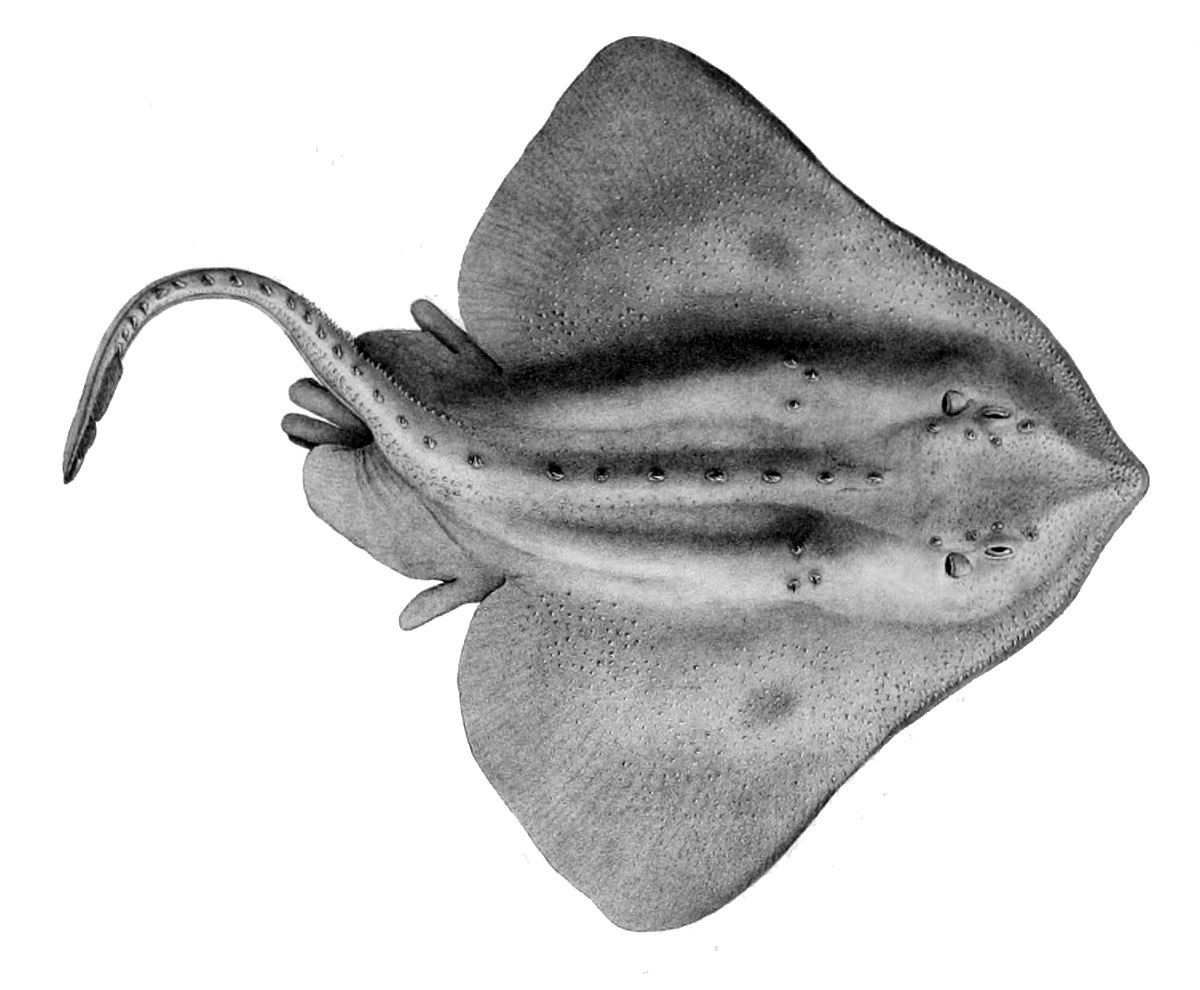
Introducing our latest blog post about the remarkable skate fish! Here, we will delve into the captivating history, intriguing facts, size, habitat, and classification of these fascinating creatures. Skates are a diverse group of fish that belong to the family Rajidae, which includes over 200 species. These unique animals have captured the curiosity of scientists and animal enthusiasts for centuries.
