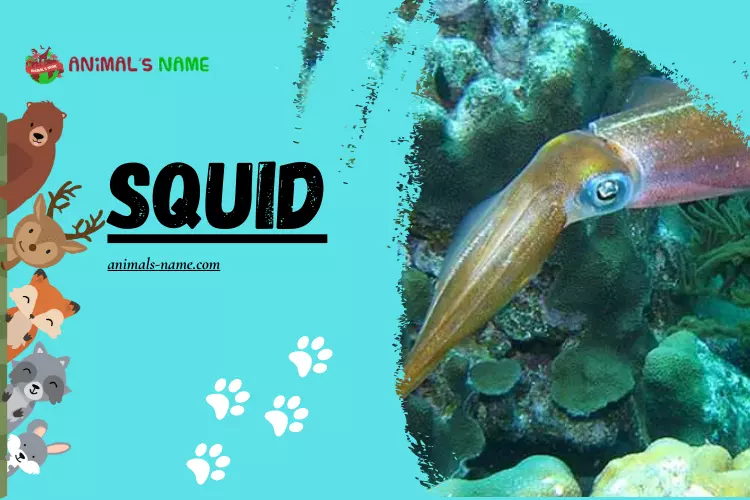
Welcome to our latest blog post, where we dive into the fascinating world of the squid animal. Squids are remarkable creatures that have captured the interest and curiosity of scientists and nature enthusiasts for centuries. This article will explore the history, facts, size, habitat, and classification of these intriguing animals.
Throughout history, squids have fascinated humans with their mysterious nature and unique features. As one of the most intelligent invertebrates, their extraordinary abilities and behaviours amaze us. With their elongated bodies and tentacles, squids are capable of swift movement, making them excellent hunters in the ocean’s depths.
In terms of size, squids are known to vary significantly. While some species are as small as a few inches long, others can reach astonishing lengths of up to 40 feet! Their remarkable size and agility make them formidable in their natural habitat.
Speaking of habitats, squids are predominantly found in marine environments across the globe. They typically reside in deep ocean waters but can also be found in shallow coastal areas. With their ability to swim swiftly and hide seamlessly, squids have adapted well to the diverse habitats they inhabit.
Regarding classification, squids belong to the mollusc family and their cephalopod relatives, such as octopuses and cuttlefish. Within this family, squids are classified into various species that exhibit distinctive characteristics and behaviours.
Join us as we embark on a journey into the captivating world of squids, exploring their history, intriguing facts, impressive size, unique habitats, and fascinating classification. By learning more about these remarkable animals, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the wonders of the natural world. So, let’s dive in and unlock the secrets of the mesmerizing squid!
History of Squid’s
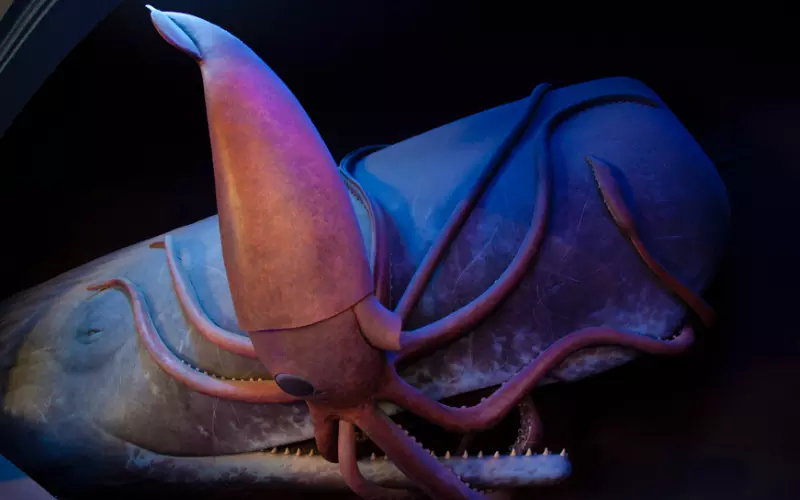

Squids are fascinating creatures living in the Earth’s oceans for millions of years. These ancient animals belong to the cephalopod family, including octopuses and cuttlefish. Squids have a long and rich history, dating back to the time of the dinosaurs.
The first squids appeared approximately 480 million years ago during the Ordovician period. However, these early squids were quite different from the ones we know today. They had hard shells on the outside, similar to snails. As time passed, squids started evolving and adapting to their environment. They developed soft bodies and could swim quickly using their powerful tentacles.
