Animals Name, specifically the mole, is an intriguing creature that captivates many curious minds. These small, furry mammals have a fascinating history and boast an array of interesting facts. Understanding their size, habitat, and classification adds a deeper appreciation for these elusive diggers of the animal kingdom. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of moles and uncover the secrets that make them truly remarkable.
First and foremost, let’s explore the history of moles. These amazing mammals have been around for millions of years, adapting and evolving to become the expert burrowers we know today. With their specialized front paws and strong muscles, moles excel in digging intricate tunnel systems beneath the ground. These tunnels not only serve as their homes but also play a crucial role in their search for food. By understanding their history, we can gain insight into their fascinating abilities and why they are uniquely suited to their underground lifestyle.
Moving on, let’s delve into some interesting facts about moles. Did you know that moles belong to the Talpidae family, which includes more than 40 species worldwide? They vary in size and color, ranging from as small as a thumb to as long as a pencil. Moles are known for their velvety fur, which aids in their ability to move smoothly through the soil. Another fascinating fact is that moles have a special sixth sense called Eimer’s organ, located on the tip of their snout, which helps them navigate their surroundings. By learning these intriguing facts, we can truly appreciate the marvel of these Animals Names.
Lastly, let’s explore the size, habitat, and classification of moles. Moles are typically small creatures, ranging from 4 to 7 inches in length. They reside in a variety of habitats, including woodlands, grasslands, and gardens. Their underground burrows provide them with safety and protection from predators. When it comes to classification, moles are part of the mammal class and the order Soricomorpha, which includes shrews and solenodons. Delving into these details not only enriches our knowledge but also allows us to better understand the essential role moles play in their ecosystems.
In summary, moles are truly fascinating Animals Names. Through a glimpse into their history, knowledge of their facts, and understanding of their size, habitat, and classification, we can appreciate the unique qualities that make them such intriguing creatures. We hope this blog post helps shed some light on the captivating world of moles and encourages further exploration of the diverse animal kingdom we share with these remarkable beings. Remember, we already have an article on 155+ Animals Names if you would like to discover more about the incredible creatures that inhabit our world.
History of Mole
The mole is a small animal that has been living on Earth for a very long time. Its history dates back millions of years, and it has evolved and adapted to its surroundings over time. The mole is known for its unique features and amazing abilities, making it a fascinating creature to study.
In the past, moles roamed different parts of the world, including Europe, Asia, and North America. They have always preferred to live in underground tunnels, using their strong front digging paws to create elaborate systems of tunnels and burrows. These tunnels help them find food and stay protected from predators.
Throughout history, moles have faced many challenges and changes in their environment. As cities and towns were built, their natural habitats were often destroyed, forcing them to adapt and find new places to live. Despite these challenges, moles have managed to survive and even thrive in various habitats, showing great resilience and adaptability.
Today, moles continue to live in many parts of the world, including gardens, fields, and forests. They have become known for their ability to dig tunnels quickly and efficiently, helping to aerate the soil and control pest populations. Although they can sometimes be considered a nuisance to humans, their important role in the ecosystem cannot be ignored.
In summary, the history of the mole is one of perseverance and adaptation. These small creatures have managed to survive and thrive despite the many changes that have occurred over millions of years. Their ability to dig tunnels and live underground has allowed them to find food and stay safe from predators. The mole’s story is a reminder of the incredible resilience and power of nature.
Importance of Mole
The mole is an important animal that plays a crucial role in our environment. It may be small, but its impact is big. Firstly, moles are expert diggers. They create intricate tunnel systems underground, which helps to aerate the soil. This allows nutrients and water to reach the roots of plants, making them grow stronger and healthier. Without moles, the soil would become compacted and hard, making it difficult for plants to grow.
Secondly, moles eat insects, grubs, and worms that live in the soil. These pests can harm plants and crops by eating their roots or leaves. By feeding on these pests, moles help to control their population, keeping them in check. This is important for farmers and gardeners who rely on healthy plants for food and beauty.
Lastly, moles are an important part of the food chain. They are prey for many animals, such as owls, foxes, and snakes. Without moles, these predators might struggle to find enough food to survive. Moles are also great indicators of a healthy ecosystem. If moles are present, it means that the soil is rich and diverse, supporting a wide variety of plants and animals.
