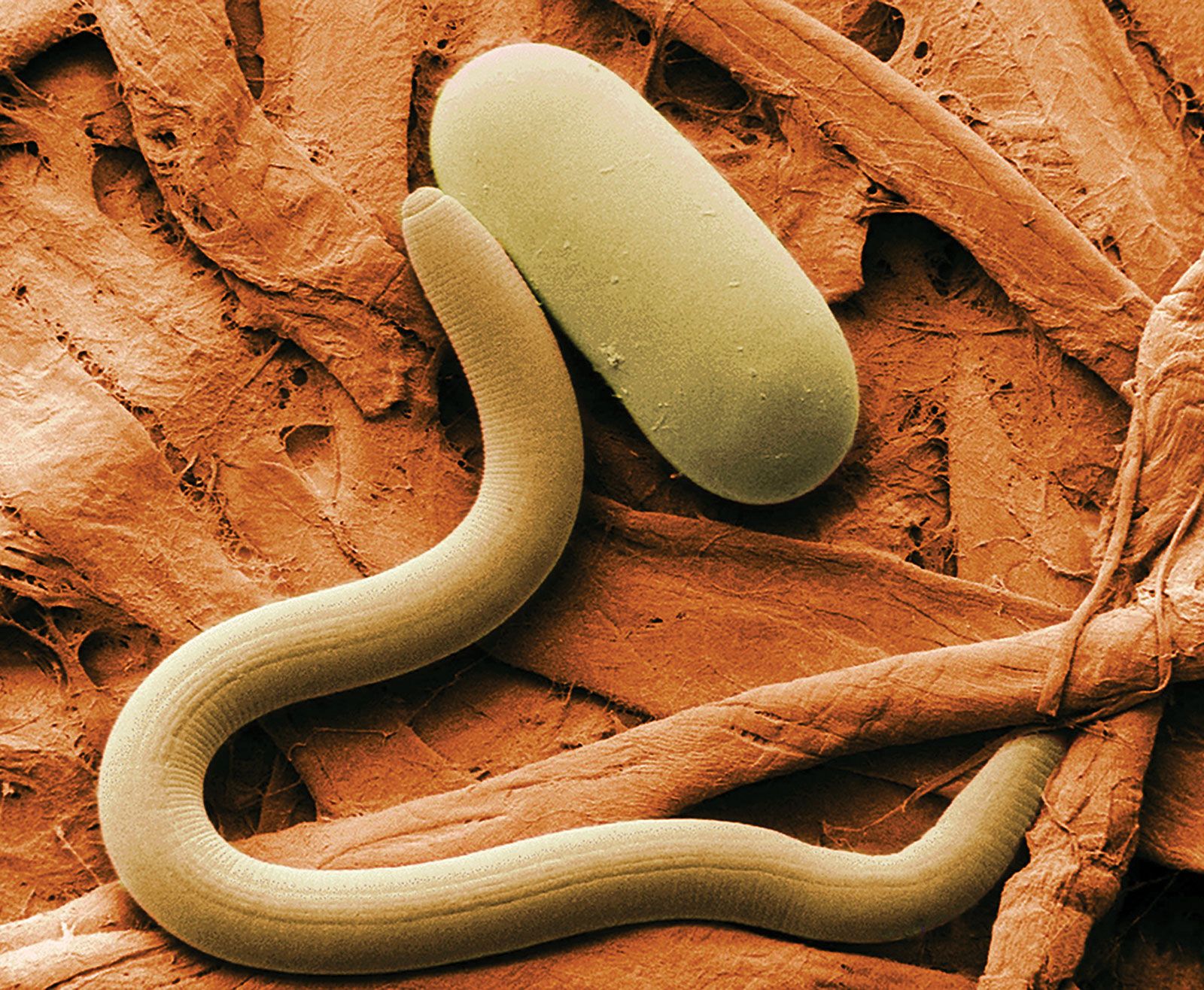
Nematodes, also known as roundworms, are fascinating creatures that have been thriving on Earth for millions of years. They belong to the animal kingdom and are part of the phylum Nematoda. These tiny organisms can be found in almost every habitat on the planet, from the depths of the oceans to the highest mountain peaks.