One of the most famous types of squids is the colossal squid, the largest invertebrate on Earth. This enormous creature can reach lengths of up to 46 feet and weighs over half a ton! Despite being a deep-sea dweller, squids have also captured the human imagination through various myths and legends. The legendary Kraken, a sea monster said to attack ships, is often described as a giant squid.
Squids have a long and storied history that spans millions of years. From their beginnings as shelled creatures to the fascinating and adaptable animals we know today, squids have managed to thrive in the diverse ecosystems of our oceans. Their impressive size and intriguing mythology continue to captivate people around the world.
Importance of Squid
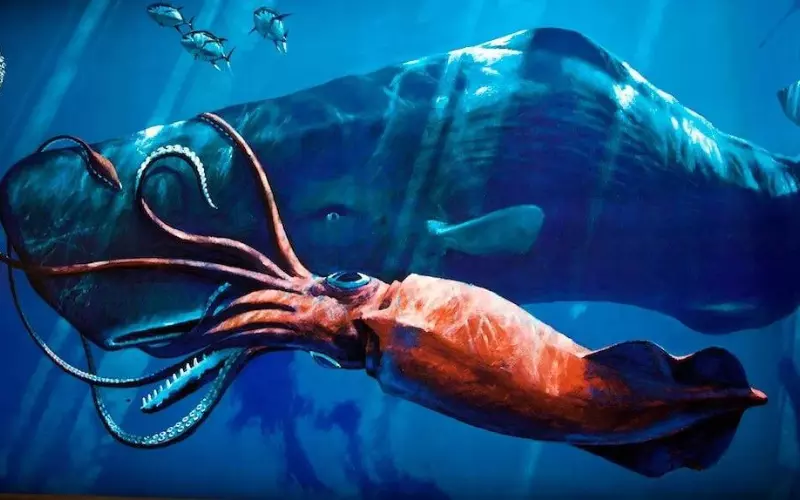

The squid is a fantastic animal that lives in the world’s oceans. It is an important part of the underwater ecosystem. Squids are known for their unique body structure, which makes them exceptional hunters. They have a soft body, but their outer skin is covered in a hard shell called a mantle. This makes them fast swimmers and helps them to escape from predators.
One of the most fascinating things about squids is their ability to change colour. Their skin has unique pigments that allow them to blend in with their surroundings. This is called camouflage, which helps them hide from their enemies and catch their prey. It’s like having a superpower!
Squids are also crucial for the food web in the ocean. They are a favourite prey for various animals, such as whales, dolphins, and sharks. Without squids, these creatures would have difficulty finding enough food to survive. In addition, when squids die, their bodies sink to the bottom of the ocean and provide nourishment for other organisms. So, even in death, squids play a vital role in the marine ecosystem.
Squids are truly remarkable creatures. Their unique body structure, ability to change colour, and significance in the food web make them essential animals in the ocean. Without squids, the balance of the underwater world would be disrupted. Let’s appreciate and protect these fascinating creatures and ensure their survival for generations.
Amazing Facts About Squid’s
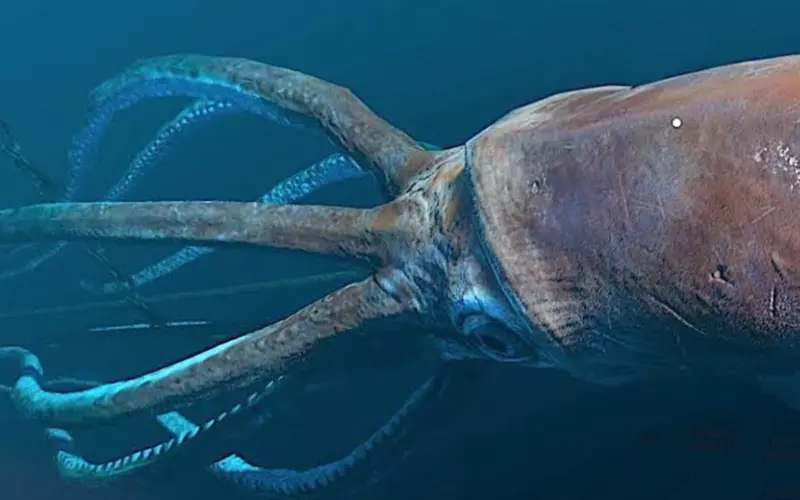

1. Squids are marine animals belonging to the cephalopod family, including octopuses and cuttlefish.
2. There are over 300 known species of squids, ranging from just a few centimetres to several meters long.
3. These creatures have elongated bodies, soft bodies, and a distinct head with large eyes.
4. Squids have a unique ability to change the colour of their skin as a form of communication, camouflage, or to scare away predators.