In conclusion, moles may seem unimportant or even annoying to some people, but they play a vital role in our environment. Their digging helps to aerate the soil, their appetite for pests helps to protect plants, and they are a crucial part of the food chain. So next time you see a mole, remember how important it is for the health of our ecosystem.
Amazing Facts About Mole
1. Moles are small mammals that belong to a group called insectivores, which means they mainly eat insects.
2. Moles have cylindrical bodies, covered in thick fur that can be gray, black, or brown, depending on the species.
3. These underground critters have powerful front limbs and sharp claws that they use for digging tunnels and burrows.
4. Moles have tiny eyes that are only able to detect light and dark, because they spend the majority of their lives underground.
5. Despite having poor eyesight, moles have highly developed senses of touch and hearing, which help them navigate in the dark tunnels.
6. Moles have no external ears. Instead, they have a layer of fur that covers their ear openings, protecting them while they dig.
7. Moles are solitary animals and are most active during the night. They spend much of their time underground, coming to the surface only occasionally.
8. These animals construct elaborate networks of tunnels called molehills, which serve as their homes and foraging areas.
9. Moles are excellent diggers and can create tunnels at an impressive rate of up to 18 feet (5.5 meters) per hour.
10. They eat a variety of insects, including earthworms, grubs, beetles, and spiders, which they find by using their sharp sense of smell.
11. Moles have a high metabolic rate, and they need to eat a lot of food every day to maintain their energy levels.
12. To ensure they have a constant food supply, moles store excess worms and insects in special underground pantries within their tunnels.
13. Moles are found in various habitats, such as grasslands, woodlands, and gardens, as long as the soil is soft enough for digging.
14. Depending on the species, moles can range in size from about 4 to 8 inches (10 to 20 centimeters) in length.
15. Moles play an essential role in aerating the soil and controlling insect populations, making them beneficial to ecosystems and gardeners alike.
Can we keep Mole as our Pet?
The mole animal is a fascinating creature that lives underground. It has a unique body shape and a strong sense of smell which helps it dig tunnels and find insects to eat. While some people may think it would be interesting to keep a mole animal as a pet, it is not suitable or ethically right to do so.
Firstly, mole animals are not designed to live in homes or cages. They spend most of their time burrowing underground, which is not possible to replicate in a house or a backyard. Moles need a large area to roam and dig, and it would be unfair to confine them to a small space. This would cause them stress and unhappiness.
Secondly, it’s important to know that mole animals play a crucial role in their ecosystem. They help to aerate the soil, control insect populations, and even contribute to plant growth. Sadly, some species of mole animals are facing extinction due to habitat loss and pollution. It is our responsibility to protect and conserve them in their natural habitats, not keep them as pets.
In conclusion, keeping a mole animal as a pet is neither practical nor ethical. They are meant to live freely in their natural habitats, not inside cages or houses. Additionally, with some mole species facing extinction, it is important to prioritize conservation efforts rather than attempt to keep them as pets. Let’s appreciate these fascinating animals from a distance and work towards preserving their habitats for future generations to enjoy.
Size of Mole
The mole is a small animal that lives underground. It is about 4 to 6 inches long, which is roughly the same size as a small ruler. The size can vary depending on the species of mole, but they are generally quite small.
Moles have short, stocky bodies with strong, shovel-like front paws that they use for digging tunnels. These tunnels are their homes and help them find food. They have thick fur that is usually gray or brown, which helps them blend in with the soil and stay warm in their underground habitats.
Even though moles are small, they are very skilled diggers. They can use their front paws to quickly burrow through the ground, creating complex tunnel systems. These tunnels can sometimes be more than 100 feet long! Moles are also active all year round, searching for earthworms, insects, and grubs to eat.
In summary, the mole is a small animal that measures around 4 to 6 inches in length. It has a stocky body and strong front paws for digging tunnels. Despite their small size, moles are skilled diggers and can create extensive networks of tunnels underground. They have thick fur and are constantly on the lookout for food.
Habitat of Mole
The mole animal lives in several different habitats and can be found in various parts of the world. They prefer living in places that have loose soil, such as forests, grasslands, and gardens. These furry creatures create intricate networks of underground tunnels, which they use to navigate and hunt for their food.
One of the most fascinating habits of moles is their ability to dig underground tunnels. They have strong, muscular bodies with powerful front paws and sharp claws that help them burrow through the soil. These tunnels are important for the mole’s survival as they provide protection from predators and harsh weather conditions. They also serve as their hunting ground, where they search for insects, worms, and other small creatures.