Nematodes come in a variety of sizes, ranging from microscopic to a few meters long. Despite their small size, they play a significant role in the ecosystem by helping decompose organic matter and recycling nutrients in the soil. There are over 25,000 known species of nematodes, and scientists believe that there may be even more waiting to be discovered.
These diverse animals have a simple body structure with a long, slender shape. They do not have legs or a complex circulatory system like other creatures. Instead, they move by thrashing their bodies back and forth. Nematodes are incredibly adaptable and can survive in extreme conditions, including freezing temperatures and droughts.
By learning about nematodes, we can gain a better understanding of the vast diversity of animal life on our planet. Stay tuned to our blog, where we explore the history, fascinating facts, sizes, habitats, and classifications of these intriguing animals. And remember, if you’re interested in discovering even more about animals, we already have an article featuring over 155 different animal names.
History of Nematode
The history of nematodes, also known as roundworms, dates back a long time ago. These tiny animals have been on Earth for millions of years! Scientists have even found fossil evidence of nematodes that lived over 500 million years ago. Can you imagine that? They have been around for a very, very long time!
Nematodes come in many different shapes and sizes. Some are so small that you need a microscope to see them, while others can grow up to several meters long. They live in all sorts of environments, from the deepest parts of the ocean to the soil in your backyard. In fact, nematodes are everywhere! There are over 25,000 known species of nematodes, but scientists believe that there could be many more yet to be discovered.
Nematodes are fascinating creatures! They play important roles in our ecosystems. Some nematodes are good for plants because they help break down dead organic matter and aid in nutrient recycling. Others are harmful parasites that infect plants, animals, and even humans. They can cause diseases and affect the health of their hosts. Although nematodes are very small, they have a big impact on the world around us.
In conclusion, nematodes have a rich and ancient history on Earth. They are diverse, with thousands of species spread all over the planet. Some nematodes are beneficial, while others can be harmful. Their impact on the environment and our health is significant. Isn’t it amazing to think about these little creatures that have been living among us for millions of years?
Importance of Nematode
Nematodes are tiny animals that live in soil, water, and even inside other plants and animals. They may be small, but nematodes play a big role in our environment. These little creatures are important because they help balance the ecosystems where they live.
Firstly, nematodes are beneficial as they break down organic matter. They eat dead plants, animals, and bacteria in the soil, helping to decompose them. By doing so, they release important nutrients back into the soil, which is essential for plants to grow healthy and strong. Without nematodes, our soil would be less fertile and it would be harder for plants to get the nutrients they need.
Secondly, nematodes play a crucial role in controlling pests. Some nematode species are natural predators of harmful insects and even other pests like slugs and snails. Instead of using harmful pesticides, farmers and gardeners can rely on these nematodes to keep the pest populations in check. This not only protects the plants but also helps maintain a balance in nature.
In summary, nematodes are important because they help decompose organic matter, enrich the soil with nutrients, and control pests. By performing these actions, they contribute to a healthy ecosystem. So, remember, even though they are tiny, nematodes have a big job to do in our environment!
Amazing Facts About Nematode
1. Nematodes, also known as roundworms, are a type of animal that can be found all around the world.
2. These animals are very small, with most species being less than 1 millimeter long and some even smaller than that.
3. Nematodes have a unique cylindrical shape, which gives them their roundworm name.
4. They have a well-defined head with sensory organs that they use to detect their surroundings.
5. Nematodes have a simple digestive system with a mouth and an anus.
6. There are countless species of nematodes, with estimates ranging from 10,000 to over 1 million species.
7. Nematodes can be found in various environments, including soil, freshwater, and marine habitats.
8. Some nematodes are parasites, which means they live and feed on other organisms.
9. Plant parasitic nematodes can damage crops by feeding on the roots, causing stunted growth and reduced yields.
10. There are also animal parasitic nematodes that can infect humans and other animals, causing diseases such as roundworm infections.
11. Nematodes have a pseudocoelom, which is a body cavity that is not completely lined by tissue derived from the mesoderm.
12. These animals have a hydrostatic skeleton, which means that their body fluid, called the pseudocoelomic fluid, supports and helps them move.
13. Nematodes have a relatively simple nervous system, consisting of a few main nerve cords and ganglia (clusters of nerve cells).
14. They reproduce sexually, with males having specialized structures called copulatory organs to transfer sperm to the female.
