Today, let’s dive into the fascinating world of animals and explore one of its incredible creatures: the Mangrove Snapper. This blog post will provide you with a wealth of information about the history, facts, size, habitat, and classification of this intriguing species. Whether you’re a nature enthusiast or simply curious about animals, this post will surely captivate your interest.
Starting with a quick history lesson, the Mangrove Snapper has been around for centuries, showcasing a rich evolutionary journey. These fish have adapted exceptionally well to their surroundings, making them a remarkable example of nature’s brilliance. From their resilience to their unique behavioral traits, there is no doubt that Mangrove Snappers hold a special place in the animal kingdom.
Now, let’s explore some exciting facts about these remarkable creatures. Known for their reddish-brown coloration and stunning blue accents, Mangrove Snappers are visually captivating. They can grow up to 24 inches in length and weigh around 10 pounds, making them a significant presence in their marine habitats. Speaking of which, you can find these snappers in the coastal areas of the Western Atlantic Ocean, from the Gulf of Mexico to Brazil.
When it comes to classification, the Mangrove Snapper belongs to the family Lutjanidae and the genus Lutjanus. This classification groups them with other similar species, providing scientists and researchers with valuable insights into their behavior, characteristics, and overall biology. Understanding this classification helps us appreciate the immense diversity within the animal kingdom.
In conclusion, the Mangrove Snapper is an extraordinary creature that has carved its place in the vast realm of animals. Its rich history, fascinating facts, unique size, natural habitat, and classification all contribute to its overall magnificence. Stay tuned for future blog posts as we continue to explore the wonders of the animal world. And remember, if you’re interested in learning about more animals, we already have an article featuring over 155 other remarkable species. Happy exploring!
History of Mangrove Snapper
The mangrove snapper is a type of fish that can be found in warm coastal waters of the Atlantic Ocean, Gulf of Mexico, and the Caribbean Sea. It is known for its reddish-brown color and the dark horizontal stripes that run along its body. This species of fish has a long and interesting history that dates back thousands of years.
Historically, the mangrove snapper has been an important source of food for many indigenous coastal communities. Native Americans and early settlers used various methods to catch these fish, including nets, spears, and traps. They recognized the value of the mangrove snapper as a nutritious food source and also used its bones and scales for making tools and jewelry.
Over the years, the popularity of sport fishing grew, and the mangrove snapper became a prized game fish. Anglers from all around the world now travel to coastal areas where the species is abundant to try their luck at catching these elusive fish. Conservation efforts have also been put in place to protect the snapper population and ensure its sustainability for future generations.
In conclusion, the mangrove snapper is a fascinating fish with a rich history. It has provided sustenance to coastal communities for centuries and continues to be a sought-after game fish for anglers today. By understanding and appreciating the history of this species, we can work towards preserving its natural habitat and ensuring its survival for many years to come.
Importance of Mangrove Snapper
The Mangrove Snapper is an important animal in the ecosystem. It plays a vital role in maintaining the balance of marine life. These snappers feed on small prey, like crustaceans and small fish. By doing so, they help control their population, preventing it from growing too much. This keeps the balance intact and allows other marine creatures to coexist peacefully.
Not only do Mangrove Snappers help control the population of smaller animals, but they also serve as prey for larger predators. They provide food for a variety of other marine animals, such as sharks and dolphins. This creates a food chain, where every animal has a role to play. Without Mangrove Snappers, the food chain would be disrupted, leading to imbalances in the ecosystem.
Additionally, Mangrove Snappers contribute to the health of coral reefs. They help control the population of herbivorous fish by preying on them. This prevents herbivorous fish from overeating the algae on coral reefs. Thus, Mangrove Snappers indirectly protect the coral reefs, which are crucial marine habitats and provide shelter for numerous other species.