5. They use jet propulsion to move through the water by drawing water into their mantle and forcefully pushing it out, allowing them to move swiftly.
6. Squids have eight arms and two longer tentacles equipped with suckers, which they use to catch prey and bring it towards their beak-like mouth.
7. Their primary diet consists of small fish, crustaceans, and other squids, which they capture with their extendable tentacles.
8. Some species of squids have bioluminescent organs on their bodies, which allow them to produce light in dark waters, helping them communicate or confuse predators.
9. They have a complex nervous system and are known to be brilliant creatures with excellent problem-solving abilities.
10. Squids have an exceptional ability to regenerate their limbs if they are damaged or lost, which aids in their survival and healing process.
11. These animals have three hearts, which help pump oxygen-rich blood to their various body parts and ensure efficient circulation.
12. Squids have an ink sac located inside their body, which they can expel when feeling threatened, creating a dark cloud that confuses predators and provides an opportunity to escape.
13. Their skin is covered in chromatophores, specialized cells that contain pigments, allowing them to change colour and blend in with their surroundings quickly.
14. Squid populations can be found in all oceans, from shallow coastal waters to deep-sea regions, and they are an essential part of the marine food chain.
15. Humans have been consuming squids for centuries, as they are a popular seafood delicacy enjoyed in various cuisines worldwide.
Can we keep Squid as our Pet?
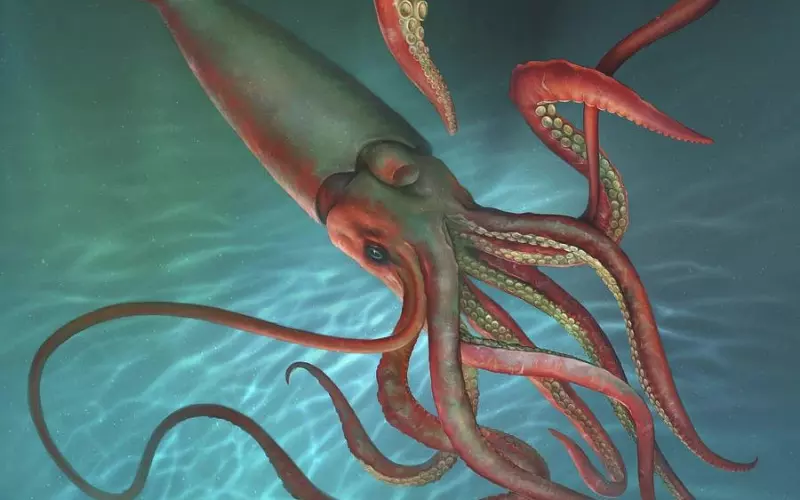

Squids, while fascinating sea creatures, may not make the best pets for us to keep at home. These intelligent and mysterious creatures are better off in their natural habitat than tanks or aquariums. With their unique needs and challenges, caring for a squid could be difficult and unsuitable for everyone.
Firstly, squids require specific conditions to thrive, such as access to a large body of saltwater and a regulated environment. This can be quite challenging to recreate in a home setting. Unlike other more common pets like cats or dogs, squids need a constant food supply, typically consisting of live fish or other marine creatures. Providing such a diet and meeting their nutritional needs can be both time-consuming and expensive.
Secondly, squids are brilliant creatures built to roam freely and explore their vast ocean home. Keeping them confined to a tank or aquarium could make them feel stressed and unhappy. Their natural behaviours, such as their ability to swim swiftly and their inquisitive nature, may be severely restricted in such a confined space.
Although squids are intriguing and delightful animals, they are not suitable pets for us to keep. The specialized care they require and their need for a sizeable oceanic environment make it impractical to have them as house pets. Instead, we should admire and respect these magnificent creatures from afar and ensure their preservation in their natural habitat.
