrna mokarran.
Q: What is the average size of a Great Hammerhead Shark?
A: The average size of a Great Hammerhead Shark is around 13 to 20 feet, with some individuals reaching up to 20 feet in length.
Q: Where can Great Hammerhead Sharks be found?
A: Great Hammerhead Sharks are found in warm coastal waters worldwide, particularly in tropical and subtropical regions.
Q: How long do Great Hammerhead Sharks live?
A: Great Hammerhead Sharks have an average lifespan of around 20 to 30 years.
Q: What is the main diet of Great Hammerhead Sharks?
A: The main diet of Great Hammerhead Sharks consists of a variety of prey, including stingrays, fish, squid, and crustaceans.
Q: Are Great Hammerhead Sharks aggressive towards humans?
A: Great Hammerhead Sharks are generally not aggressive towards humans unless provoked or threatened.
Q: How do Great Hammerhead Sharks hunt?
A: Great Hammerhead Sharks use their unique hammer-shaped head to improve their ability to sense prey and capture it effectively.
Q: Do Great Hammerhead Sharks migrate?
A: Yes, Great Hammerhead Sharks are known to undertake long-distance migrations in search of food, breeding grounds, and suitable habitats.
Q: Are Great Hammerhead Sharks endangered?
A: Yes, Great Hammerhead Sharks are listed as endangered by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) due to overfishing and habitat destruction.
Q: How do Great Hammerhead Sharks reproduce?
A: Great Hammerhead Sharks reproduce through internal fertilization, with females giving birth to live young after a gestation period of around 9 to 12 months.
Q: Can Great Hammerhead Sharks be kept in captivity?
A: Great Hammerhead Sharks are difficult to keep in captivity due to their large size, specialized needs, and high energy requirements.
Q: What are the main threats to Great Hammerhead Sharks?
A: The main threats to Great Hammerhead Sharks include overfishing, bycatch in fisheries, habitat degradation, and climate change.
Q: Do Great Hammerhead Sharks have any predators?
A: Adult Great Hammerhead Sharks are apex predators and have few natural predators. However, smaller sharks and larger predatory fish may prey upon juvenile individuals.
Q: What are the unique characteristics of the Great Hammerhead Shark?
A: The Great Hammerhead Shark is known for its distinctively shaped hammer-shaped head, or cephalofoil, which provides enhanced sensory capabilities.
Q: Can Great Hammerhead Sharks communicate with each other?
A: While the specific communication abilities of Great Hammerhead Sharks are not extensively studied, they are known to exhibit social behaviors and may communicate through body movements and chemical signals.
Q: How can I help in the conservation of Great Hammerhead Sharks?
A: You can contribute to the conservation of Great Hammerhead Sharks by supporting organizations working towards shark conservation, advocating for sustainable fishing practices, and spreading awareness about the importance of these apex predators in marine ecosystems.

Hi there, I’m Emily Buono, and I’m thrilled to introduce myself! Currently, I’m part of two fantastic places: I work as a VisEx at the New England Aquarium and as an RAS at MGH CCM.
I completed my education at the Mass General Research Institute and Stonehill College, which is located in Valatie Colony, New York, in the United States.
Now, here’s the exciting part: I absolutely adore animals! They captivate me, and I’m always eager to learn more about them. In fact, I write articles all about these incredible creatures.
In the past, I’ve worn many hats, such as being a biologist at the Maria Mitchell Association, a cashier, a floor organizer, and a visitor experience and research animal specialist.
My passion lies in exploring the world of animals and helping others understand them better. So, if you ever have questions about animals, feel free to reach out. I’m here to make animal info easy and fun to grasp!