To sum up, Mangrove Snappers play a crucial role in maintaining the marine ecosystem’s balance. By feeding on small prey, these snappers control their population and prevent imbalances. They also serve as an important link in the food chain, providing food for larger predators. Moreover, by controlling the population of herbivorous fish, they indirectly protect coral reefs. Thus, the presence of Mangrove Snappers is essential for the overall health and sustainability of the marine environment.
Amazing Facts About Mangrove Snapper
1. Mangrove snapper is a type of fish that can be found in the warm waters of the western Atlantic Ocean, from the Gulf of Mexico down to Brazil.
2. These snappers have a slender, elongated body shape with a dark gray or brownish coloration on their back and sides, and a lighter colored belly.
3. They have a more streamlined body compared to other snapper species, which helps them swim swiftly through the water.
4. Mangrove snappers have a strong, pointed snout and sharp teeth that they use to feed on a variety of prey including fish, shrimp, crabs, and even small octopuses.
5. They are typically found near coastal mangrove forests, hence their name, but they can also be found near rocky reefs, wrecks, and other structures.
6. These fish are highly adaptable and can survive in a range of environments, from freshwater areas to saltwater estuaries.
7. Mangrove snappers are usually solitary hunters, but they can form small schools, especially during spawning season.
8. The average size of a mangrove snapper is between 10 to 20 inches, but they can grow up to 30 inches and weigh around 15 pounds.
9. They have a lifespan of around 20 years, which allows them to reach their full size and reproductive potential.
10. These snappers are highly prized by both recreational and commercial anglers due to their strong fighting ability and delicious taste.
11. Male mangrove snappers reach sexual maturity at around 2 to 3 years of age, while females reach maturity at around 3 to 4 years.
12. Spawning usually occurs during warmer months, where females release their eggs into the water column and males release their sperm to fertilize them.
13. The eggs then hatch into larvae, which drift in the open ocean for several weeks before settling into the coastal waters.
14. Mangrove snappers have a fairly high growth rate, with individuals growing about 4 inches per year during their juvenile stage.
15. While not considered endangered, mangrove snappers face threats from overfishing, habitat destruction, and pollution, emphasizing the importance of sustainable fishing practices and conservation efforts.
Can we keep Mangrove Snapper as our Pet?
Mangrove snapper are beautiful fish found in the warm waters of the western Atlantic Ocean. They have a striking red color and are known for their feisty nature. However, it is not recommended to keep mangrove snapper as pets. These fish are not suitable for home aquariums because they need a large, natural habitat to thrive.
Mangrove snapper are native to coastal areas and are adapted to living in the wild. They require specific conditions that are difficult to replicate in a home aquarium. They need plenty of swimming space and a complex environment with rocks, caves, and hiding spots. Additionally, they have specific dietary needs that can be challenging to meet outside of their natural habitat.
Moreover, it is important to conserve these fish in their natural environment to maintain a healthy ecosystem. Mangrove snapper play a crucial role as predators in the marine food chain. If they were removed from their natural habitat, it could disrupt the balance of the ecosystem and harm other marine species.
Unfortunately, due to environmental factors such as habitat destruction and overfishing, mangrove snapper populations are declining in some areas. If this continues, the species may become extinct in the future. Therefore, it is essential to protect and preserve their natural habitat rather than trying to keep them as pets. By ensuring the survival of mangrove snapper in the wild, we can maintain the beauty and balance of our oceans for generations to come.
Size of Mangrove Snapper
Mangrove snapper is a small to medium-sized fish commonly found in coastal areas of the Atlantic Ocean, Caribbean Sea, and Gulf of Mexico. These snappers are known for their vibrant reddish-brown coloration and bright blue streaks along their sides. They have a streamlined body, which allows them to swiftly move through the water. On average, adult mangrove snappers grow to about 10-18 inches in length and weigh around 1-4 pounds. However, some individuals can grow even larger, reaching up to 24 inches in length.
