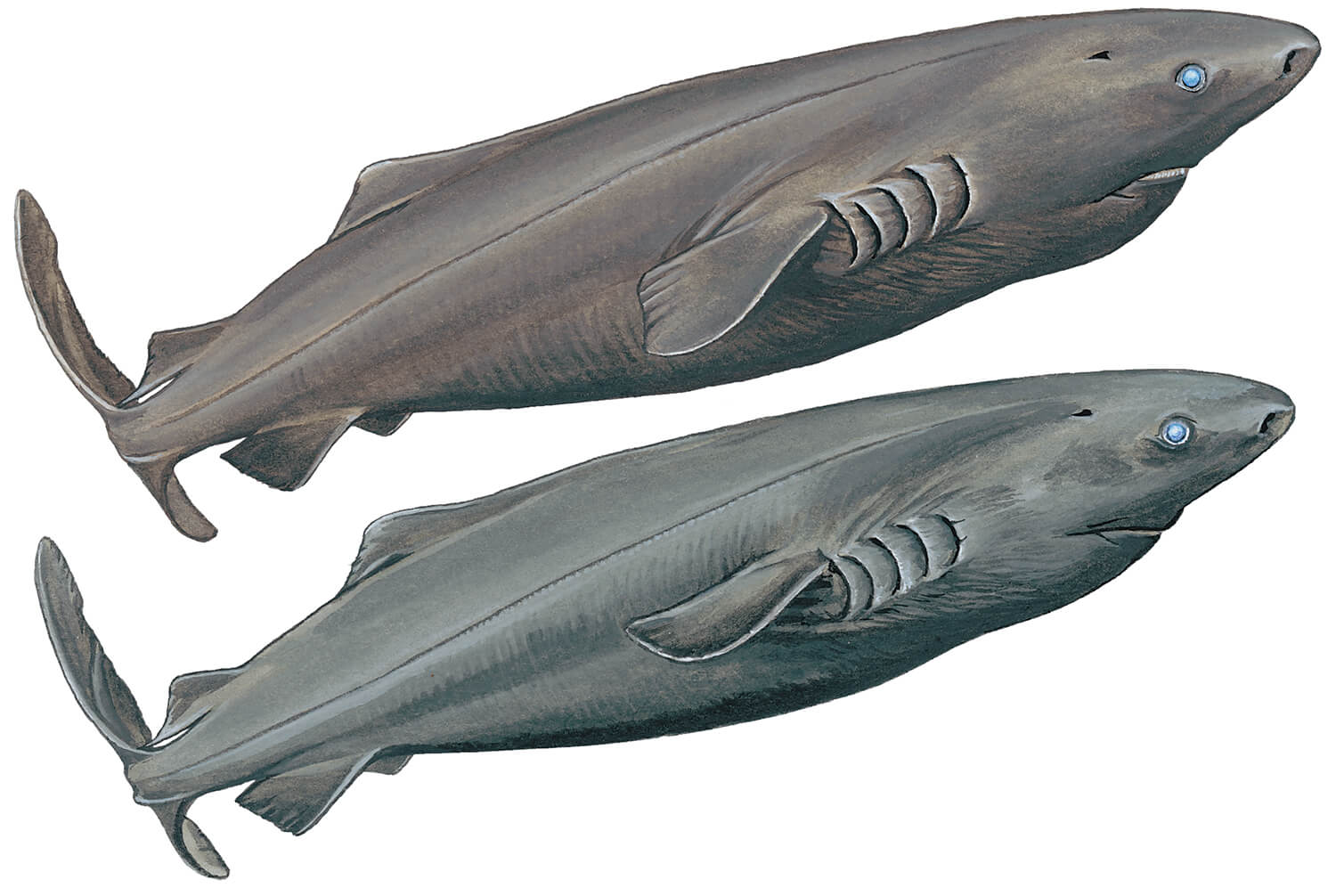
Hello there! Today, we are diving into the intriguing world of animals to explore one fascinating creature: the Sleeper Shark. These amazing beings have a long history that stretches back millions of years. In this blog post, we will uncover some captivating facts about them, such as their size, habitat, and classification.
Sleeper Sharks, also known as Somniosus, are magnificent creatures that inhabit the deep, cold waters of various oceans around the world. These majestic animals have been swimming the oceans for centuries, and their species has survived through many changes in the Earth’s climate. They are a true testament to the resilience of nature.