15. Nematodes play important roles in ecosystems, such as decomposing organic matter and recycling nutrients in soil.
Can we keep Nematode as our Pet?
We cannot keep nematode animals as pets because they are very tiny and not suitable for domestication. Nematodes are microscopic worms that live in many different environments, such as soil, water, and even in plants and animals. While there are millions of species of nematodes on Earth, they are not commonly kept as pets because they are too small and not very interactive or entertaining for humans.
Unfortunately, it is also not possible to have pet nematodes because they do not survive well in captivity. Nematodes have specific living conditions and require a particular ecosystem to thrive. They feed on bacteria, fungi, and other microscopic organisms found in their natural habitats. Therefore, it would be challenging to recreate these conditions in a controlled setting to keep them as pets.
Furthermore, it should be noted that nematodes are not extinct animals. In fact, they are one of the most abundant groups of animals on Earth. Their tiny size and ubiquity help them survive and adapt to various environments and climates. However, they are not suitable or appropriate for pet keeping, as they do not provide the companionship or interaction that people typically desire from their pets.
In conclusion, nematodes cannot be kept as pets due to their small size, lack of interactivity, and specific living requirements. As they are not extinct but rather highly abundant, there would be no need to discuss their extinction or the reasons behind it. It is best to appreciate nematodes for their ecological roles and study them in their natural habitats, rather than keeping them as pets.
Size of Nematode
Nematodes are tiny animals that belong to the phylum Nematoda. They are found in a variety of habitats, including soil, water, and even inside the bodies of other animals. These little creatures are incredibly small, with an average size ranging from 0.1 millimeters to 2.5 millimeters in length. To put it in perspective, they are even smaller than a grain of rice!
Despite their small size, nematodes have a unique body structure. They have long, slender bodies that are covered in a tough, flexible outer layer called a cuticle. This cuticle protects them and gives them their characteristic shape. Nematodes have a simple digestive system, with a mouth and anus for the intake and removal of food. Some nematodes are parasitic, which means they live in or on other organisms, while others are free-living and can be found in the soil or water.
Nematodes play an important role in our environment. They have the ability to decompose organic matter, helping to break down dead plant and animal material. They are also an essential part of the food chain, serving as a food source for many other organisms, including birds and fish. Additionally, some nematodes are used to control pests in agriculture, as they can prey on harmful insects and protect crops.
In conclusion, nematodes may be small in size, but they have a big impact on the world around us. Their unique body structure and diverse habitats enable them to thrive in various environments. While they may often go unnoticed, these tiny animals play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems and supporting life on Earth.
Habitat of Nematode
Nematodes are tiny animals, but they can be found almost everywhere in the world. They live in different habitats such as soil, water, plants, and even in other animal’s bodies. These small creatures are often referred to as roundworms. They have a long and slender body that is covered with a tough outer layer called the cuticle.
In soil, nematodes play an essential role in the ecosystem. They help with the decomposition of organic matter, such as dead plants and animals. Some nematodes also feed on plant roots, which can be harmful to crops. However, many nematodes are beneficial as they prey on insects and other pests, helping to control their population. These helpful nematodes are often used as a natural pest control method in agriculture.
In water, nematodes can be found in both freshwater and marine environments. They are commonly found in sediment at the bottom of lakes, rivers, and oceans. Some nematodes are even able to survive in extreme conditions, such as deep-sea trenches and high-salt environments. They are an essential part of the food chain, providing a food source for other animals like fish and birds.
Nematodes also live inside the bodies of other animals, including humans. Some types of nematodes can cause diseases in animals and humans, while others live harmlessly as a part of our gut microbiome. While nematodes may be tiny, their adaptability allows them to thrive in a wide range of habitats, making them one of the most widespread animal groups on Earth.
Evolution of Nematode
Nematodes are tiny worms that have been around for a really long time, even before the dinosaurs! These interesting creatures have evolved and changed a lot over millions of years to become what they are today. Let’s take a closer look at the evolution of nematodes.
Long ago, the first nematodes appeared in the ocean. They were simple creatures with a tubular body and no legs. Over time, some nematodes started to live in the soil and others in freshwater or saltwater. As they adapted to different environments, they developed new features to help them survive.