The size of mangrove snapper varies depending on several factors, including their age, habitat, and available food sources. Juvenile snappers typically start at around 1-2 inches in length and grow rapidly during their first year. As they mature, they may move to deeper waters or migrate to specific coastal habitats, such as mangrove forests, where they find refuge among the tangled roots. These habitats provide protection and abundant food, allowing the snappers to reach their maximum size.
Despite their relatively small size compared to other fish species, mangrove snappers are highly sought after by both recreational and commercial fishermen. Their delicious flavor and firm, white flesh make them a popular choice for seafood lovers. However, due to their popularity as a food source, it is important to practice responsible fishing and adhere to size and bag limits to ensure the sustainability of this species.
Overall, the size of mangrove snappers can vary, but they generally range from 10-18 inches in length and weigh around 1-4 pounds. These small to medium-sized fish are known for their beautiful colors and are highly valued for their taste. It is crucial to protect their habitats and regulate fishing practices to maintain healthy populations of mangrove snappers in our oceans.
Habitat of Mangrove Snapper
Mangrove snappers, a type of fish, are found in the warm waters of the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Mexico. Their habitat mainly consists of mangrove forests, which are coastal areas with unique trees and plants that can tolerate salty water. These forests provide the perfect environment for the mangrove snapper to thrive.
One important aspect of the mangrove snapper’s habitat is the presence of dense mangrove roots. These roots create a network of shelter and hiding places for the fish. They provide protection from predators and offer a safe space for the snappers to lay their eggs. Additionally, the roots provide a rich source of food, as they attract small crustaceans and other invertebrates that the snappers feed on.
Another key feature of the snappers’ habitat is the presence of shallow and warm waters. Mangrove forests are often situated in areas where the waters are calm, shallow, and sun-drenched. These conditions are ideal for the growth of the mangrove trees, but they also suit the mangrove snapper’s needs. The warm waters provide a comfortable temperature for the fish to live in, and the shallowness allows them to easily swim and hunt for food.
Overall, the mangrove snapper relies on the unique habitat of mangrove forests for its survival. These fish are well adapted to the mangrove ecosystem, using the dense roots as shelter and the warm, shallow waters as their home. This habitat provides them with the necessary resources, protection, and breeding grounds for them to thrive and continue their life cycle.
Evolution of Mangrove Snapper
Mangrove snappers, known scientifically as Lutjanus griseus, are fascinating creatures that have evolved over many years to adapt to their environment. These snappers belong to a larger group of fish called snappers, which are found in warm waters around the world. While we won’t talk about mangrove snappers specifically, their evolution can tell us a lot about how animals change over time.
In the beginning, the ancestors of mangrove snappers were probably simple fish that lived in the oceans. Over time, some of these fish started to move closer to the shore, where there were mangrove forests. These forests provided the perfect habitat for these fish to thrive. The snappers adapted to the shallow, warm waters and began to develop features that helped them survive in this new environment.
One important adaptation is their ability to breathe air. Mangrove snappers have a special organ in their mouth called a labyrinth organ, which allows them to take in oxygen from the air. This helps them survive in the low-oxygen mangrove swamps. Another important change is their ability to camouflage. The snappers developed a color pattern that helps them blend in with their surroundings, making it easier for them to catch prey or hide from predators.
In conclusion, the evolution of the mangrove snapper showcases how animals can adapt to their environment over time. Through changes in their physical features, such as the ability to breathe air and their camouflage patterns, these fish have become well-suited to their habitat in the warm mangrove forests. This process of evolution is fascinating to study and helps us understand the incredible diversity of life on Earth.