When it comes to size, the Sleeper Shark is a true giant of the sea. They can grow up to a staggering length of 20 feet, making them one of the larger shark species out there. Their large size allows them to be apex predators, meaning they are at the top of the food chain in their habitat.
The Sleeper Shark’s habitat is mostly in the deep waters, specifically in regions with low temperatures, such as the Arctic and Antarctic regions. They have a specialized body structure and unique adaptations that enable them to thrive in these harsh environments. It’s truly remarkable how these animals have adapted to survive in such extreme conditions.
Before we continue, we would like to mention that we already have an article on our blog that features over 155 different animal names. Feel free to explore it after reading this post to discover more fascinating creatures!
That’s it for now! Stay tuned for the following paragraphs in this blog post, where we will delve deeper into the fascinating world of Sleeve Sharks and uncover more intriguing facts about their behavior, diet, and conservation efforts. So, let’s continue our journey together into the mesmerizing realm of animals and learn more about these incredible creatures that share our planet.
History of Sleeper Shark
The Sleeper Shark is a fascinating creature that has been swimming in our oceans for thousands of years. These sharks can be found in the cold and deep waters of the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. Despite their name, sleeper sharks are far from lazy, as they are known to swim long distances in search of their prey.
These ancient creatures have a long history, with their existence dating back to the time of the dinosaurs. Fossils of the Sleeper Shark have been found that are over 30 million years old! This suggests that they have survived through many changes on Earth, adapting and thriving in various environments.
Sleeper sharks have been able to survive for so long due to their unique features and adaptations. They have a large liver, which provides them with the energy they need to survive in the cold waters. They also have a dark-colored body, which helps them camouflage and blend in with their surroundings. This allows them to sneak up on their prey, which mainly consists of fish and other marine animals.
In conclusion, the Sleeper Shark is an ancient creature with a rich history. They have been swimming in our oceans for millions of years, adapting and surviving in different environments. With their unique features and adaptations, they are well-equipped to thrive in the cold and deep waters they call home.
Importance of Sleeper Shark
The Sleeper Shark is a fascinating creature that lives in the cold oceans of the Arctic and North Pacific. Despite its name, this shark is not known for being a predator that hunts actively. Instead, it often spends most of its time resting on the ocean floor, hence the name “sleeper.” The importance of the Sleeper Shark lies in its role in maintaining the balance of the marine ecosystem.
Firstly, Sleeper Sharks play a crucial role in controlling the population of other marine animals. They feed on a variety of prey, including fish, squid, and even other sharks. By doing so, they prevent the overpopulation of certain species, which can have negative effects on the whole ecosystem. The presence of the Sleeper Shark helps to maintain a healthy balance among the various species in the ocean.
Secondly, the Sleeper Shark contributes to the recycling of nutrients in the marine environment. When these sharks consume their prey, they break it down into smaller pieces during digestion. These small pieces are then released into the ocean, providing nourishment to other organisms such as bacteria and plankton. This nutrient recycling process is crucial for the overall health of the marine ecosystem.
Lastly, the Sleeper Shark serves as an indicator species for scientists studying the effects of climate change. As these sharks inhabit deep, cold waters, any changes in their behavior, population size, or distribution can provide valuable insight into the impact of global warming on these fragile ecosystems. By monitoring the Sleeper Shark, scientists can better understand the implications of climate change and take necessary steps to protect our oceans.
In conclusion, the Sleeper Shark plays a vital role in maintaining the balance of the marine ecosystem. It helps control the population of other marine animals, contributes to nutrient recycling, and serves as an indicator species for studying the effects of climate change. Protecting and conserving this fascinating creature is essential for the overall health and wellbeing of our oceans.
Amazing Facts About Sleeper Shark
1. Sleeper sharks, also known as Greenland sharks, are large and slow-moving sharks that can reach lengths of up to 20 feet.
2. These sharks can live for a very long time, with some individuals estimated to be over 200 years old.
3. They have a unique appearance with a slender body, small eyes, and a broad, rounded snout.
4. Sleeper sharks have a thick, oily liver that helps them stay buoyant in deep waters.
5. These sharks are not picky eaters and are known to consume a wide variety of prey, including fish, seals, and even other sharks.
6. They are mostly found in the cold waters of the Arctic and sub-Arctic regions, but can also be found in the North Atlantic and North Pacific oceans.
7. Due to their slow metabolism, sleeper sharks can survive in extreme environments with low oxygen levels and cold temperatures.