Size of Squid’s
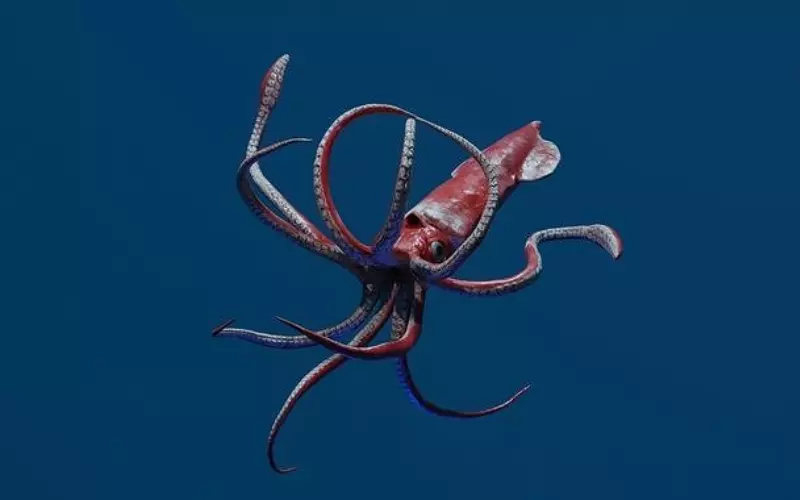

The squid is a fascinating creature that lives in the ocean. When we talk about the size of squid, we marvel at how big they can get! The size of a squid can vary depending on the species, but some of them can grow to be very large.
One of the giant squid species is the colossal squid. This considerable creature can reach lengths of up to 46 feet, longer than a school bus! Just imagine seeing a squid that big swimming in the ocean! It’s undoubtedly a sight to behold. Another large species is the giant squid, which can grow about 43 feet long. These incredible sizes amaze scientists and ocean explorers.
Squids have a unique ability to change their size. They can expand or contract their bodies to fit their surroundings. This means they can appear bigger or smaller depending on their needs. Squids use this ability to their advantage when hunting for prey or evading predators. It’s like they have their superpower!
Squids come in different sizes, but some can grow to be enormous! The colossal and giant squid are among the largest species, with lengths ranging from 43 to 46 feet. Additionally, squids have the remarkable ability to change their size to adapt to their environment. They truly are incredible creatures that continue to awe and inspire us with their immense size!
Habitat of Squid’s
Squid animals live in the deep sea, the ocean’s dark part. They make their home in the ocean’s water, where it is freezing and deep. Squids are found all around the world in oceans that are cold and warm. They like to live in areas called oceanic zones. These zones are places in the ocean with many life and different kinds of animals.
In their habitat, squids have to be able to survive in very harsh conditions. The deep sea is very dark, so squids have adapted to see in the dark water. They also have unique skin that can change colours, which helps them hide from their predators. Squids can also swim very fast and have a body shape that helps them move smoothly in the water.
Squids often live in groups called schools. They use their strong tentacles to catch food, mainly small fish and smaller squids. Squids are also very good at camouflaging with their surroundings, making catching their prey easier. In their habitat, squids can be found at different ocean depths, from the surface to the bottom.
Squids prefer to live in the deep sea of the world’s oceans. They have adapted to cold, dark conditions and have developed unique features and abilities to survive in their habitat. Squids are skilled hunters and live in groups, using their special skills to catch their food.
Classification of Squid’s
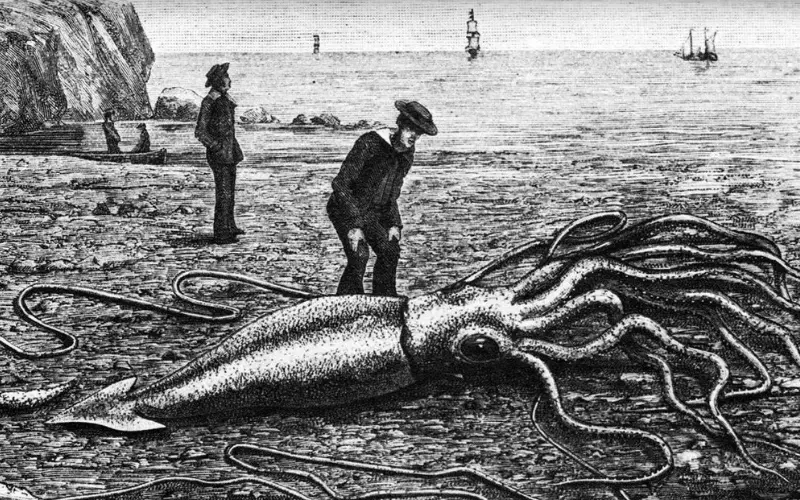

Squids are fascinating creatures that live in the ocean. They belong to a group of animals called cephalopods, including octopuses and cuttlefish. Squids are known for their unique features, such as soft bodies and long, tentacle-like arms. They come in various sizes, from as small as an inch to as large as 60 feet!