Classification of Mangrove Snapper
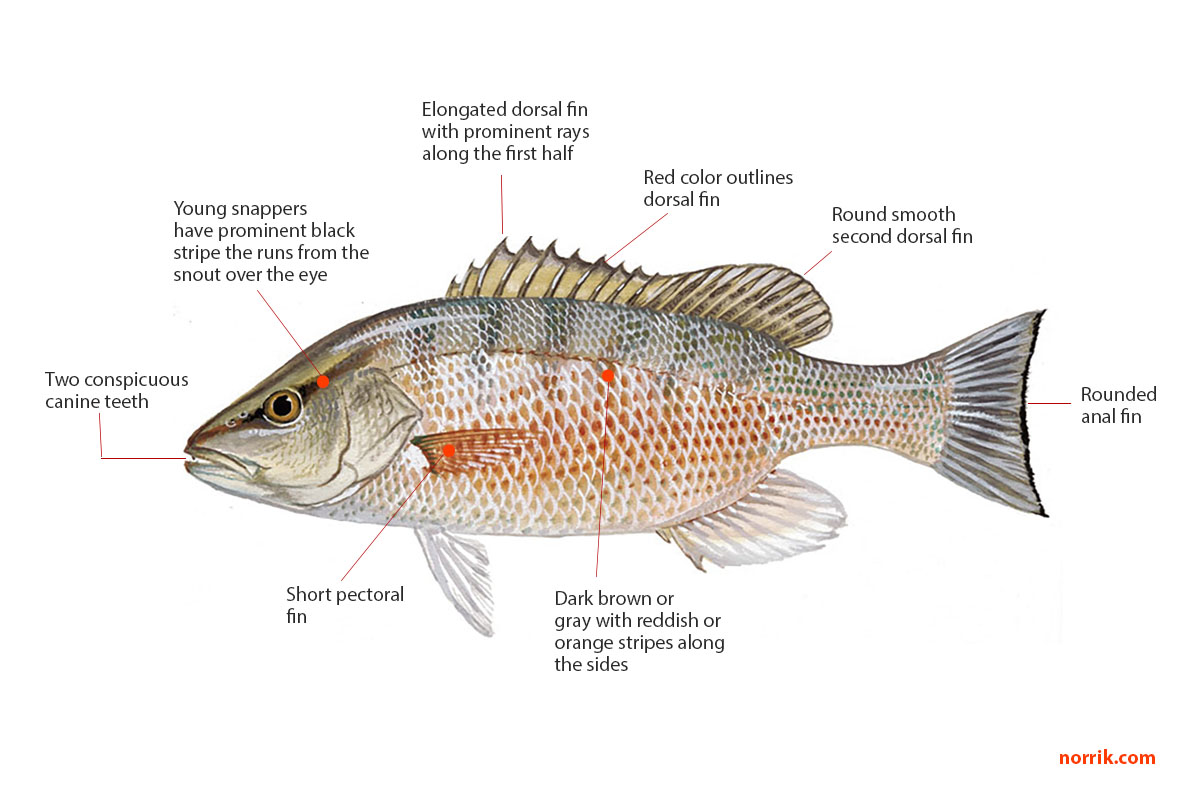
The Mangrove Snapper is a fascinating animal that belongs to the family of Lutjanidae. It is commonly found in warm coastal waters, particularly in mangrove forests. These beautiful fish have a reddish-brown color on their upper body and a silver-white shade on their belly. They also have distinctive canine teeth that help them capture their prey. The Mangrove Snapper is known for its curious behavior and is a popular choice among anglers.
In terms of classification, the scientific name given to the Mangrove Snapper is Lutjanus griseus. It is classified under the Animalia Kingdom, the Chordata Phylum, and the Actinopterygii Class. The Mangrove Snapper belongs to the Perciformes Order, which consists of more than 40% of all fish species known to us. Within the Lutjanidae family, there are various species of snappers, and the Mangrove Snapper is one of them.
The Mangrove Snapper can be found in different regions, including the Caribbean Sea, the Gulf of Mexico, and parts of the Western Atlantic Ocean. They prefer areas with shallow waters, such as mangrove swamps and estuaries. These fish are not typically very large, with an average length of around 20-30 centimeters. However, there have been reports of larger Mangrove Snappers measuring up to 50 centimeters.