Skate fish have a rich history that dates back millions of years. Fossils have been found from as far back as the Jurassic period, providing valuable insights into the evolution and survival of these ancient creatures. Their unique physical features, such as their flattened bodies and large pectoral fins, have adapted over time to enable them to thrive in various aquatic environments.
In terms of size, skate fish can range from petite to impressively large. Some species can reach up to 9 feet in length, while others measure only a few inches. Their size and shape contribute to their ability to glide gracefully through the water, utilizing their large pectoral fins to propel themselves forward.
Skate fish are widely distributed and can be found in all oceans around the world, from the icy depths of the Arctic to the warm tropical waters. They are often found on the ocean floor, where they use their specialized senses to detect prey and avoid predators. These remarkable creatures have a vital role in maintaining the balance of marine ecosystems.
So, if you are curious to learn more about these captivating creatures, stay tuned for our upcoming blog post on skate fish! Remember, we already have an article on 155+ different animal species, so don’t forget to check that out as well. Get ready to dive into the extraordinary world of animals and expand your knowledge about the fascinating creatures that inhabit our planet.
History of Skate Fish
Skate fish, also known as a cartilaginous fish, has a fascinating history that dates back millions of years. These creatures have survived through various environmental changes and continue to thrive today. Their story is filled with interesting facts and amazing adaptations.
During the early days of the Earth’s history, around 400 million years ago, skate fish species first appeared. They belong to a group of cartilaginous fishes that also includes sharks and rays. Unlike bony fish, they have skeletons made of cartilage, which is a flexible type of tissue. This unique characteristic allows them to move in a unique way, gliding gracefully through the water.
Skate fish have been able to adapt to different environments in order to survive. They can be found in oceans all over the world, from the shallow coastal areas to the deep sea. These remarkable creatures have evolved various features to help them thrive in their environments. For example, they have flat bodies with wide pectoral fins that resemble wings. These fins help them to swim, allowing them to glide over the ocean floor effortlessly.
In conclusion, skate fish have a long history that spans millions of years. They have evolved in remarkable ways to adapt to their surroundings, allowing them to survive and thrive. From their flexible cartilage skeletons to their unique body shapes, skate fish are a testament to the incredible diversity of life on our planet.
Importance of Skate Fish
The skate fish is a fascinating animal that plays an important role in the underwater world. One reason why skate fish are important is because they help to keep the marine ecosystem balanced. They feed on smaller organisms like crabs and worms, which helps to control their populations. This prevents these smaller creatures from becoming too numerous and upsetting the balance of the ecosystem.
Skate fish are also important because they serve as a source of food for other marine animals. They are preyed upon by larger fish, sharks, and even sea birds. Without the presence of skate fish, these predators would have a harder time finding food, which could disrupt the food chain. This highlights the crucial role that skate fish play in sustaining the marine food web.
Furthermore, skate fish are important from an ecological perspective. They contribute to the biodiversity of the ocean, adding to the variety of species that call the seas their home. Each species, including the skate fish, plays a unique role in maintaining the health and stability of the ecosystem. Many people also enjoy observing and studying skate fish, as they provide valuable insights into the underwater world.
In conclusion, the skate fish is an important animal in the marine ecosystem. They help to balance the ecosystem, serve as a food source for other marine animals, and contribute to the overall biodiversity of the ocean. Understanding and appreciating the importance of skate fish is crucial for the conservation and preservation of our oceans and the countless organisms that rely on them for survival.
Amazing Facts About Skate Fish
1. The Skate fish, also known as the Common Skate, is a type of large flat fish that belongs to the family of rays.
2. Skate fish can be found in the coastal waters of the northeastern Atlantic Ocean, from Norway to Morocco.
3. These fish have a unique shape with a diamond or rhombus-shaped body, which is why they are often called skate or ray fish.
4. Skate fish can grow up to 6.5 feet in length and can weigh over 200 pounds, making them one of the largest species of rays.
5. They have a rough skin covered in small, tooth-like scales, which helps to protect them from predators.
6. Skate fish are bottom dwellers and are commonly found in sandy or muddy areas, where they blend in with their surroundings.
7. They have a wide mouth located on the underside of their bodies, allowing them to feed on small fish, crabs, and shellfish that live on the ocean floor.