8. They have a relatively low body temperature, which allows them to adapt to icy waters.
9. Sleeper sharks are often referred to as “sleeper” because they appear to be sluggish and inactive, drifting along the ocean floor.
10. These sharks have been found at depths of over 6,500 feet, making them one of the deepest-diving sharks.
11. They have a unique feeding strategy called “couch potato feeding,” where they lie on the ocean floor and wait for prey to come near before ambushing them.
12. Due to their deep-sea habitat, sleeper sharks have rarely been observed, making them a mysterious and enigmatic species.
13. They have very slow growth rates, taking several years to reach maturity, and reproduce at a low rate, making them vulnerable to overfishing.
14. Sleeper sharks have few natural predators due to their size and habitat, but are occasionally preyed upon by killer whales and larger shark species.
15. Scientists are still learning more about sleeper sharks, their behavior, and their role in the ecosystem, as they are difficult to study in their deep-sea environment.
Can we keep Sleeper Shark as our Pet?
Sleeper sharks, also known as Greenland sharks, are fascinating creatures that live in the deep, cold waters of the Arctic and North Atlantic oceans. However, it is not possible for us to keep these sharks as pets. Firstly, sleeper sharks are wild animals that belong in their natural habitat, not in our homes. It is important to respect their natural way of life and understand that they have specific needs that cannot be met in captivity.
Furthermore, sleeper sharks are not suitable pets because of their large size and unique requirements. These sharks can grow up to 20 feet long and weigh over a ton! They require massive tanks or specialized enclosures that are simply not feasible for most people to provide. Moreover, their diet consists of marine mammals, fish, and other large sea creatures, which is difficult to replicate in a captive environment.
Lastly, it is worth noting that the Greenland shark species is not currently extinct. However, they face several conservation challenges, such as habitat degradation and overfishing. These factors have led to a decline in their population. It is crucial to focus on protecting them in their natural habitat rather than attempting to keep them as pets, as this would not contribute to their conservation efforts.
In conclusion, while sleeper sharks are captivating creatures, they are not suitable pets. They are wild animals that thrive in their natural environment and have specific needs that cannot be met in captivity. Additionally, they grow to be very large and have unique dietary requirements. Instead of keeping sleeper sharks as pets, it is important to focus on preserving their natural habitats and ensuring their survival for future generations.
Size of Sleeper Shark
The Sleeper Shark is a fascinating creature that can grow to be quite big. In fact, it is one of the largest sharks in the world! These sharks can reach an impressive size of up to 23 feet long. This means that they can be as long as two cars parked end to end! That’s HUGE! Their size, combined with their thick bodies, makes them look quite intimidating.
Not only are Sleeper Sharks long, but they are also quite heavy. They can weigh up to 3,000 pounds, which is about as heavy as a small car! Can you imagine how strong their muscles must be to support that massive weight? It’s truly amazing!
Despite their enormous size, Sleeper Sharks are not aggressive towards humans. In fact, they are quite slow and gentle creatures. They mainly feed on smaller fish, like salmon and herring, and even the remains of other marine animals. These sharks have been found in the cold waters of the Arctic and Antarctic oceans, where they can easily find food and live peacefully.
In conclusion, the Sleeper Shark is a gigantic creature that can grow up to 23 feet long and weigh as much as 3,000 pounds. Although they may seem intimidating due to their size, they are generally harmless to humans. So if you ever come across a Sleeper Shark, there’s no need to worry, as they are slow and gentle giants of the sea.
Habitat of Sleeper Shark
The sleeper shark is a fascinating creature that lives in the deep oceans of the world. In its habitat, known as the mesopelagic zone, it can be found swimming in the cold and dark waters. This zone is located between the sunlit surface waters and the pitch-black depths of the ocean floor.
The sleeper shark prefers to live in areas where the water is less than 4 degrees Celsius. These frigid temperatures do not bother the sleeper shark because it has a special adaptation called counter-current heat exchange. This allows it to retain body heat and keep warm even in freezing waters. Additionally, the dark environment of the mesopelagic zone provides the perfect camouflage for the sleeper shark, making it difficult for predators to spot them.
The sleeper shark also has the ability to dive to extreme depths, reaching down to 2,000 meters or more. These deep dives allow it to search for its prey, which often includes smaller fish and squid that also occupy the mesopelagic zone. By diving to such depths, the sleeper shark can take advantage of the abundance of food available in these deep waters.