Regarding classification, squids are part of Cephalopoda under the phylum Mollusca. This means they are closely related to other molluscs like snails and clams. Within the class Cephalopoda, squids are further categorized into the order Teuthida. This order consists of all the different types of squids in the world.
Squids are also classified based on their families and species. One well-known family of squids is the Loliginidae family, which includes common squids frequently used as food. Examples of species in this family are the California market squid and the European squid. Another family is the Architeuthidae family, which includes giant squids that can reach enormous sizes. The giant squid is the largest known invertebrate on Earth!
Squids are fascinating creatures that belong to the class Cephalopoda. They are part of the phylum Mollusca, which includes other molluscs like snails and clams. Squids are further classified into Teuthida, and different species are classified into families. Some well-known families include the Loliginidae family and the Architeuthidae family. Learning about the classification of squids helps scientists better understand these incredible creatures and their place in the animal kingdom.
Different Types of Squid’s

1. Common Squid (Loligo): The most common squid in coastal waters worldwide. They have a streamlined body, long tentacles, and sharp beaks to catch prey. Common squids are an important food source for many marine animals.
2. Giant Squid (Architeuthis): The giant squid is one of the largest invertebrates on Earth, reaching up to 43 feet. They live in deep ocean waters and are known for their enormous eyes and long tentacles. Giant squids are elusive creatures, and little is known about their behaviour.
3. Humboldt Squid (Dosidicus gigas): Also known as jumbo squid, Humboldt squid is found in the eastern Pacific Ocean. They have a reddish-brown color, powerful beaks, and sharp hooks on their tentacles. Humboldt squid are known for their aggressive behaviour and hunting in groups called shoals.
4. Vampire Squid (Vampyroteuthis infernalis): The vampire squid is a harmless deep-sea dweller despite its spooky name. They have unique web-like structures connecting their arms and glowing organs called photophores. Vampire squids survive by capturing tiny drifting particles, mainly living in oxygen-minimum zones.
5. Pygmy Squid (Idiosepius): These cute little squids are tiny, growing to only about half an inch in length. They are found in warm coastal waters and can change colour and texture to blend in with their surroundings. Pygmy squids feed on small marine creatures.
6. Bobtail Squid (Euprymna): Bobtail squids are known for their symbiotic relationship with bioluminescent bacteria. Their unique light organ on their undersides helps them produce light to camouflage themselves from predators. These squids bury themselves in the sand during the day and hunt at night.
7. Firefly Squid (Watasenia scintillans): Native to the Sea of Japan, firefly squids are known for their incredible bioluminescence. When disturbed, they emit a blue-green glow, resembling twinkling stars. Firefly squids have light organs on their tentacles and use their light to attract prey and communicate.
8. Caribbean Reef Squid (Sepioteuthis sepioidea): These squids are commonly found in warm Caribbean waters. They can change colours rapidly, making them skilled at communication and camouflage. Caribbean reef squids are social creatures and often move in groups called schools.
9. Glass Squid (Cranchiidae): Glass squids are named for their transparent bodies, which help them to blend in with their surroundings in the deep ocean. They have large eyes and light-producing organs that allow them to attract prey and communicate with other squids. They primarily feed on fish and crustaceans.
10. Arrow Squid (Nototodarus): Arrow squids are found in the Southern and Pacific Oceans. They have long, slender bodies and powerful tentacles with sharp hooks. These squids are fast swimmers, propelling themselves through the water using jet propulsion. Arrow squids are an essential part of the marine food chain.
Geographical Presence of Squid

1. The squid is found in various regions around the world. These regions include the oceans of both warm and cold waters, such as the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Ocean. They are also commonly found in coastal areas near continents and islands. Squids can be found at various depths in the ocean, ranging from the surface to over 3,000 feet deep.
2. However, there are certain regions where squids are not found. They are not typically found in freshwater environments such as lakes and rivers since they are adapted to live in saltwater. Similarly, squids are not found in icy regions like polar areas; they prefer waters with moderate temperatures.