8. Skate fish have a long, whip-like tail that enables them to swim efficiently and maneuver smoothly in the water.
9. Their bodies are flattened, which allows them to glide along the ocean floor, similar to a stingray.
10. Skate fish have a unique reproductive system called oviparity. The females lay leathery egg cases, commonly known as mermaid’s purses, which contain the embryos.
11. These egg cases are usually black and measure about 4-8 inches in length, providing protection for the growing skate embryos until they hatch.
12. Skate fish have a slow growth rate, and it takes several years for them to reach maturity, usually around 9-12 years of age.
13. Unfortunately, skate fish populations have declined significantly in recent years due to overfishing and habitat destruction.
14. Conservation efforts are being made to protect the skate fish, as they play an important role in maintaining the balance of marine ecosystems.
15. Some countries have implemented fishing regulations and restrictions to help safeguard skate fish populations and prevent their extinction.
Can we keep Skate Fish as our Pet?
Skate fish, also known as “skates,” are a type of flat fish found in oceans and seas around the world. Sadly, due to their natural habitat and biological needs, skate fish cannot be kept as pets. In fact, they are not commonly found in aquariums or pet stores.
Skate fish evolved around 200 million years ago and have adapted to life on the ocean floor. They have a unique body structure that allows them to swim and glide effortlessly through the water. However, maintaining a suitable environment for skate fish in captivity is incredibly challenging and not practical for most people.
Moreover, it is important to consider the conservation status of skate fish. Some species of skate fish are facing extinction due to overfishing, habitat destruction, and climate change. These factors have greatly reduced their populations, making it crucial to protect them in their natural environment rather than keeping them as pets.
In conclusion, skate fish cannot be kept as pets due to their specific needs and the difficulties in recreating their natural habitat in captivity. It is our responsibility to protect the remaining skate fish by conserving their habitats and ensuring sustainable fishing practices. By doing so, we can help preserve this unique species for future generations to appreciate and study.
Size of Skate Fish
The Skate fish animal is a fascinating creature that lives in the ocean. It belongs to the family of rays and can be found in different parts of the world. These fish can grow to various sizes, depending on the species.
Some species of Skate fish can be quite small. For example, the Little Skate is one of the smallest ones, reaching about 12 inches in length. On the other hand, some Skate fish can grow to be quite large. The Big Skate is one of the biggest species and can reach up to 5 feet in length.
Skate fish have a unique body shape that sets them apart from other fish. They have a flat body with pectoral fins that resemble wings, making them look like they are gracefully gliding through the water. Their size varies depending on the species, but most Skate fish are medium-sized, ranging from 2 to 4 feet long.
In conclusion, Skate fish come in different sizes, from small species like the Little Skate to larger ones like the Big Skate. Their flat body and unique fins make them stand out in the ocean. It’s incredible to think about the diversity of these animals and how they adapt to their underwater environment.
Habitat of Skate Fish
Skate fish, also known as skates, are fascinating creatures that live in various habitats around the world. These unique animals can be found in both saltwater and freshwater environments, making them adaptable to different conditions. Let’s explore the habitats where skate fish thrive!
One common habitat for skate fish is the ocean floor. They inhabit sandy or muddy bottoms, where they can camouflage themselves perfectly. Their flat bodies and rough skin help them blend in with their surroundings, making it difficult for predators to spot them. This ocean habitat provides the skate fish with plenty of food sources, such as small fish, crustaceans, and mollusks.
Another habitat where skate fish can be found is in freshwater rivers and lakes. They prefer calm and slow-moving waters, where they can glide gracefully through the currents. Skates adapt to the freshwater conditions by having a unique ability to regulate the salt levels in their bodies. These freshwater habitats provide them with a different range of prey, including small fish, worms, and insects.
Lastly, some skate fish species are even found in colder regions, like the Arctic and Antarctic. These icy habitats pose unique challenges for the skate fish, as they need to withstand freezing temperatures. However, they have developed special adaptations to survive, such as a thick layer of fat and unique blood proteins that prevent freezing.
In conclusion, skate fish are remarkable creatures that inhabit various habitats around the world. From ocean floors to freshwater rivers and even freezing Arctic waters, these adaptable animals have found ways to thrive in different environments. Observing and protecting the habitats where skate fish live is crucial to ensure their survival and maintain the balance of their ecosystems.