One important change that happened to nematodes is the development of a tough outer covering called a cuticle. This cuticle allowed them to protect their bodies and made them stronger. They also developed a more efficient digestive system to process their food. These adaptations helped nematodes become successful and spread across the world.
Another fascinating evolution in nematodes is their ability to parasitize other organisms. Some nematodes became parasites and started living inside plants, animals, or even humans. They have special structures that allow them to attach and feed on their hosts. This change helped them find a constant source of food and ensured their survival.
In conclusion, nematodes have evolved over millions of years and adapted to various environments, developing new features along the way. The evolution of their tough outer covering, efficient digestive system, and ability to become parasites have made them successful creatures in the world today.
Classification of Nematode
Nematodes are a group of animals that belong to the phylum Nematoda. They are also commonly known as roundworms and are found in various habitats such as soil, water, and even living organisms. Nematodes have a simple body structure with a tubular shape and a pointed head. Despite their small size, these creatures can have a big impact on the environment and the organisms they interact with.
The classification of nematode animals is based on their physical characteristics and the habitats they occupy. Nematodes can be categorized into different classes, including Secernentea and Adenophorea. The class Secernentea consists of nematodes that have a simple buccal cavity, while the class Adenophorea includes nematodes with a more complex mouth structure.
Within these classes, nematodes are further divided into numerous families, genera, and species. Each classification level helps scientists to distinguish and study different types of nematodes. For example, the family Trichuridae includes nematodes that are parasitic in nature and can be found in the intestines of animals, including humans. Another well-known family is Rhabditidae, which includes free-living nematodes found in soil and other environments.
Understanding the classification of nematodes is crucial for researchers and scientists studying their impact on ecosystems and human health. By identifying and studying different nematode species, we can gain a better understanding of their biology, behavior, and potential roles as parasites or beneficial organisms. This knowledge allows us to develop strategies for managing harmful nematodes and utilizing beneficial ones for various applications, such as in agriculture for natural pest control.
In summary, the classification of nematode animals helps scientists organize and study these small but significant creatures. Nematodes are classified into different classes, families, genera, and species based on their physical features and habitats. This classification system enables researchers to differentiate between various types of nematodes and better understand their ecological roles and potential impacts on humans and the environment.
Types of Nematode
1. Roundworms: Roundworms are the most common type of nematode found in various habitats, including soil, water, and animals. They have a tubular body with a pointed head and are often parasites in humans and animals, causing diseases like diarrhea and digestive disorders.
2. Hookworms: These nematodes have a distinctive hook-like mouthpart that they use to attach to the lining of the small intestine. They feed on blood, causing anemia and nutritional deficiencies, particularly in tropical and subtropical regions where sanitation is poor.
3. Pinworms: Pinworms are tiny nematodes that infect the human lower intestine. They lay their eggs around the anus, causing intense itching, especially at night. The infection occurs through ingestion of the eggs, mainly through contaminated hands or objects.
4. Whipworms: These nematodes reside in the human colon and cause a condition called trichuriasis. Whipworm infection can lead to abdominal pain, diarrhea, and long-term complications if left untreated, such as malnutrition and impaired growth in children.
5. Threadworms: Threadworms, also known as filarial worms, are transmitted to humans through mosquito bites. They infect the lymphatic system or subcutaneous tissues, causing conditions like elephantiasis, characterized by severe swelling of limbs or genitals.
6. Cyst nematodes: These plant-parasitic nematodes attack various agricultural crops and cause significant economic losses. They form cysts around themselves within the host plant’s root system, disrupting nutrient absorption and stunting plant growth.
7. Root-knot nematodes: Another group of plant parasites, root-knot nematodes invade roots, causing the formation of swollen, knot-like galls that impair a plant’s ability to take up water and nutrients. This leads to stunted growth and reduced crop yields.
8. Soybean cyst nematodes: Considered a major pest in soybean cultivation, these nematodes infect the roots of soybean plants, causing yellowing, wilting, and stunted growth. They feed on plant tissue, reducing the yield of soybean crops.
9. Pine wood nematodes: These nematodes are responsible for pine wilt disease, a devastating condition that affects various pine tree species across the world. Infected trees show rapid wilting and death due to the spread of the nematodes through the tree’s water-conducting vessels.