Moles build their nests at the end of these tunnels, which is called a ‘burrow’. The burrow is usually located deeper in the ground, ensuring maximum safety for the mole. It is constructed with different chambers for specific purposes, such as sleeping, storing food, and raising their babies. The tunnels and burrows that moles create can often be seen as raised mounds on the surface of the ground, which indicate their presence.
In conclusion, moles are well-adapted to their underground habitat, where they build a complex network of tunnels and burrows. They live in loose soil environments like forests and grasslands, where they can easily dig and navigate through the dirt. By creating extensive networks of tunnels, moles can safely search for food and raise their young underground, away from threats and disruptions.
Evolution of Mole
The mole is a fascinating animal that has evolved over time to survive underground. It all began millions of years ago when their ancestors were living on the land just like many other mammals. These early creatures soon realized that there were benefits to living beneath the surface. By burrowing underground, they could escape predators and harsh weather conditions. This adaptation eventually led to the evolution of the mole we know today.
Over time, moles developed several specialized features that helped them thrive underground. They developed long, strong claws, which allowed them to dig tunnels quickly and efficiently. Their bodies became compact and muscular, ideal for maneuvering in tight spaces. They also developed tiny eyes and ears, as their lifestyle didn’t require them to rely heavily on sight or hearing.
As they continued to adapt to their underground habitat, moles also developed remarkable senses. They have an incredible sense of touch, using their sensitive snouts to navigate and find food. Their noses are long and pointed, allowing them to easily detect prey like earthworms and insects, which are essential to their diet.
In conclusion, the evolution of the mole is a testament to the incredible adaptability of nature. Through millions of years, these animals transformed from land-dwellers to expert diggers, perfectly suited to their subterranean lifestyle. Their unique features and senses have made them highly proficient at navigating and finding food underground. The mole is a remarkable example of evolution and how animals can change over time to survive in challenging environments.
Classification of Mole
Moles are small mammals that belong to the Talpidae family. They are found in many parts of the world, including Europe, Asia, and North America. These intriguing creatures are known for their distinct physical features and underground lifestyles.
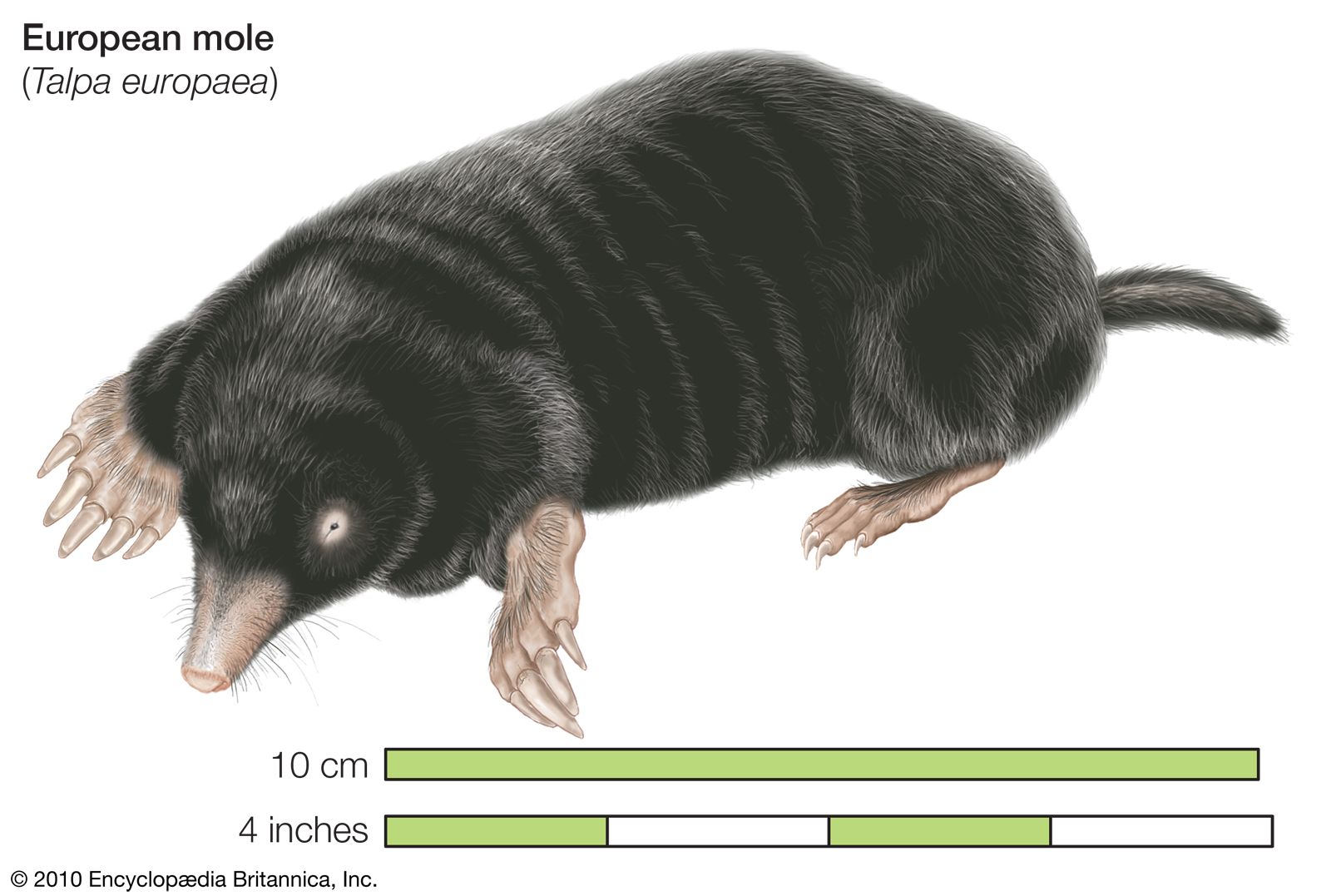
The classification of the mole animal starts with their family, Talpidae, which consists of different species. The most common ones are the European mole (scientifically known as Talpa europaea) and the Eastern mole (Scalopus aquaticus). Both species have similar characteristics, such as a cylindrical body, velvety fur, and powerful forelimbs designed for digging. They also have tiny eyes and ears due to their subterranean lifestyle.