In conclusion, the sleeper shark calls the mesopelagic zone its home. This dark and cold habitat provides the perfect conditions for the sleeper shark to thrive. With its adaptability to freezing temperatures and its ability to dive to great depths, the sleeper shark is a fascinating creature that has found its place in the deep oceans of the world.
Evolution of Sleeper Shark
Sleeper sharks are fascinating creatures that live deep beneath the ocean’s surface. They have evolved over millions of years to adapt to their unique environment. Let’s take a look at the evolution of these incredible animals.
In the beginning, sleeper sharks were quite different from what we see today. They are believed to have originated from ancient sharks that lived around 200 million years ago. These early sharks were smaller in size and had different body structures. As the years passed and the oceans changed, sleeper sharks evolved to become larger and more powerful hunters. They developed strong jaws and teeth that helped them catch their prey with ease.
As the oceans cooled, sleeper sharks began to venture into colder waters. This led to another evolution in their bodies. They developed a layer of fat, called blubber, that helped them stay warm in frigid temperatures. This adaptation allowed them to survive and thrive in the harsh Arctic and Antarctic environments. Over time, sleeper sharks also developed a slower metabolism, enabling them to survive in low food availability conditions.
Today, sleeper sharks continue to evolve to meet the challenges of their changing environment. As climate change causes the melting of polar ice, these sharks are being forced to adapt to new conditions. It is fascinating to think about how these ancient creatures have gone through such incredible transformations to survive in the deep, cold depths of the ocean. Their evolution is a reminder of the incredible diversity and resilience found within the animal kingdom.
Classification of Sleeper Shark
Sleeper sharks are fascinating creatures that belong to the family Somniosidae. They are a type of shark that can be found in the cold and dark waters of the oceans. These sharks are known for their ability to survive in extreme conditions and their unique characteristics.
The classification of sleeper sharks starts with their kingdom, which is Animalia. This means that they are multicellular organisms that can move and react to their surroundings. They also belong to the phylum Chordata, which is a group of animals that have a spinal cord and a complex nervous system.
Moving on to the next level of classification, sleeper sharks are classified under the class Chondrichthyes. This class includes organisms that have skeletons made of cartilage instead of bone, like sharks and rays. It is interesting to note that sleeper sharks are also considered a type of fish because they live in the water and have gills to breathe.
Finally, sleeper sharks are further classified under the order Squaliformes and the family Somniosidae. These sharks have elongated bodies, sharp teeth, and large eyes. They are known for their slow swimming behavior, hence the name “sleeper” shark. Some popular species of sleeper sharks include the Greenland shark and the Pacific sleeper shark.
In conclusion, sleeper sharks are classified as members of the Animalia kingdom, the Chordata phylum, the Chondrichthyes class, the Squaliformes order, and the Somniosidae family. They are intriguing creatures with unique adaptations that allow them to thrive in harsh marine environments. Despite their name, sleeper sharks are anything but lazy in their survival tactics.
Different Types of Sleeper Shark
1. Greenland Sleeper Shark: This large shark can reach lengths of up to 24 feet and is known for its slow swimming speed. It primarily feeds on fish, seals, and other marine mammals, often sneaking up on its prey from below.
2. Pacific Sleeper Shark: Found in the northern Pacific Ocean, this species can grow up to 14 feet long. It has a broad diet that includes fish, squid, octopus, and even other sharks. They are known for their docile nature and slow metabolism.
3. Southern Sleeper Shark: Occurring in the Southern Ocean, this shark typically reaches lengths of 10 to 12 feet. It feeds on various marine animals, including fish, squid, and small sharks. These sharks are known for their adaptability to cold temperatures.
4. Smalltooth Sleeper Shark: Despite its name, this shark can grow up to 10 feet long. It is commonly found in colder waters and has a diet consisting of fish, squid, and other small marine creatures. These sharks are an important part of the deep-sea ecosystem.
5. Pacific Spiny Dogfish: This particular sleeper shark prefers the waters of the Pacific Ocean. It has a unique appearance, with spines covering its fins. They feed on a variety of fish species and are known for their defensive behavior when approached by predators.
6. Fearsome Sleeper Shark: Growing up to 20 feet in length, this shark is feared for its powerful bite and aggressive behavior. It primarily feeds on fish, octopus, and even seals. Due to its ability to dwell in deep waters, it is rarely seen near the surface.