3. The regions where squids are found vary depending on the species. For example, the giant squid, an enormous species that can grow up to 43 feet long, is found in deep waters all around the globe. On the other hand, the Humboldt squid, known for its aggressive behaviour, is predominantly found in the Eastern Pacific, particularly around Peru and Chile. Overall, squids are fascinating creatures that inhabit various oceanic regions and contribute to the rich diversity of marine life.
Diet of Squid’s

Squid have a unique and exciting diet, mainly populated by other sea creatures. They are carnivorous, meaning they only eat meat. Their diet includes fish, shrimp, crabs, and even other squid! They are skilled hunters and use their long tentacles to capture their prey.
Squid have a special technique for catching food called “ambush predation”. They remain still in the water until their prey swims by, and then they quickly reach out and grab it with their tentacles. They have sharp, beak-like mouthparts that help them tear their food into small pieces so they can easily swallow it. Squids have big appetites and must eat a lot to stay healthy and grow.
One interesting fact about squid is that they can change their diet based on what is available in their environment. They can adapt and find other food sources if their usual prey is scarce. This flexibility in their diet allows the squid to survive in different conditions and always have enough to eat.
Squids have a carnivorous diet and eat a variety of sea creatures. They use their tentacles to catch their prey and have sharp mouthparts to tear their food into small pieces. Squid can change their diet depending on what is available in their environment, which helps them survive and thrive in the ocean.
Locomotion of Squid’s

Squids use a unique way to move through the water called jet propulsion. They have a special sack in their bodies called a mantle that helps them move. Squids take water into their mantle and forcefully push it through a small tube called a siphon. By doing this, they create a strong jet of water behind them that propels them forward. They can even change direction quickly by adjusting the direction of the water jet. This movement is efficient and helps squid swim quite fast in the ocean.
In addition to jet propulsion, squid also have fins on either side of their bodies that they use to help with steering and stability. These fins, called “fins,” are thin and flexible, allowing the squid to move them differently to control their movements. Sometimes, squid also expand and contract their fins to move up or down in the water. With the combination of jet propulsion and flexible fins, squid are skilled swimmers who can move rapidly and gracefully in their ocean habitat.
Social and Sexual Behaviour of Squids
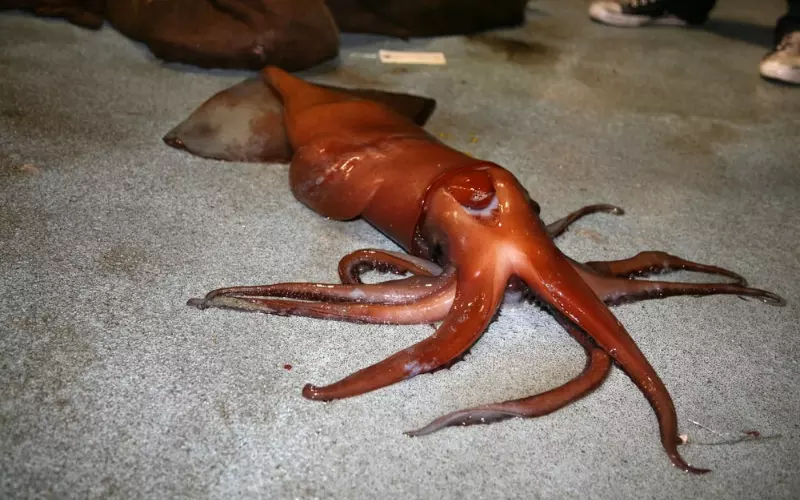

Squids are exciting creatures that live in oceans around the world. They have complex social and sexual behaviours crucial for survival and reproduction.
In terms of social behaviour, squid often live in groups called shoals. These shoals can consist of hundreds or even thousands of squid swimming together. Being part of a shoal helps protect them from predators and allows them to find food more efficiently. Within a shoal, squid communicates with each other using a variety of signals, such as changing their body color and shape or by using unique patterns on their skin. These signals help them coordinate their movements and stay together as a group.
Regarding sexual behaviour, squid has a unique and fascinating way of reproducing. Male squid has a specialized arm called a hectocotylus to transfer sperm packets to the female. The male squid then leaves the female and may look for other mates. The female squid stores the sperm packets and later uses them to fertilize her eggs when ready to lay them. This means that female squid have control over when and where they reproduce.
Squids have complex social behaviours that help them live and survive in groups, and they also have interesting sexual behaviours that involve transferring sperm packets. These behaviours are essential for their survival and successful reproduction in the ocean ecosystem. So next time you see a squid, remember how amazing and unique their social and sexual behaviours genuinely are.