In conclusion, the Mangrove Snapper is an interesting fish belonging to the family Lutjanidae. Its scientific name is Lutjanus griseus, and it can be found in warm coastal waters. Despite its relatively small size, this beautiful fish captures the attention of many anglers. With its distinct coloration and curious behavior, the Mangrove Snapper is a fascinating creature to observe in its natural habitat.
Different Types of Mangrove Snapper
1. Size: Mangrove snappers are medium-sized fish that typically grow to a length of 2-3 feet. They have a slender body and are known for their vibrant reddish-brown coloration.
2. Habitat: These snappers are commonly found near the roots of mangrove trees in coastal regions, particularly in warm, tropical waters. They seek shelter and protection among the tangled roots, making them well adapted to this unique environment.
3. Feeding habits: Mangrove snappers are carnivorous and mainly feed on smaller fish, shrimp, crabs, and other invertebrates. They are stealthy hunters and use their sharp teeth to capture their prey.
4. Nocturnal behavior: These snappers are primarily active during the night, often hiding among the mangrove roots during the day. They emerge after sunset to forage for food, taking advantage of the cover of darkness.
5. Breeding patterns: During mating season, mangrove snappers move to deeper waters to reproduce. The females release a large number of eggs into the water column, which are then fertilized by the males. The eggs hatch into tiny larvae that eventually settle into coastal habitats.
6. Social behavior: Mangrove snappers are known to form loose groups or schools, especially when they are young. These schools provide protection against predators and increase their chances of finding food.
7. Economic importance: Mangrove snappers are highly prized by commercial and recreational fishermen due to their delicious taste and fighting ability when caught. Their high demand makes them valuable in the fishing industry.
8. Environmental significance: Mangrove ecosystems are crucial for the health of coastal regions as they provide protection against erosion, act as nurseries for various marine species, and improve water quality. The presence of mangrove snappers indicates a healthy and balanced habitat.
9. Threats and conservation: Overfishing, habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change pose significant threats to mangrove snapper populations. It is important to protect and conserve their habitats and implement sustainable fishing practices to ensure their survival.
10. Role in the food chain: Mangrove snappers serve as an important link in the food chain, as both predators and prey. They help control populations of smaller fish and invertebrates, and in turn, are preyed upon by larger fish, birds, and marine mammals.
Geographical Presence of Mangrove Snapper
The Mangrove Snapper, often known as grey snapper or black snapper, is commonly found in the warm waters of the western Atlantic Ocean. They can be seen swimming along the coasts from North Carolina in the United States to Brazil, including the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea. These fish prefer habitats with mangrove trees and are commonly found in shallow coastal areas, estuaries, and lagoons. This region provides the ideal conditions for the mangrove snapper to thrive and reproduce.
However, there are certain regions where the mangrove snapper is not found. They are not typically found in colder waters such as those in the northern Atlantic Ocean. As the temperature drops in these regions, it becomes difficult for mangrove snappers to survive. Therefore, they are not usually seen in areas like Canada, Greenland, or Europe.
Additionally, mangrove snappers are not present in freshwater environments like rivers, lakes, or ponds. They require the specific saltwater conditions found in their natural habitat to survive and thrive. So, you won’t find them in places where the water is not salty enough for them, such as freshwater lakes or rivers.
In conclusion, mangrove snappers are primarily found along the coasts of the western Atlantic Ocean, from North Carolina to Brazil. They prefer warm waters and habitats with mangrove trees. However, they are not found in colder waters or freshwater environments such as rivers and lakes.
Scientific Name of Mangrove Snapper
The scientific name of the Mangrove Snapper animal is Lutjanus griseus. The Mangrove Snapper is a type of fish that belongs to the family Lutjanidae. This fish species is commonly found in the warm coastal waters of the Atlantic Ocean, specifically along the coasts of North and South America.