Evolution of Skate Fish
Skate fish, a fascinating creature that we won’t discuss today, has undergone a remarkable evolution over millions of years. Let’s journey back in time to discover how these incredible animals have transformed and adapted to their environment.
Long, long ago, skate fish originated in the oceans. They were cartilaginous fish, similar to sharks, and possessed a flat body with two large, wing-like fins. These fins enabled them to glide gracefully through the water, much like the skates we see at ice rinks today.
As time passed, skate fish faced various environmental challenges. To survive, they had to adapt and evolve. Gradually, their bodies became more streamlined and their fins transformed into stronger and sturdier structures. This transformation allowed skate fish to swim more efficiently, giving them an advantage when hunting for food or escaping from predators.
Additionally, their skin developed rough, sandpaper-like denticles that provided protection and camouflage. This rough skin not only helped them blend in with the ocean floor but also deterred potential threats from coming too close. Over time, these adaptations allowed skate fish to become vastly successful, occupying oceans all around the world.
In conclusion, skate fish have come a long way in their evolution. From their humble beginnings as flat-bodied fish with wing-like fins, they have adapted to changes in their environment, developing streamlined bodies, strong fins, and unique skin. These remarkable changes have made skate fish highly efficient swimmers and survivors, ensuring their continued existence in our diverse oceans.
Classification of Skate Fish
Skate fish, also known as rays, are a special type of fish that live in the ocean. They are different from other fish because they have a flattened body shape, similar to a disc or a pancake. Skate fish have cartilaginous skeletons, which means their bones are made of flexible cartilage instead of hard bones like us humans. They also have unique wing-like fins that they use to glide through the water.
There are many different kinds of skate fish, but they can generally be classified into two main groups based on how they look. One group is called the round rays, which have a round or oval-shaped body. The other group is called the diamond rays, which have a diamond-shaped body. Each group then has several species within them, like the spotted skate or the common skate.
Skate fish are known for their amazing camouflage skills. They have special colors and patterns on their skin that help them blend in with their surroundings. Some skate fish have dark spots or stripes, while others have sandy or mottled colors. This helps them hide from predators and sneak up on their prey. Skate fish are also bottom-dwellers, which means they like to live close to the ocean floor. They use their strong jaws and flat teeth to crush and eat small animals that live in the sand.
In summary, skate fish are a unique type of fish that have a flat body and wing-like fins. They can be classified into round rays and diamond rays, and within each group, there are different species. Skate fish have cool camouflage skills and live close to the ocean floor. They are fascinating creatures that have adapted to their environment in amazing ways!
Different Types of Skate Fish
1. Thornback Skate: The thornback skate is a popular species with a distinctive shaped body and thorny projections on its back. It can be found in temperate waters and often hides on sandy or muddy bottoms to camouflage from predators.
2. Big Skate: Also known as the gray skate or California skate, the big skate is the largest species of skate fish. It has a diamond-shaped body and is often found in rocky areas along the Pacific coast of North America.
3. Common Skate: The common skate is a large species that can grow up to 8 feet in length. It is mainly found in the North Atlantic and is recognizable by its dark coloration and smooth skin.
4. Smooth Skate: As the name suggests, the smooth skate has a smooth skin without thorny projections. It is commonly found in the waters of the Northeast Atlantic and the Mediterranean Sea. Its diet consists of small fish and invertebrates.
5. Longnose Skate: The longnose skate is characterized by its elongated snout which gives it its name. It inhabits the cold waters of the North Atlantic and is often found in deep-sea habitats. It feeds on bottom-dwelling organisms such as crustaceans and mollusks.
6. Shortnose Skate: The shortnose skate is similar in appearance to the longnose skate but has a shorter snout. It can be found along the Atlantic coast of North America and is known for its slow reproductive rate, making it vulnerable to overfishing.
7. White Skate: The white skate is a rare and critically endangered species. It has a white or pale gray coloration and can be found in the Northeast Atlantic. Its population has significantly declined due to overfishing and habitat destruction.
8. Mottled Skate: The mottled skate is easily recognizable by its mottled brown and white coloration. It is found in the waters of the Northwest Atlantic and feeds on a variety of small fish and invertebrates.
9. Black Skate: The black skate, also known as the Anacanthobatis marmorata, is a large species that can grow up to 6 feet in length. It has a dark brown or black coloration and is primarily found in the Eastern Pacific Ocean.