Moles are further classified as mammals because they have warm-blooded bodies and produce milk to nourish their young. They are also placental animals, meaning the mother carries her babies inside her body and gives live birth. Moles are insectivores, which means they primarily feed on insects, worms, and other invertebrates found in the soil. This diet is essential for their survival, as it provides the necessary nutrients and energy for their active tunnel-building lives.
In conclusion, moles are fascinating animals with unique characteristics and behaviors. They belong to the Talpidae family and are classified as mammals. Found in various parts of the world, moles have adapted to their underground lifestyle with features such as cylindrical bodies, velvety fur, and powerful forelimbs for digging. Their diet consists mainly of insects and worms, which they find in the soil. Understanding the classification of moles helps us appreciate and protect these amazing creatures in their natural habitats.
How did Mole Extinct?
1. Eastern Mole: The eastern mole is a small, burrowing mammal found in North America. With its distinctive paddle-like front feet and velvety fur, the eastern mole is well adapted for digging underground tunnels to search for food such as earthworms and insects.
2. Star-nosed Mole: The star-nosed mole is known for its unique nose, which has 22 fleshy, pink tentacles used for sensing prey underwater. Found in North America, this mole is an excellent swimmer and feeds on small invertebrates like worms. Its unusual nose makes it a fascinating creature to study.
3. Townsend’s Mole: Townsend’s mole is found in the western United States and is known for its powerful forelimbs and sharp claws, making it a skilled burrower. It mainly feeds on earthworms and insects, and its underground tunnels provide protection from predators and harsh weather conditions.
4. European Mole: The European mole is one of the most common and widespread mole species, inhabiting various regions in Europe. It has cylindrical body shape, strong limbs, and shovel-like hands for digging intricate tunnel systems. European moles primarily devour earthworms, but may also consume small vertebrates and plant material.
5. Broad-footed Mole: Native to western North America, the broad-footed mole possesses broad, flat feet that assist in digging through loose soil. They prefer living in grasslands and forests, mainly feeding on insects and occasionally small vertebrates. Their fur has a velvety texture, providing insulation during cold climates.
6. Hairy-tailed Mole: As the name suggests, the hairy-tailed mole possesses a tail covered in fur, which aids in gripping the soil during burrowing. This mole species is native to the Pacific Northwest region of North America and feeds on earthworms and insects.