The Mangrove Snapper gets its name from its habitat preference. It is often found in and around mangrove forests, which are dense areas of trees and shrubs that grow in coastal areas. These forests provide the snapper with shelter and protection, allowing them to blend in with their surroundings and avoid predators.
Mangrove Snappers have a streamlined body shape and can vary in color, ranging from gray to reddish-brown. They have sharp canine teeth and powerful jaws that allow them to eat a variety of prey including fish, shrimp, crabs, and other small invertebrates.
In summary, the Mangrove Snapper, scientifically known as Lutjanus griseus, is a type of fish that is commonly found in the coastal waters of the Atlantic Ocean. They are known for their association with mangrove forests and have adaptations that help them survive in their habitat. With their streamlined body shape and specialized teeth, they are able to feed on a variety of prey.
Diet of Mangrove Snapper
The mangrove snapper is a fascinating animal that lives in warm saltwater, usually near mangrove forests. It has a varied and healthy diet that helps it stay strong and grow big. The main food of the mangrove snapper consists of small fish and crustaceans like shrimp and crabs. They are a skilled hunter and can quickly snatch their prey with their sharp teeth.
In addition to fish and crustaceans, mangrove snappers also eat other small creatures, such as worms and insects. They have a keen sense of smell, which helps them find food hidden in the water. Sometimes, they even eat smaller snappers or other fish that are unlucky enough to cross their path! They are opportunistic eaters and will consume anything they can catch and fit in their mouth.
These snappers rely on their excellent eyesight to locate their prey. They have specially adapted jaws that allow them to capture and swallow their food quickly. Their powerful stomachs can easily digest the food they eat, allowing them to extract all the nutrients they need. This helps them grow big and strong and continue to thrive in their habitat.
Overall, the diet of the mangrove snapper is diverse and includes a variety of small fish, crustaceans, worms, and insects. These amazing creatures are skilled hunters and eat almost anything they can find in their environment, ensuring they have enough energy to survive and grow.
Locomotion of Mangrove Snapper
Mangrove snappers are known for their impressive swimming skills. These fish have a unique way of moving through the water called locomotion. Locomotion is the way an animal moves from place to place. In the case of mangrove snappers, they use their muscular bodies and strong tails to propel themselves forward in the water.
When swimming, mangrove snappers flex their strong bodies and move their tails in a side-to-side motion. This flapping movement allows them to move through the water quickly and with ease. They can change direction swiftly by adjusting the angle of their tail movements. This type of locomotion is important for them to find food, avoid predators, and navigate their habitat efficiently.
In summary, mangrove snappers have a special way of swimming known as locomotion. Their strong bodies and tails help them move through the water in a side-to-side motion, allowing them to swim fast and change direction quickly. This locomotion is essential for their survival as it helps them find food and stay away from danger in their natural environment.
Social and Sexual Behaviour of Mangrove Snapper
The mangrove snapper is a fascinating fish that lives in warm and tropical waters. When it comes to their social behavior, these snappers like to gather in large groups called schools. These schools can have hundreds or even thousands of fish swimming together. Being part of a school helps protect them from predators and allows them to find food more easily. Within these schools, mangrove snappers establish a hierarchy, where the larger and more dominant individuals have a higher rank and control over the group.
When it comes to their sexual behavior, mangrove snappers are quite interesting. They are what we call “sequential hermaphrodites,” which means they can change from females to males as they grow older. They start their lives as females, and as they reach a certain size and age, some of them will become males. This change in sex can happen because of the needs of their population. It helps to ensure that there are enough males to reproduce with the females. In this way, mangrove snappers are able to adapt and maintain a healthy balance in their species.
In summary, mangrove snappers are highly social fish that live in large schools. They establish a social hierarchy to maintain order within the group. When it comes to their sexual behavior, they are sequential hermaphrodites, transitioning from females to males as they grow older. This change helps to ensure the reproduction and survival of their species.