Reproduction and Lifecycle of Squid’s
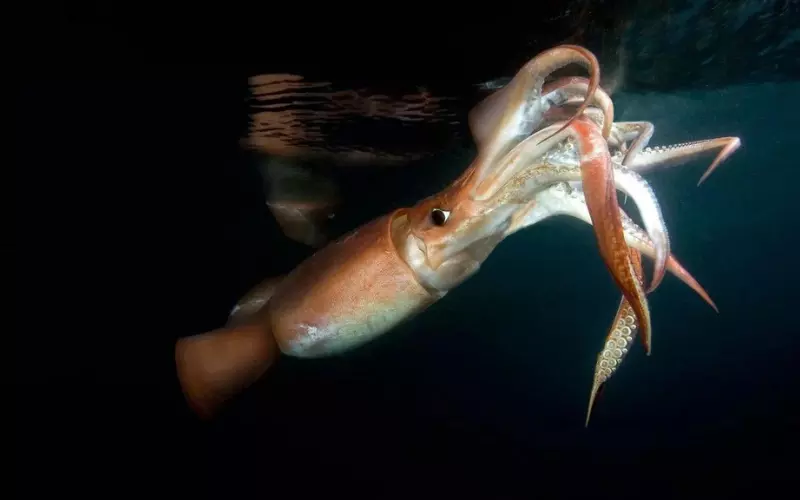

Squids have a very interesting way of reproducing. They lay eggs in the water. Female squids release thousands of tiny eggs called spawn. The male squids then fertilize the eggs, adding sperm to the eggs. This process is called external fertilization because it happens outside the female’s body. Once the eggs are fertilized, they can float in the water for some time. As they grow, they hatch into baby squids called larvae. The larvae look very different from adult squids and have to undergo metamorphosis to become adults.
The life cycle of a squid begins when the larvae hatch from the eggs. These tiny larvae are not good swimmers and drift in the water using their tails. They eat tiny organisms like plankton to get energy. As they grow, they go through several stages called moults, where they shed their skin and grow a new one. During each moult, the squid larvae look more and more like adults. Eventually, they reach adulthood and can reproduce. Adult squids have a short life span and live only about a year or two.
Squids reproduce by laying eggs in the water, which are fertilized by male squids. The eggs hatch into larvae, which go through moulting stages before adulthood. The adults have a short life span and can reproduce before eventually passing away.
Threats to Squid’s
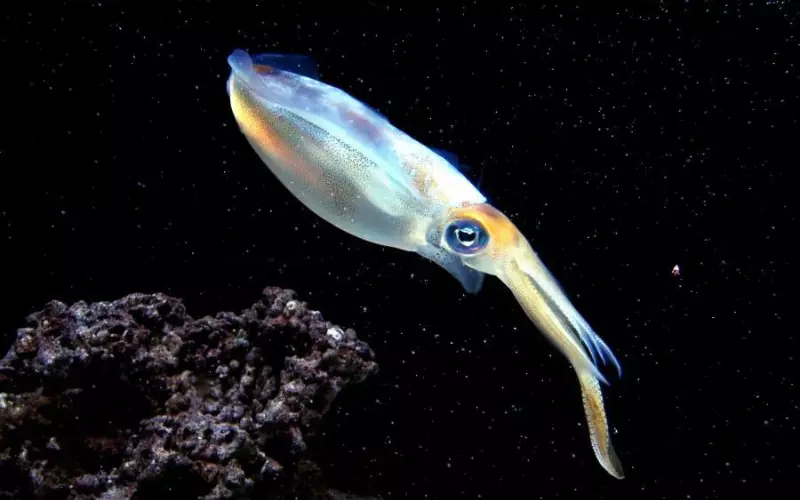

Squids, like many creatures on our planet, face several threats that put their survival at risk. One of the main threats to squids is overfishing. Humans catch a lot of squids for food, both for themselves and for their pets. When too many squids are taken from the sea, it becomes difficult for them to reproduce and maintain their population. This can lead to a decline in squid numbers and disrupt the balance of marine ecosystems.
Pollution is another major threat to squids. When factories and other human activities release harmful chemicals into the water, squids can be greatly affected. These toxins may contaminate the water where squids live, making it harder for them to survive and reproduce. Additionally, oil spills and plastic debris can harm squids directly. They can get tangled in discarded fishing nets or mistake plastic for food, which can be fatal for them.