7. Bigeye Sleeper Shark: This shark gets its name from its large eyes, which allow it to locate prey in the dark depths of the ocean. It mainly feeds on fish, squid, and crustaceans. It is found in various deep-sea environments worldwide.
8. Blackbelly Sleeper Shark: Known for its dark-colored belly, this species can grow up to 12 feet long. It has a diverse diet, including fish, squid, and octopus. These sharks roam the depths of the Atlantic Ocean, often living in cold waters.
9. Tropical Sleeper Shark: Found in warmer tropical waters, this shark can reach lengths of about 8 feet. It feeds on small fish and cephalopods and is known for its nocturnal hunting behavior. It is relatively small compared to other sleeper shark species.
10. Longnose Sleeper Shark: As its name suggests, this shark has an elongated snout. It typically measures around 15 feet in length and feeds on a variety of fish and cephalopods. It inhabits the cold waters of the North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans.
Geographical Presence of Sleeper Shark
The Sleeper Shark is found in the Arctic and sub-Arctic regions of the world. These regions include the North Atlantic and North Pacific Oceans. The Sleeper Shark is specially adapted to live in the cold waters of these regions. It has a large body and liver that helps it stay buoyant in the frigid waters. These sharks are known to live at great depths, sometimes reaching up to 7,200 feet below the surface. They are often found in deep-sea trenches and near the continental slope.
On the other hand, Sleeper Sharks are not found in warmer waters such as tropical oceans. These sharks prefer the cold temperatures of the Arctic and sub-Arctic regions. This is because their bodies are designed to withstand the extreme cold and they have unique biological adaptations that allow them to thrive in these icy environments. Due to these adaptations, Sleeper Sharks would not be able to survive in the warm waters found in tropical oceans.
Overall, the Sleeper Shark is found in the Arctic and sub-Arctic regions, including the North Atlantic and North Pacific Oceans. They are specially adapted to live in these cold waters and cannot be found in warmer waters such as tropical oceans. These unique creatures have captured the interests of scientists and continue to amaze us with their ability to survive in some of the harshest environments on Earth.
Scientific Name of Sleeper Shark
The scientific name of the sleeper shark animal is Somniosus pacificus. Sleeper sharks are a type of fish that belong to the family Somniosidae. They are called sleeper sharks because they are often slow-moving and may appear sleepy.
Sleeper sharks can be found in the cold waters of the Pacific Ocean. They have a long, slender body and can grow to be quite large. Some species can reach lengths of up to 20 feet! These sharks have a unique adaptation that allows them to swim in extremely cold temperatures. They have a special fluid in their body that helps them tolerate the cold and stay warm.
One interesting thing about sleeper sharks is that they have been found in the deep sea, as well as near the surface of the water. They are known to feed on a variety of prey, including fish, seals, and even other sharks. Despite their size and ability to be active hunters, sleeper sharks are not considered a threat to humans. They are generally slow and docile creatures, more interested in their natural prey than in interacting with people.
Diet of Sleeper Shark
The sleeper shark is a mysterious creature that lives deep in the ocean. It is a top predator, which means it eats other animals to survive. The diet of a sleeper shark mainly consists of fish, squid, and sometimes even other sharks! They have been known to eat just about anything they can find in their habitat.
Sleeper sharks have an interesting way of hunting for food. They have powerful jaws with sharp teeth that allow them to catch and swallow their prey whole. They have a very strong sense of smell, which helps them locate their food. These sharks are also very patient and can wait for a long time before making their move. When they find their prey, they quickly swim towards it and snatch it up in their mouths.
Sleeper sharks are opportunistic feeders, which means they take advantage of any food source that comes their way. They primarily hunt near the seafloor, where they can find a variety of deep-sea dwellers. They have been known to eat fish that are already dead and even scavenged carcasses from other animals. This makes them very adaptable and helps them survive in their harsh environment.
In conclusion, the sleeper shark is a powerful and versatile predator that feeds on fish, squid, and sometimes other sharks. They have strong jaws, sharp teeth, and an incredible sense of smell that allows them to find and catch their prey. These sharks are opportunistic feeders and can adapt to different food sources.
Locomotion of Sleeper Shark
The sleeper shark is a big animal that lives in the cold waters of the deep sea. It has a unique way of moving called locomotion. Locomotion is how animals move from one place to another.