10. Blue Skate: The blue skate is a species of skate fish that is predominantly found in the waters of the North Atlantic. It has a bluish-gray coloration and feeds on a diet consisting of crabs, shrimp, and small fish.
Geographical Presence of Skate Fish
Skate Fish are found in a variety of regions around the world. These fascinating creatures can be seen in the cold waters of the Atlantic Ocean, particularly in the North Atlantic. They are also commonly found in the Mediterranean Sea, as well as in the Pacific Ocean. Skate Fish are well adapted to live in these marine habitats, where they can thrive and survive.
However, Skate Fish are not found in all regions of the world. They are not typically seen in warmer waters, such as those found in the tropical regions, like the Caribbean Sea. These fish prefer colder temperatures and are more commonly found in areas with colder ocean currents. Additionally, Skate Fish tend to prefer deeper water habitats, so they may not be as commonly seen in shallow coastal regions.
Skate Fish play an important role in their respective ecosystems, serving as both predator and prey. They are well-camouflaged against the ocean floor, using their flat bodies and unique patterns to blend in with their surroundings. These fish have adapted to their environments over time and are able to survive in these specific regions where they are found. Understanding the regions where Skate Fish are typically found is crucial for researchers and conservationists to protect their populations and maintain the balance of these marine ecosystems.
Scientific Name of Skate Fish
The scientific name of the skate fish animal is ‘Raja’. Skates are a type of fish that belong to the family Rajidae. They can be found in oceans all over the world. Skates have a unique flat body shape, which is quite different from other fish. They have wide pectoral fins that resemble wings and a long tail. These features help them swim gracefully through the water.
Skates have a special adaptation called the ‘rostrum’, which is a long, pointed snout. This snout helps them find food hidden in the sand or mud at the ocean floor. Skates are bottom dwellers, meaning they spend most of their time near the ocean floor searching for prey like worms and small fish. They have a rough skin that feels like sandpaper, which helps protect them from predators.
Skates have an interesting life cycle. They lay leathery egg cases known as ‘mermaids’ purses’. These cases are often found washed ashore on beaches. Inside these purses, baby skates develop and hatch. They are then born as miniature versions of their parents. As they grow, they undergo various changes in size and shape. Skates are fascinating creatures that play an important role in maintaining the balance of marine ecosystems.
Diet of Skate Fish
The skate fish, just like any other living creature, needs to eat to survive and thrive. Its diet can vary but generally consists of small fishes, such as herring, capelin, and sand eels, as well as crustaceans like crabs and shrimp. These yummy treats provide the necessary nutrients and energy that the skate fish needs to grow and stay healthy.
Skate fish have a unique way of catching their food. They are bottom-dwellers, meaning they usually hide and search for food on the ocean floor. Once they spot their prey, they use their strong jaws to gobble it up. They have sharp teeth that help them catch and eat their food easily. Skate fish are also pretty skilled at camouflaging themselves, which means they can blend into their surroundings and sneak up on their unsuspecting prey.
Another interesting fact about the diet of skate fish is that they are not picky eaters. They will munch on whatever food they can find in their environment. This is because they live in different areas of the ocean and have to adapt to the available food sources. They use their excellent senses, like their sense of smell and sight, to locate their next meal and make sure they get enough to eat.
In conclusion, the diet of skate fish is quite simple yet effective. They thrive on a variety of small fishes and crustaceans found in the ocean. With their unique hunting skills and ability to adapt to different food sources, these incredible creatures not only survive but also play an important role in maintaining a balanced ecosystem underwater.
Locomotion of Skate Fish
Skate fish, just like many other amazing creatures that live in the ocean, have a unique way of moving around called locomotion. Locomotion is how animals travel from one place to another. Skate fish have adapted a very interesting way of getting around in the water.
The locomotion of skate fish is quite different from the usual swimming motion we see with other fish. They use their pectoral fins, which are large and flat, to move through the water. Instead of moving their entire body, skate fish flap their wings-like fins to glide across the seabed. This movement is very similar to how we humans move when riding a skateboard, which is why they are called skate fish!