10. Free-living nematodes: Some nematodes are non-parasitic and live freely in soil or freshwater environments. They play important roles in decomposition, nutrient cycling, and maintaining soil health. Some free-living nematodes are even used as indicators of soil quality and environmental pollution levels.
Geographical Presence of Nematode
Nematodes are tiny animals that can be found in almost every region of the world. These creatures are incredibly diverse, with over 25,000 different species identified so far. They can be found in various environments, including soil, freshwater, and even the deep sea. In fact, nematodes are considered one of the most abundant types of animals on Earth, with an estimated one million individuals per square meter in some soil habitats.
However, there are a few places where nematodes are not commonly found. One of these is in extremely cold regions, such as the Arctic and Antarctic. The freezing temperatures and harsh conditions make it difficult for nematodes to survive. Additionally, nematodes are not typically found in very dry areas, such as deserts. The lack of moisture and extreme heat make it challenging for them to live and reproduce.
In conclusion, nematodes can be found in almost every region of the world, from the depths of the ocean to the soil beneath our feet. They are incredibly diverse and abundant, with numerous species adapting to various environments. However, they are not commonly found in extremely cold regions like the Arctic and Antarctic, as well as in very dry areas such as deserts.
Scientific Name of Nematode
The scientific name of a nematode, a type of tiny animal, is Caenorhabditis elegans. Caenorhabditis elegans is a very important organism in scientific research because it has a transparent body and a simple structure, making it easy for scientists to study. Because of its characteristics, it is often used as a model organism to understand how different processes work in animals, including humans.
Nematodes are very small animals that have long, slender bodies. They are found in many different environments, such as soil, water, and even inside other animals. Despite their tiny size, nematodes play important roles in ecosystems. Some nematodes can be harmful to plants and animals, causing diseases and damage to crops. However, there are also helpful nematodes that feed on harmful insects and help keep their population in check.
Caenorhabditis elegans is a specific type of nematode that has been extensively studied. Scientists have learned a lot about genetics, development, and nervous system functioning by studying this tiny animal. The information gained from research on Caenorhabditis elegans has helped scientists understand more about human biology and diseases. By studying this simple nematode, scientists have made discoveries that have had important implications for human health.
Diet of Nematode
The diet of nematode animals is quite unique. These tiny creatures have a simple digestive system that allows them to gobble up their food quickly and efficiently. Despite their small size, nematodes can be incredibly diverse in the types of food they eat.
Some nematodes are predators, which means they hunt and eat other animals. They may feed on small insects, other tiny worms, or even bacteria. These predatory nematodes have a special structure called a stylet, which they use to pierce through the bodies of their prey and suck out their contents.
On the other hand, many nematodes are herbivores, meaning they consume plant material. They might feast on roots, leaves, or fruits of plants. Some of these herbivorous nematodes can be harmful to crops and cause damage to farmers’ plants. They wriggle their way through the soil to find their next meal and can multiply rapidly if suitable food is available.
Lastly, some nematodes are omnivores, which means they eat both plants and other animals. These versatile creatures can adapt their diets to whatever is available in their environment. They may scavenge on decaying matter, feed on fungi, or even consume small microorganisms.
In conclusion, nematodes have a varied diet that includes being predators, herbivores, or omnivores. Despite their small size, they play an important role in the ecosystem by recycling nutrients and controlling populations of other organisms. Whether they are hunting down prey, munching on plants, or devouring various food sources, nematodes are always on the lookout for their next meal!
Locomotion of Nematode
Nematodes are tiny worm-like animals that can be found all around us, even in soil and water. When it comes to moving around, these creatures have a unique way of getting from one place to another.
Nematodes use a type of locomotion called undulation. They have small, hair-like structures called cilia that cover their bodies. By contracting and relaxing these cilia in a coordinated way, nematodes are able to create waves of movement that help them propel forward. It’s like when you wave your hand in a swimming motion to move through the water. This undulating motion allows nematodes to wriggle and squirm their way through soil or water.
Interestingly, nematodes can also move by using the muscles in their bodies. They can contract these muscles in a wave-like pattern, causing their body to bend and straighten. This helps to push them forward, almost like a spring action. Imagine a toy snake bending and straightening to slither across the ground – that’s a bit similar to how nematodes move. With the help of their cilia and muscles, these tiny animals are able to navigate through their environments and find food or shelter.