Reproduction and Lifecycle of Mangrove Snapper
The mangrove snapper is a type of fish that lives in warm coastal waters. These snappers have a unique reproductive process. They begin their lives as tiny larvae, hatching from eggs that are released into the water by adult snappers. These larvae float in the water, drifting with the currents, until they find a suitable place to settle.
Once the larvae find a safe spot, such as a mangrove tree or a shallow patch of reef, they transform into juvenile snappers. At this stage, their bodies have developed scales and they start to resemble adult snappers. The young snappers will then spend the next few years growing and maturing in these safe areas, feasting on small fish and crustaceans to fuel their growth.
As they continue to grow, the snappers reach sexual maturity. This means that they are now ready to reproduce and have their own offspring. During the breeding season, adult snappers gather in large groups near reefs or mangrove forests. The females release their eggs into the water, while the males fertilize them externally. The eggs hatch into larvae, starting the life cycle of the mangrove snapper all over again.
In this way, the mangrove snapper is able to reproduce and ensure the survival of its species. Through their unique life cycle, these fish constantly replenish their populations, allowing them to thrive in their warm coastal habitats. The mangrove snapper’s life cycle is an important part of the diverse and fascinating world of marine creatures.
Threats to Mangrove Snapper
The mangrove snapper animal faces several threats that can harm its population and survival. One major threat to these snappers is overfishing. Many people catch these fish in large quantities for food or sport, which reduces their numbers in the wild. If too many snappers are caught, their population may not be able to recover, causing a decline in their overall numbers.
Another threat to mangrove snappers is the destruction of their natural habitats. Mangrove forests, where these snappers live, are often cleared to make way for human activities like agriculture and development. When these trees are cut down, the snappers lose their homes and may struggle to find a new place to live. Without suitable habitats, their numbers can decline, and they may face difficulties in finding enough food and avoiding predators.
Pollution is also a significant threat to mangrove snappers. Human activities, such as industrial waste and oil spills, can contaminate the water in which these snappers live. This pollution can harm the snappers directly, leading to health problems or death. Additionally, it can affect their food sources, making it harder for them to find enough to eat. Pollution can have long-lasting effects on mangrove snapper populations, reducing their overall numbers and making it harder for them to survive.
In order to protect the mangrove snapper animal, it is important to limit overfishing and implement sustainable fishing practices. Furthermore, efforts should be made to conserve and restore mangrove habitats, ensuring that these fish have suitable places to live and reproduce. Additionally, strict regulations should be enforced to prevent pollution in the waters where these snappers reside. By addressing these threats, we can help ensure the survival and well-being of the mangrove snapper animal.
Population of Mangrove Snapper
The population of the Mangrove Snapper animal is believed to be quite large. It is estimated that there are millions of these snappers living in various parts of the world, particularly in the warm waters of the Atlantic Ocean, the Gulf of Mexico, and the Caribbean Sea. These fish are known to gather in large schools, which makes it easier for them to find food and protect themselves from predators.
Sadly, if the Mangrove Snapper were to go extinct, it would mean that there are no more of these animals in the world. Extinction happens when the entire population of a species dies out. When this occurs, it is usually because of factors like habitat destruction, pollution, overfishing, or climate change. In the case of the Mangrove Snapper, if it did become extinct, it would have a negative impact on the ecosystem because it plays an important role in maintaining the balance of marine life.
To prevent the extinction of the Mangrove Snapper and other important species, it is crucial that we take care of their habitats, reduce pollution, and practice sustainable fishing methods. It is our responsibility to protect these animals and ensure that future generations can also enjoy their beauty and play a part in the delicate web of life on Earth.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Mangrove Snapper is a fascinating fish that can be found in warm coastal waters around the world. These snappers have a rich history and are known for their unique characteristics.
Firstly, let’s talk about their size. Mangrove Snappers can grow up to 24 inches long, making them quite a big fish! They have a slender body and a prominent jaw that helps them catch their prey. These snappers are also known for their vibrant colors, with a dark brown or grayish body and a reddish hue on their fins.