This incredible way of locomotion allows skate fish to move gracefully and efficiently along the ocean floor. By flapping their fins, they create forward thrust that propels them forward. While their movements may seem slow and gentle, skate fish are actually very skilled and can cover a lot of ground in this manner. So, the next time you imagine a fish swimming, remember that skate fish have their own cool way of getting around!
Social and Sexual Behaviour of Skate Fish
Skate fish, like many other creatures in the animal kingdom, have their own unique social and sexual behaviors. These behaviors help them survive and reproduce in their environment.
In terms of social behavior, skate fish are usually not very social creatures. They tend to be solitary and prefer to spend most of their time alone. They do not form complex social groups or engage in group activities like some other fish species. Instead, they mostly keep to themselves and focus on finding food and shelter.
When it comes to sexual behavior, skate fish have a fascinating reproductive process. The male skate fish will often compete with each other to win the attention of a female. They do this by performing elaborate courtship displays, such as swimming in circles or showing off their colorful patterns. Once the female selects a male, they will mate by joining their bodies together and the female will lay eggs. These eggs are then fertilized by the male and left on the ocean floor until they hatch.
In summary, skate fish are not very social animals and prefer to live alone. Their sexual behavior involves males competing for females’ attention through courtship displays, and once selected, they mate and lay eggs to reproduce. Understanding these behaviors helps us appreciate the diverse ways in which animals interact and survive in their natural habitats.
Reproduction and Lifecycle of Skate Fish
Skate fish, like many other species, have a fascinating reproduction and life cycle. Let’s explore how these amazing creatures bring new life into the world.
The reproduction of skate fish begins when a male and a female skate fish find each other. The male has special organs called claspers near his pelvic fins, which he uses to transfer his sperm to the female. The female stores the sperm until she is ready to lay her eggs. When the time is right, the female skate fish lays small, leathery eggs that attach to underwater plants or rocks. These eggs are often hidden from predators to increase the chances of the babies surviving.
After some time, tiny skate fish hatch from their eggs. These hatchlings are called pups. At birth, the pups look like miniature versions of their parents and have the ability to swim and hunt for food. They have a tough, scaly skin that protects them from predators. The pups feed on small fish, worms, and crustaceans, and they grow and develop as they consume more food.
As the skate fish pups continue to grow, they go through different stages of development. Their bodies change, and they start to develop distinct features, such as their dorsal fins. Over time, the pups grow into mature adult skate fish and follow the same reproductive cycle as their parents did. This life cycle repeats itself, ensuring the survival of skate fish populations in our oceans.
In summary, skate fish have an interesting reproduction and life cycle. They start by reproducing through the transfer of sperm from the male to the female, resulting in the laying of eggs. These eggs hatch into tiny skate fish pups, which grow and develop as they feed on small marine creatures. Eventually, the pups mature into adult skate fish and continue the cycle by finding a mate and reproducing. And so, the cycle of life continues for these fascinating creatures.
Threats to Skate Fish
Skate fish, also known as cartilaginous fish, are facing various threats in their natural habitat. Firstly, overfishing is a major concern for the survival of skate fish. Many fishing communities catch these creatures extensively for their meat, which is considered a delicacy in certain regions. As a result, skate fish populations are dwindling rapidly, leading to a decline in their numbers.
Secondly, habitat destruction poses a significant threat to skate fish. These creatures prefer to live in the ocean’s sandy or muddy bottoms, where they can camouflage themselves and find food. However, industrial activities such as bottom trawling, a fishing method that scrapes the ocean floor, can destroy their habitats. This not only displaces skate fish but also disrupts the delicate balance of the marine ecosystem.
Lastly, climate change is another serious threat to skate fish. Rising ocean temperatures and changing currents can alter their feeding patterns and reproductive behaviors. This could negatively impact their ability to find prey and reproduce successfully. Additionally, climate change can also lead to ocean acidification, which affects the availability of food sources for skate fish.
In conclusion, the skate fish animal faces significant threats due to overfishing, habitat destruction, and climate change. These factors not only endanger their survival but also have broader implications for the marine ecosystem. It is crucial that immediate measures are taken to protect these fascinating creatures and ensure their existence for future generations.
Population of Skate Fish
The population of skate fish is quite difficult to determine accurately. However, it is estimated that there are around 200 species of skate fish in the world. Some of these species are more abundant than others, but overall, skate fish populations are believed to be declining due to various threats.