Social and Sexual Behaviour of Nematode
Nematodes are tiny creatures found in soil, water, and even inside our bodies. They may look simple, but they have fascinating social and sexual behavior. These behaviors help them survive and find mates.
Firstly, nematodes often live in large groups, forming communities underground or in water. They communicate with each other by releasing chemicals, like little messages. These chemical signals help them find food, avoid danger, and even attract mates. It’s like they have their own secret language!
Secondly, when it comes to mating, nematodes have different ways of getting together. Some nematodes are free-living and can mate with any partner. Others are more picky and will only mate with very specific partners. Once they find a suitable mate, they join together in a process called copulation. They transfer their sperm to each other, and then the female lays eggs that will grow into new nematodes.
In conclusion, nematodes may be small, but they have interesting social and sexual behaviors. They communicate with chemicals to find food, avoid danger, and attract mates. They have different ways of mating, and some are choosy with their partners. Despite their tiny size, nematodes show us that there is a lot happening beneath our feet!
Reproduction and Lifecycle of Nematode
Nematodes are tiny animals that live in soil, water, and even inside other living organisms. They have a simple body structure, with a long, round tube-like body. Nematodes reproduce and go through a life cycle involving different stages.
The life cycle of nematodes starts with the laying of eggs. Female nematodes produce hundreds or even thousands of eggs, which are released into the environment. These eggs are usually protected by a tough outer coat, allowing them to survive in harsh conditions like extreme temperatures or drying out.
Once the eggs hatch, tiny nematode larvae emerge. These larvae begin to feed on organic matter in their surroundings. As they grow, they molt several times, shedding their old skins and developing a new one. This process is called molting, and it helps them to increase in size.
As the nematodes continue to grow, they reach their adult stage. At this stage, they are fully developed and capable of reproducing. Nematodes can reproduce both sexually and asexually. In sexual reproduction, male and female nematodes come together, and the male transfers sperm to the female to fertilize her eggs. In asexual reproduction, the female nematode produces embryos without the need for males. These embryos develop inside the female’s body and are released as fully formed young nematodes.
The life cycle of nematodes is relatively short, and they can complete their life cycle within a few weeks or even days, depending on the species and the environmental conditions. This rapid reproduction and life cycle help nematodes to thrive in different habitats around the world.
Threats to Nematode
Nematodes are tiny worms that live in soil, water, and various other habitats. While they may seem harmless, there are several threats that can affect these small animals. One major threat is the use of chemical pesticides in agriculture. Farmers often use pesticides to kill pests that harm their crops, but these chemicals can also harm nematodes. When pesticides are sprayed on fields, they can seep into the soil and kill nematodes, disrupting the food chain and ecosystem balance.
Another threat to nematodes is pollution. Pollution from factories, vehicles, and other human activities can contaminate the soil and water that nematodes live in. This pollution can make the environment toxic for nematodes, leading to reduced populations. Additionally, pollution can also affect the nematodes’ food sources, further impacting their survival.
Climate change is also a significant threat to nematodes. As temperatures rise and weather patterns shift, the habitats of nematodes can be greatly affected. Some nematodes may not be able to adapt to these changes and may struggle to find suitable conditions for survival. This can result in a decline in nematode populations and have a ripple effect on other organisms that depend on them for food.
In conclusion, nematodes face threats from chemical pesticides, pollution, and climate change. These threats can harm their populations and disrupt the delicate balance of ecosystems. It is important for us to understand these threats and take steps to protect nematodes and their habitats, as they play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy and balanced environment.
Population of Nematode
The population of nematode animals is estimated to be incredibly vast. Scientists believe that there are over a million species of nematodes worldwide, making them one of the most abundant creatures on Earth. These tiny, worm-like animals can be found in almost every environment, from the deepest oceans to the highest mountains.
Unfortunately, due to their small size and hidden lifestyle, it is difficult to determine the exact number of nematodes in existence. However, experts estimate that there may be as many as 10 billion individual nematodes in just one square meter of soil! That’s like having more nematodes in the ground than there are humans on the whole planet!