7. Coast Mole: Found in coastal regions of California, Oregon, and Washington, the coast mole has adapted to a semi-aquatic lifestyle. It prefers moist environments and feeds on earthworms, insects, and other small invertebrates. This mole has dense fur that repels water, allowing it to swim more efficiently.
8. Russian Desman: The Russian desman is a mole-like aquatic creature native to Russia and Ukraine. It has webbed hind feet and a long, scaly tail, enabling it to navigate and feed underwater. Their diet mainly consists of aquatic insects, fish, and amphibians.
9. Congo Golden Mole: The Congo golden mole is a small, subterranean creature found in the Democratic Republic of Congo. It has a golden-brown fur, small eyes, and specialized front claws for digging. They predominantly feed on insects and worms, as well as small crustaceans found in their underground habitats.
10. Japanese Mole: The Japanese mole is endemic to Japan and possesses unique physical characteristics, including a short, stout body and reduced eyesight. It constructs complex tunnel systems and feeds on earthworms and insects. Due to its limited distribution and distinctive traits, the Japanese mole attracts attention from researchers and wildlife enthusiasts.
Geographical Presence of Mole
The mole animal can be found in various regions around the world. They are most commonly found in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia. Mole habitats can include grasslands, woodlands, and even some urban areas. These small creatures are adapted for a life underground, and their burrowing habits help them find food and stay safe from predators.
However, there are regions where moles are not found. For example, moles are not typically found in desert regions where the soil is too dry and lacks the necessary moisture for them to survive. Similarly, they are not commonly found in colder regions such as the Arctic, where the ground is frozen for most of the year. Mole populations are also scarce in certain parts of Africa and South America.
It is important to note that moles can create problems for gardeners and farmers due to their burrowing activities. Their tunnels can damage plant roots and create unsightly molehills. As a result, efforts are often made to control mole populations in these regions. It is essential to find sustainable and humane solutions to minimize conflicts between humans and moles.
In summary, moles are found in regions such as North America, Europe, and parts of Asia, where they thrive in various habitats like grasslands and woodlands. However, they are not typically found in deserts, Arctic regions, and some parts of Africa and South America. While moles can sometimes cause disruption to human activities, it is crucial to approach any conflicts with empathy and find ways to coexist peacefully.
Scientific Name of Mole
The scientific name for the mole animal is Talpidae. Talpidae is a family of small mammals that are mainly found in North America, Europe, and Asia. These animals are known for their unique adaptations that help them live underground.
Moles have cylindrical bodies with velvety fur that can be various shades of brown or black. Their front paws are extremely strong and have sharp claws, perfectly designed for digging tunnels. These tunnels serve as their homes and provide protection from predators. Mole tunnels also allow them to hunt for their main source of food, which consists of insects, worms, and other small invertebrates found in the soil.
One of the most fascinating features of moles is their specialized snouts. These snouts are long, pointed, and covered in small sensory hairs that help them navigate their dark underground world. Their eyesight is poor, but their acute sense of touch and hearing compensate for it. By using their specialized snouts, moles can detect vibrations and movement in the soil. This allows them to locate food and avoid obstacles as they tunnel through the ground.
In summary, the scientific name for the mole animal is Talpidae. Moles have unique adaptations for living underground, such as strong front paws for digging tunnels and specialized snouts for sensing their environment. These fascinating creatures rely on their senses to navigate in the dark and find their main source of food in the soil.
Diet of Mole
Moles are small burrowing animals that spend most of their lives underground. They have specific dietary habits to keep them nourished and healthy. The diet of a mole consists primarily of insects, worms, and other small invertebrates. These tiny creatures are the main source of nutrition for moles.
Moles have strong front legs and sharp claws that help them dig through the soil searching for food. They create tunnels and burrows, allowing them access to their favorite snacks. Their sensitive snouts and long, sharp teeth are also perfectly adapted for catching and eating earthworms, grubs, and beetle larvae. Moles are believed to have a voracious appetite and can consume several hundred worms per day!
In addition to insects and worms, moles may also feed on some plant matter. While they are primarily carnivorous, moles occasionally eat small invertebrates like slugs, spiders, and centipedes. Their underground diet provides them with the essential nutrients and energy they need to survive.
In conclusion, moles have a diet consisting mostly of insects, worms, and other small invertebrates. They are well-adapted diggers, using their strong front legs, claws, and sharp teeth to search for food underground. By consuming a large number of worms and insects each day, moles ensure they have the necessary nutrition to thrive and prosper in their subterranean habitats.