Climate change also poses a threat to squids. Rising sea temperatures and changes in ocean currents can impact food availability for squids. They depend on certain fish and shrimp species as their primary food source. If these species decline due to climate change, squids may struggle to find enough food to survive. Furthermore, water temperature and acidity changes can also affect the development and hatching of squid eggs, further decreasing their population.
Overfishing, pollution, and climate change are some threats that squids face. It is important for humans to be aware of these dangers and take steps to protect the oceans and the creatures that live in them. This way, we can ensure a sustainable future for squids and maintain the delicate balance of our marine ecosystems.
Conclusion
Squid may not be as popular as other animals, but they have a fascinating history and many interesting facts. These incredible creatures have been around for hundreds of millions of years and have adapted to various habitats worldwide. They come in different sizes, with some growing as long as a school bus! Squids are also known for their ability to change their colours and shapes, allowing them to blend in with their surroundings and avoid predators.
Regarding classification, squid belongs to the mollusc family, including snails and clams. They are also part of a larger group called cephalopods, which means “head-footed” in Greek. This refers to their unique body structure, with their head and feet combined into one.
Squids mainly live in the ocean, with some species found in shallow and deep waters. They can be found in all the world’s oceans, from the cold Arctic to the warm tropical seas. They are excellent swimmers and use their powerful fins and tentacles to move swiftly through the water. Their habitat is essential for survival as it provides food and protection from predators.
Squids are an intriguing species of animals with a long history and unique characteristics. From their incredible ability to change colour to their cephalopod classification, there is much to learn and appreciate about these creatures. Their diverse habitats and impressive swimming abilities further add to their allure. Next time you’re near the ocean, keep an eye out for these magnificent creatures and remember how fascinating they are!
Frequently Asked Questions about Squid’s (FAQ’s)
What is a squid?
A squid is a marine cephalopod mollusc of Teuthida, known for its elongated body, large eyes, and tentacles.
How many species of squid are there?
There are over 300 known species of squid.
How big can squids get?
Squids can vary in size, with some species growing up to 43 feet in length.
Where are squids found?
Squids can be found in ocean waters worldwide, from shallow coastal areas to deep-sea environments.
What do squids eat?
Squids are carnivorous and feed on fish, shrimp, and other small marine animals.
How do squids catch their prey?
Squids have long tentacles equipped with suction cups to capture their prey and bring it closer to their beak-shaped mouths.
Are squids intelligent?
Yes, squids are considered to be brilliant creatures with complex behaviours and nervous systems.
How do squids defend themselves?
Squids have various defence mechanisms, such as releasing ink to confuse predators, changing colour and texture to blend in with their surroundings, or using their tentacles to deliver a powerful bite.
Can squids swim fast?
Squids are excellent swimmers capable of reaching impressive speeds owing to their streamlined bodies and muscular mantle.
Do squids have any predators?
Yes, squids are preyed upon by larger marine animals such as sharks, whales, seals, and some fish species.
What is the lifespan of a squid?
The lifespan of squids can vary depending on the species, but most individuals live for about 1 to 2 years.
Can squids communicate with each other?
Squids communicate through changing skin colour, body pattern, and a series of unique body movements.
Can squids regenerate lost limbs?
Yes, squids can regenerate lost tentacles if they are injured or detached.
Are squids related to octopuses?
Yes, squids and octopuses are cephalopods with common ancestry.
Are squids dangerous to humans?
Most squids are not dangerous to humans unless provoked, but a few species can inflict a painful bite if mismanaged.

Hi there, I’m Emily Buono, and I’m thrilled to introduce myself! Currently, I’m part of two fantastic places: I work as a VisEx at the New England Aquarium and as an RAS at MGH CCM.
I completed my education at the Mass General Research Institute and Stonehill College, which is located in Valatie Colony, New York, in the United States.
Now, here’s the exciting part: I absolutely adore animals! They captivate me, and I’m always eager to learn more about them. In fact, I write articles all about these incredible creatures.
In the past, I’ve worn many hats, such as being a biologist at the Maria Mitchell Association, a cashier, a floor organizer, and a visitor experience and research animal specialist.
My passion lies in exploring the world of animals and helping others understand them better. So, if you ever have questions about animals, feel free to reach out. I’m here to make animal info easy and fun to grasp!