Sleeper sharks use their powerful tails to swim smoothly and quickly through the water. They move their tails from side to side, just like a fish does. This helps them to glide through the water at a fast pace. They also have long and slender bodies, which helps them to move through the water with less resistance. This is important because the deep sea is a very dark and cold place, so they need to be able to swim quickly to find their food. The locomotion of sleeper sharks is well suited to their environment and allows them to navigate the deep sea with ease.
Social and Sexual Behaviour of Sleeper Shark
Sleeper sharks are fascinating creatures found in the deep, chilly waters of the world’s oceans. When it comes to their social behavior, these sharks are typically solitary beings. They prefer to roam alone through the vast expanses of the ocean, rarely interacting with others of their kind. However, there have been some instances where small groups of sleeper sharks have been observed feeding on a single carcass, showing a temporary form of social behavior.
In terms of sexual behavior, sleeper sharks follow a reproductive strategy known as ovoviviparity. This means that the females give birth to live young after the eggs hatch inside their bodies. These sharks are not known to engage in complex courtship rituals or mate for life like some other animals. Instead, they reproduce when a male shark fertilizes the eggs inside a female shark’s body, and then she carries and protects the developing embryos until they are ready to be born.
Overall, sleeper sharks have a rather solitary lifestyle and are not particularly social animals. Their sexual behavior revolves around the reproductive process of ovoviviparity, where females give birth to live young. While these sharks may not be the most social or flashy of creatures, they play an important role in the balance of the underwater world they call home.
Reproduction and Lifecycle of Sleeper Shark
Sleeper sharks are amazing creatures that live in the cold waters of the deep sea. Like many other animals, sleeper sharks reproduce to create new life. The reproduction process of sleeper sharks starts when a male and female shark come together to mate. They do not have any specific mating season, which means they can mate at any time of the year.
After mating, the female sleeper shark carries the eggs inside her body until they are ready to hatch. This process is called internal fertilization. Once the baby sharks are fully developed, they are born alive, just like humans! The female gives birth to a number of pups, which can range from a few to up to 12 to 14 at a time.
As the newborn sleeper sharks grow, they begin their life journey. They rely on their mother for protection and guidance for some time before they are ready to venture out on their own. During this period, they learn essential survival skills such as hunting for food and avoiding predators. This phase is crucial for their development and helps them become independent and capable hunters.
As the young sleeper sharks mature, they go through various stages of growth and development. They will gradually grow in size, gaining strength and adaptability to survive in their environment. Once they reach adulthood, they can reproduce and continue the life cycle of sleeper sharks, completing the circle of life that has been happening for generations in the deep, dark depths of the ocean.
Threats to Sleeper Shark
Sleeper sharks face several threats that can impact their survival. One significant threat is commercial fishing activities. Sleeper sharks can get caught accidentally in fishing nets meant for other species, such as tuna or halibut. When they get trapped in these nets, they may struggle to swim to the surface to breathe, which can result in their death. This accidental capture, known as bycatch, is a major concern for the survival of sleeper sharks.
Pollution is another threat to sleeper sharks. When harmful chemicals, such as oil or plastic, enter the ocean, they can contaminate the water and harm marine life, including sleeper sharks. These chemicals can enter the food chain, starting with smaller fish and eventually affecting the sleeper sharks as they consume larger prey. Pollution not only damages the habitat of sleeper sharks, but it also poses a risk to their overall health and well-being.
Climate change is also a significant threat to sleeper sharks. Rising temperatures and changing ocean currents affect the availability of food sources for sleeper sharks. As their prey migrates to different areas due to changing temperatures, sleeper sharks may struggle to find enough food to survive. Additionally, the melting of sea ice, which is caused by climate change, can affect the availability of suitable habitat for sleeper sharks, impacting their ability to reproduce and raise their young.
In summary, sleeper sharks face threats from commercial fishing activities, pollution, and climate change. These factors can negatively impact their survival by causing accidental capture, contaminating the water, and affecting their food availability and habitat. Protecting sleeper sharks and their environments is crucial to ensure the continued existence of these unique and important creatures.
Population of Sleeper Shark
The population of the Sleeper Shark animal is not well known, but it is believed to be quite low. Scientists estimate that there may be only a few thousand left in the world. This is because they live in deep, cold waters and are often hard to find and study. Due to their elusive nature, it is challenging to gather accurate information about their population size.
Unfortunately, if the Sleeper Shark were to become extinct, it would mean that there are no more of them left in the world. This would be a sad event because each animal plays an essential role in maintaining the balance of their ecosystem. Extinction can occur for many reasons, such as habitat destruction, pollution, overfishing, or climate change. It is crucial for humans to take action to protect and conserve these animals’ habitats to prevent their extinction.