Locomotion of Mole
The mole animal moves in a special way called locomotion. It has adapted to living underground, so its body is designed for digging through soil. The mole has strong front legs with big claws that help it to dig tunnels. It uses these front legs to push the soil away and move forward. This digging motion helps the mole to create underground tunnels where it lives and searches for food. The mole’s body is long and slim, allowing it to slide through the narrow tunnels it creates. It also has short, powerful hind legs that it uses to push off and move quickly. By alternating the movement of its front legs and hind legs, the mole can burrow through the earth efficiently. It moves through the soil in a wavelike motion, similar to a swimming motion. This allows the mole to move smoothly and quickly through the underground tunnels, searching for insects and worms to eat. The mole’s impressive ability to dig and move through the soil helps it survive and thrive in its underground world.
Social and Sexual Behaviour of Mole
The mole animal is known for its interesting social and sexual behavior. These creatures are usually solitary, which means they prefer to live alone. They dig tunnels underground where they build their homes and spend most of their time. Mole tunnels can stretch for many meters and have different chambers for different purposes, such as storing food or caring for their young.
When it comes to their mating habits, moles are polygamous, meaning that one male might mate with multiple females. The male moles search for females by making high-pitched sounds to attract them. Once they find a mate, they engage in a brief courtship ritual before mating.
After mating, the female moles give birth to a litter of blind and hairless babies. The mother takes care of her young ones in a special nest within the tunnels. As the babies grow, they gradually develop fur and their eyesight. It doesn’t take too long before they are independent and ready to explore the world on their own.
In conclusion, moles are fascinating creatures with unique social and sexual behavior. They prefer to live alone and create elaborate tunnel systems. With their polygamous mating habits, moles mate with multiple partners, and the females raise their babies in underground nests until they are old enough to venture out into the world.
Reproduction and Lifecycle of Mole
Moles are amazing creatures that have a unique life cycle. Let’s explore how they reproduce and grow.
Moles have a specific mating season, usually during the springtime. During this time, male moles search for a mate by digging tunnels and leaving scent markings. When a female mole is ready to mate, she makes a special call to attract a male. Once they find each other, they engage in a brief mating ritual.
After mating, the female mole becomes pregnant and carries her babies inside her body for about a month. Then, she gives birth to a litter of tiny moles, usually ranging from three to six babies. These newborn moles are blind, hairless, and completely dependent on their mother for nourishment and protection.
Over the next few weeks, the baby moles grow rapidly. Their fur begins to appear, and their eyes gradually open. While their mother provides them with milk, she also teaches them important skills, such as how to dig tunnels and find food. As the baby moles grow stronger and more independent, they eventually leave their mother’s burrow to build their own tunnels and find their own food.
In this way, moles go through a fascinating life cycle. From finding a mate to giving birth and raising their young, moles show great dedication and survival skills. They adapt to their environment and continue the cycle of life, ensuring the survival of their species.
Threats to Mole
Moles are fascinating creatures that live underground. However, they face several threats that can harm their populations. One of the main threats to moles is habitat loss. As humans expand their cities and towns, they often destroy the natural habitats where moles live. As a result, moles are forced to find new places to live, which can be difficult and dangerous for them.
Another threat to moles is predators. Many animals, such as foxes, snakes, and birds of prey, see moles as a tasty meal. These predators hunt moles both above and below ground, making it challenging for them to stay safe. Additionally, humans sometimes introduce non-native predators, like cats and dogs, into areas where moles live. These new predators can disrupt the natural balance and pose an additional threat to mole populations.
Lastly, moles face threats from humans themselves. Some people consider moles as pests because they create tunnels and mounds in their lawns and gardens. As a result, they use harmful chemicals and traps to get rid of them. Unfortunately, these actions not only harm the moles but can also harm other animals and pollute the environment.
In conclusion, moles face various threats to their survival. Habitat loss, predators, and human actions all contribute to the challenges they face. It is crucial for us to understand and respect the importance of moles in ecosystems to ensure their well-being and the balance of nature.
Population of Mole
The population of the mole animal is estimated to be around 6 billion worldwide. Moles are small, burrowing creatures that live underground and have adapted to a variety of environments such as forests, grasslands, and gardens. They have a unique body structure, with sharp claws and a long, streamlined body, which helps them navigate easily through tunnels.