Unfortunately, some species of skate fish have become extinct. Extinction means that a species no longer exists on our planet. It is a very sad occurrence because it means that once thriving populations have completely disappeared. Extinction can happen for different reasons, such as habitat loss, pollution, overfishing, and climate change. These factors can greatly affect the survival of skate fish and many other animals too.
To help prevent further declines and possible extinctions, it is important for us to protect skate fish and their habitats. This can be done by implementing fishing regulations and creating protected areas where skate fish can live and reproduce safely. Additionally, reducing pollution and taking measures to combat climate change is crucial for the survival of not just skate fish but all the wonderful creatures that call our oceans home.
Conclusion
In this blog post, we learned about the fascinating skate fish. These amazing creatures have been around for millions of years and have a rich history dating back to ancient times. They are found in different parts of the world and can vary in size, with some growing as large as six feet long.
Skate fish are well adapted to their marine habitat, with a unique body structure and specialized features that help them survive. They have a flat body shape, which allows them to easily glide through the water. Their strong tails enable them to swim swiftly, and their sharp teeth help them catch their prey.
When it comes to classification, skate fish belong to the cartilaginous fish family, along with sharks and rays. This means that they have skeletons made of cartilage instead of bone. They are also considered benthic animals, which means they live on or near the ocean floor.
In conclusion, skate fish are fascinating creatures with a long history and unique characteristics. They are well adapted to their marine environment and play an important role in the ocean ecosystem. From their body structure to their classification, these fish have many interesting features that make them worth learning about. So next time you’re near the ocean, keep an eye out for the skate fish and appreciate their role in the animal kingdom.
Frequently Asked Questions about Skate Fish (FAQ’s)
Q: What is a skate fish?
A: A skate fish is a type of cartilaginous fish that belongs to the family Rajidae.
Q: How big do skate fish grow?
A: Skate fish can grow up to 5 feet in length, depending on the species.
Q: Where do skate fish live?
A: Skate fish are found in coastal waters worldwide, preferring sandy or muddy bottoms.
Q: Do skate fish have any predators?
A: Yes, larger predatory fish and sharks are known to prey on skate fish.
Q: What do skate fish eat?
A: Skate fish are bottom feeders and primarily feed on small fish, crustaceans, and mollusks.
Q: How do skate fish reproduce?
A: Skate fish reproduce by laying eggs, which are protected in leathery egg capsules known as mermaid’s purses.
Q: Can skate fish sting humans?
A: No, skate fish do not have venomous spines, unlike some other species of rays.
Q: Are skate fish harmful to humans?
A: Generally, skate fish are not harmful to humans unless provoked. However, their rough skin can cause abrasions.
Q: Are skate fish edible?
A: Yes, skate fish are commonly eaten in many cuisines around the world.
Q: Do skate fish have any commercial value?
A: Skate fish have commercial value, primarily for their meat, which is used in seafood dishes.
Q: Are skate fish endangered?
A: Some species of skate fish are considered vulnerable or endangered due to overfishing and habitat destruction.
Q: How long do skate fish live?
A: Skate fish have an average lifespan of 10 to 20 years, depending on the species.
Q: Can skate fish live in freshwater?
A: No, skate fish are primarily marine creatures and require saltwater environments to survive.
Q: Are skate fish social animals?
A: Skate fish are mostly solitary creatures and do not exhibit social behavior.
Q: Can skate fish leap out of the water?
A: Yes, some species of skate fish are capable of leaping out of the water, but they generally stay close to the seabed.

Hi there, I’m Emily Buono, and I’m thrilled to introduce myself! Currently, I’m part of two fantastic places: I work as a VisEx at the New England Aquarium and as an RAS at MGH CCM.
I completed my education at the Mass General Research Institute and Stonehill College, which is located in Valatie Colony, New York, in the United States.
Now, here’s the exciting part: I absolutely adore animals! They captivate me, and I’m always eager to learn more about them. In fact, I write articles all about these incredible creatures.
In the past, I’ve worn many hats, such as being a biologist at the Maria Mitchell Association, a cashier, a floor organizer, and a visitor experience and research animal specialist.
My passion lies in exploring the world of animals and helping others understand them better. So, if you ever have questions about animals, feel free to reach out. I’m here to make animal info easy and fun to grasp!