In conclusion, the population of the Sleeper Shark animal is relatively unknown, but it is assumed to be quite small. If these animals were to become extinct, it would be a significant loss for the biodiversity of our planet. As responsible stewards, it is our duty to care for these remarkable creatures and their habitats to ensure their survival for generations to come.
Conclusion
To sum up, the Sleeper Shark is a fascinating creature that roams the deep and cold waters of the Arctic and Antarctic regions. This large, predatory species is known for its slow swimming speed and its ability to hibernate when food is scarce. Despite its intimidating appearance and size, the Sleeper Shark is generally harmless to humans.
In terms of classification, the Sleeper Shark belongs to the genus Somniosus and is closely related to the Great White Shark and the Greenland Shark. These animals are classified as elasmobranchs, which are a type of cartilaginous fish that also includes rays and skates.
In conclusion, the Sleeper Shark is an intriguing animal that has captured the curiosity of researchers and ocean enthusiasts alike. Its unique characteristics, such as its ability to hibernate and its slow swimming speed, make it a remarkable species to study. Despite its classification as a large predatory shark, the Sleeper Shark poses no significant threat to humans. As we continue to explore the wonders of the ocean, let us appreciate the diversity of life that exists within it, including the remarkable Sleeper Shark.
Frequently Asked Questions about Sleeper Shark (FAQ’s)
Q: What is a sleeper shark?
A: A sleeper shark is a type of large, slow-moving shark species found in cold oceanic waters.
Q: What is the average size of a sleeper shark?
A: Sleeper sharks can grow to be quite large, with an average size ranging from 10 to 18 feet long.
Q: Where are sleeper sharks typically found?
A: Sleeper sharks are commonly found in the Arctic and North Pacific oceans.
Q: How do sleeper sharks get their name?
A: They are called sleeper sharks due to their sluggish swimming behavior and slow metabolism.
Q: What do sleeper sharks eat?
A: Sleeper sharks are opportunistic feeders and their diet consists of various marine animals including fish, squid, and even other sharks.
Q: Are sleeper sharks considered dangerous to humans?
A: While sleeper sharks are large predators, there have been no recorded attacks on humans so far.
Q: How long can sleeper sharks live?
A: The lifespan of sleeper sharks can vary, but some individuals have been estimated to live up to 50 years.
Q: Are sleeper sharks a threatened species?
A: Currently, there is no substantial evidence to suggest that sleeper sharks are a threatened species.
Q: How do sleeper sharks reproduce?
A: Sleeper sharks are ovoviviparous, meaning that the embryos develop inside eggs within the mother’s body until they hatch.
Q: Can sleeper sharks survive in warmer waters?
A: Sleeper sharks are adapted to thrive in cold water environments and may experience stress or physiological challenges in warmer waters.
Q: Do sleeper sharks have any predators?
A: While adult sleeper sharks have few natural predators, they may be preyed upon by killer whales and larger shark species.
Q: What is the behavior of sleeper sharks during the day?
A: Sleeper sharks are known to be relatively inactive during the day, often resting on the ocean floor.
Q: How deep can sleeper sharks dive?
A: Sleeper sharks have been recorded diving to depths of over 6,000 feet in search of prey.
Q: Are sleeper sharks bioluminescent?
A: No, sleeper sharks do not possess bioluminescent capabilities.
Q: Are there different species of sleeper sharks?
A: Yes, there are several species of sleeper sharks, including the Pacific sleeper shark and the Greenland shark.

Hi there, I’m Emily Buono, and I’m thrilled to introduce myself! Currently, I’m part of two fantastic places: I work as a VisEx at the New England Aquarium and as an RAS at MGH CCM.
I completed my education at the Mass General Research Institute and Stonehill College, which is located in Valatie Colony, New York, in the United States.
Now, here’s the exciting part: I absolutely adore animals! They captivate me, and I’m always eager to learn more about them. In fact, I write articles all about these incredible creatures.
In the past, I’ve worn many hats, such as being a biologist at the Maria Mitchell Association, a cashier, a floor organizer, and a visitor experience and research animal specialist.
My passion lies in exploring the world of animals and helping others understand them better. So, if you ever have questions about animals, feel free to reach out. I’m here to make animal info easy and fun to grasp!