Moles play an important role in the ecosystem by aerating the soil and controlling populations of insects and worms. However, due to factors such as habitat loss, pollution, and hunting, the mole population is declining rapidly. If this trend continues, it is likely that the mole animal may become extinct in the near future.
It is essential for us humans to take steps to protect these fascinating creatures and their habitats. By conserving natural areas, reducing pollution, and promoting sustainable farming practices, we can help ensure the survival of the mole animal. Let’s remember that every species is interconnected, and by protecting one, we are preserving the balance and biodiversity of our planet.
Conclusion
In summary, moles are fascinating creatures that have captured the curiosity of many animal enthusiasts. Their history traces back several centuries, with references to them in ancient texts and folklore. Despite being small in size, moles have made a significant impact on their surroundings, especially through their intricate tunnel systems. These underground dwellers have adapted well to their habitats and play an essential role in maintaining soil health.
Moles are part of the mammal classification, belonging to the Talpidae family. While you may think of them as pests due to their tunneling activities in gardens and lawns, they serve an important ecological purpose. By aerating the soil and eating insects, moles help to control pests and keep the ecosystem in balance. Their specialized bodies, including powerful front claws and a cylindrical shape, aid them in moving swiftly underground.
In conclusion, learning about moles expands our knowledge of the animal kingdom. These incredible animals have a rich history and unique characteristics that make them intriguing to study. By understanding moles’ role in their ecosystems, we can appreciate the importance of all animals in maintaining a healthy environment. So the next time you encounter a mole or any other creature, remember to observe and appreciate the fascinating world of animals.
Frequently Asked Questions about Mole (FAQ’s)
Q: What is a mole animal?
A: A mole animal is a small, burrowing mammal that is part of the Talpidae family.
Q: What does a mole look like?
A: Moles typically have small eyes, a long snout, and velvety fur. They can vary in color from gray to brown or black.
Q: Where do moles live?
A: Moles are commonly found in underground burrows that they dig in grassy areas, gardens, and farmlands.
Q: What do moles eat?
A: Moles primarily feed on earthworms and insect larvae, but they may also consume small invertebrates, such as slugs and snails.
Q: How do moles dig tunnels?
A: Moles have powerful forelimbs and strong claws that allow them to dig intricate tunnel systems underground.
Q: Are moles harmful to humans?
A: While moles can cause damage to lawns and gardens due to their underground burrowing, they do not pose any direct harm to humans.
Q: Can moles see well?
A: No, moles have poor eyesight and rely mainly on their sense of touch and smell to navigate their underground tunnels.
Q: Do moles hibernate?
A: No, moles do not hibernate. They are active throughout the year, although they may spend more time in their burrows during the winter months.
Q: How long do moles live?
A: The average lifespan of a mole is around 3 to 6 years in the wild, but some captive moles have been known to live up to 10 years.
Q: Do moles make any sounds?
A: Moles are not known for making vocalizations. However, they can produce a variety of squeaks, chirps, and clicks by using their front teeth.
Q: Do moles have any predators?
A: Yes, moles have several predators, including owls, hawks, snakes, foxes, weasels, and domestic cats.
Q: Can moles swim?
A: Although moles are primarily land-dwelling animals, they are capable of swimming if necessary, using their paddle-like feet.
Q: How many species of moles are there?
A: There are over 40 known species of moles, spread across different regions of the world.
Q: Are moles solitary animals?
A: Yes, moles are generally solitary creatures, except during the breeding season when males and females may briefly interact.
Q: Are moles considered pests?
A: Moles can be considered pests when they damage lawns and gardens, but they also provide ecological benefits by aerating the soil and controlling insect populations.

Hi there! I’m Morgan Gutierrez, and I love animals! I work as a Seasonal Animal Care Specialist at Brookfield Zoo and also teach people about animals, which is super fun. I studied at Valparaiso University in Lockport, Illinois, where I learned even more about these amazing creatures.
I’m not just about taking care of animals; I write articles about them, too! I explore and share many interesting animal stories, from cute kittens to giant elephants.
In the past, I’ve worked with veterinarians, helped with research, and even been an Animal Ambassador, bringing animals closer to people. Animals are my passion, and I enjoy helping others learn about them. So, if you ever want to know about animals, feel free to ask. I’ll explain it in a way that’s easy to understand, just like talking to a friend!