Next, let’s discuss their habitat. As the name suggests, Mangrove Snappers can often be found in mangrove areas. These fish seek shelter and food among the roots of mangroves, using them as natural protection. They are known to be quite adaptable and can also be found near wrecks, reefs, and seagrass beds.
Lastly, let’s touch upon their classification. The Mangrove Snapper belongs to the Lutjanidae family and is scientifically known as Lutjanus griseus. This species is part of the animal kingdom and the chordate phylum. It is truly a remarkable creature that adds diversity to the marine ecosystem.
In summary, the Mangrove Snapper is a captivating fish known for its size, habitat, and classification. Its large size, vibrant colors, and adaptability make it a remarkable addition to the underwater world. So, next time you’re exploring coastal waters, keep an eye out for these fascinating creatures!
Frequently Asked Questions about Mangrove Snapper (FAQ’s)
Q: What is a mangrove snapper?
A: The mangrove snapper is a species of fish found in the western Atlantic Ocean and Gulf of Mexico.
Q: How big do mangrove snappers grow?
A: Mangrove snappers can grow up to 24 inches in length and weigh up to 19 pounds.
Q: What do mangrove snappers eat?
A: They primarily feed on small fish and shrimp, but also consume crabs and other marine invertebrates.
Q: Where do mangrove snappers live?
A: Mangrove snappers are commonly found near mangrove forests, reefs, docks, and other structures along the coast.
Q: How long do mangrove snappers live?
A: They typically live for around 10-15 years in the wild.
Q: Are mangrove snappers aggressive?
A: Mangrove snappers can be aggressive predators, especially when hunting for food.
Q: Can mangrove snappers be kept as pets?
A: Some people keep mangrove snappers in large aquariums, but they require specific conditions and expertise to thrive.
Q: Are mangrove snappers good to eat?
A: Mangrove snappers are highly sought-after for their delicious white flesh and are considered excellent table fare.
Q: How do mangrove snappers reproduce?
A: They are known to spawn offshore, and the eggs hatch into larvae which then migrate to mangrove habitats for further development.
Q: What are the predators of mangrove snappers?
A: Some of the predators of mangrove snappers include larger fish, such as groupers, barracudas, and sharks.
Q: Can mangrove snappers be caught for sport fishing?
A: Yes, mangrove snappers are a popular species among sport fishermen due to their strong fight and tasty meat.
Q: Are there any regulations for catching mangrove snappers?
A: Regulations regarding the size and bag limits for catching mangrove snappers vary depending on the location and fishing regulations.
Q: Do mangrove snappers have any commercial value?
A: Yes, mangrove snappers are commercially harvested and sold in seafood markets and restaurants.
Q: How can you identify a mangrove snapper?
A: Mangrove snappers have a reddish-brown to grayish body with a dark lateral line running down their side.
Q: What is the scientific name of mangrove snapper?
A: The scientific name of mangrove snapper is Lutjanus griseus.
Q: Are mangrove snappers an important part of the ecosystem?
A: Yes, mangrove snappers play a vital role in the coastal ecosystem by controlling populations of smaller fish and maintaining a balance in the food web.

Hi there, I’m Emily Buono, and I’m thrilled to introduce myself! Currently, I’m part of two fantastic places: I work as a VisEx at the New England Aquarium and as an RAS at MGH CCM.
I completed my education at the Mass General Research Institute and Stonehill College, which is located in Valatie Colony, New York, in the United States.
Now, here’s the exciting part: I absolutely adore animals! They captivate me, and I’m always eager to learn more about them. In fact, I write articles all about these incredible creatures.
In the past, I’ve worn many hats, such as being a biologist at the Maria Mitchell Association, a cashier, a floor organizer, and a visitor experience and research animal specialist.
My passion lies in exploring the world of animals and helping others understand them better. So, if you ever have questions about animals, feel free to reach out. I’m here to make animal info easy and fun to grasp!