Although nematodes are thriving today, it is important to mention that extinction can also occur in the animal kingdom. Extinction means that a particular species no longer exists on Earth. If a nematode species were to become extinct, it would mean that every single member of that species has died out. Thankfully, there are no known cases of nematode extinction so far. These fascinating creatures continue to play important roles in the ecosystems they inhabit, serving as decomposers, predators, and sometimes even as parasites to other animals and plants.
Conclusion
To sum up, the history, facts, size, habitat, and classification of the nematode provide us with a deeper understanding of this tiny and unique creature. Nematodes, often referred to as roundworms, are a type of animal found in various habitats around the world. They have been around for millions of years, evolving and adapting to different environments.
The nematodes come in different sizes, with the largest ones measuring about one meter long, while others are microscopic. They can be found in almost every type of habitat, from soil and freshwater to saltwater and even inside the bodies of other animals. This diversity in habitat is a testament to their adaptability and resilience.
Classifying nematodes can be a complex task due to their immense numbers and variations, but scientists have identified over 25,000 different species so far. These amazing animals have their own place in the animal kingdom, exhibiting unique characteristics and interactions with other species. Learning about nematodes not only helps us appreciate the diversity of life on our planet but also brings us closer to understanding the intricate web of interactions among different animals and their environments.
Frequently Asked Questions about Nematode (FAQ’s)
Q: What is a nematode animal?
A: A nematode animal, also known as a roundworm, is a type of invertebrate belonging to the phylum Nematoda.
Q: How big are nematodes?
A: Nematodes can vary in size, ranging from less than 1 millimeter to several meters in length, depending on the species.
Q: How many nematode species are there?
A: It is estimated that there are over 25,000 known species of nematodes, but the actual number may be much higher.
Q: Where do nematodes live?
A: Nematodes can be found in various habitats, including soil, freshwater, marine environments, and as parasites in plants and animals.
Q: Are nematodes harmful to humans?
A: While most nematodes are harmless to humans, some species can cause diseases in plants, animals, and humans.
Q: How do nematodes reproduce?
A: Nematodes reproduce sexually, with separate males and females, or asexually through parthenogenesis, where females can produce eggs without mating.
Q: What do nematodes eat?
A: Nematodes have diverse feeding habits, with some being predators, others feeding on plant material, and some being parasites that feed on the tissues of other organisms.
Q: How do nematodes move?
A: Nematodes move by contracting and relaxing their muscles, creating a wave-like motion known as peristalsis, allowing them to wriggle and crawl through their environment.
Q: Can nematodes survive extreme conditions?
A: Nematodes are known for their ability to survive in harsh environments, such as extreme temperatures, low oxygen levels, and high pressures.
Q: Can nematodes regenerate lost body parts?
A: Nematodes have a limited ability to regenerate some body parts, such as the tail, but the extent of regeneration varies among different species.
Q: Are nematodes helpful in any way?
A: Yes, nematodes play important ecological roles, such as decomposing organic matter, cycling nutrients, and controlling populations of other organisms, both as predators and parasites.
Q: Can nematodes be used as biological control agents?
A: Yes, certain species of nematodes are used as biological control agents to manage pests, such as insects and other harmful organisms in agriculture and horticulture.
Q: Can nematodes infect plants?
A: Yes, nematodes can be plant parasites, causing diseases that lead to stunted growth, wilting, and crop losses.
Q: How do nematodes affect human health?
A: Some nematodes can infect humans and cause diseases, ranging from intestinal infections to more severe conditions like filariasis and trichinellosis.
Q: Do nematodes have any economic importance?
A: Yes, nematodes have economic significance both as crop pests and beneficial organisms in industries such as agriculture, aquaculture, and pharmaceuticals.

Hi there! I’m Morgan Gutierrez, and I love animals! I work as a Seasonal Animal Care Specialist at Brookfield Zoo and also teach people about animals, which is super fun. I studied at Valparaiso University in Lockport, Illinois, where I learned even more about these amazing creatures.
I’m not just about taking care of animals; I write articles about them, too! I explore and share many interesting animal stories, from cute kittens to giant elephants.
In the past, I’ve worked with veterinarians, helped with research, and even been an Animal Ambassador, bringing animals closer to people. Animals are my passion, and I enjoy helping others learn about them. So, if you ever want to know about animals, feel free to ask. I’ll explain it in a way that’s easy to understand, just like talking to a friend!