Welcome to a thrilling journey to the Red Planet, Mars! Have you ever wondered how many people and animals might call Mars their home one day? Well, in this blog post, we’re going to explore the fascinating topic of the population of Mars, including people and the names of the animals.
Even though Mars might seem far from our own, scientists and space enthusiasts have been dreaming about the possibility of humans and animals, like “Rover,” the robotic explorer, living there someday.
We’ll dive into the latest research, missions to Mars, and the challenges humans and animal friends like “Rover” might face if they ever become Martians. So, fasten your seatbelts, and let’s blast off into the world of Mars and its potential human and animal inhabitants!
1. Mars Has a Population of Zero

Currently, Mars is a lonely planet with a population of zero. It’s like a big, red desert in space, and no humans or creatures from Earth live there yet. Even though scientists have sent robots and rovers to explore Mars, no people are walking around, building houses, or having Martian picnics.
But here’s the exciting part: Many intelligent scientists and engineers are working hard to change that! They’re planning missions to send astronauts to Mars in the future. These astronauts will become the first Martians and might build colonies, just like early settlers did in America long ago.
Living on Mars will be challenging, though. It’s very different from Earth, with harsh conditions like extreme cold and thin air. So, for now, Mars remains a planet waiting for its first human residents, and we’ll have to keep dreaming and exploring to make it happen.
2. Mars is The Fourth Planet from the Sun
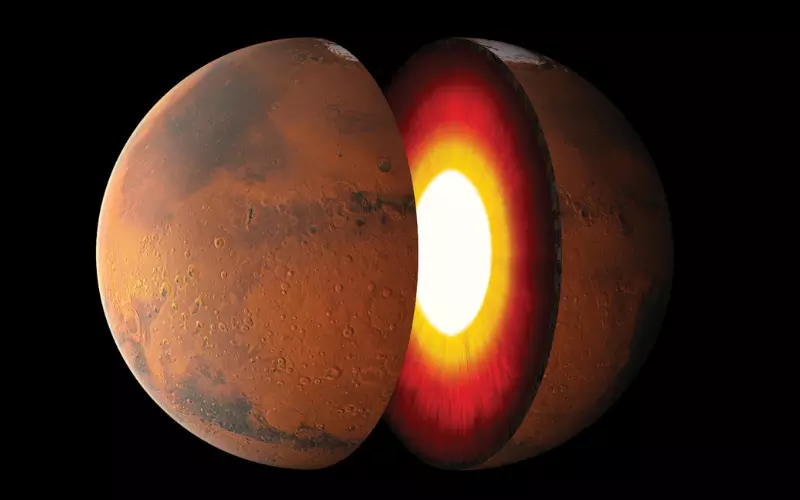
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun, like Earth’s neighbour in space. Imagine our solar system as a big family; the Sun is like the parent. Earth is the third child, and Mars is the fourth child.
Mars is often called the “Red Planet” because it looks reddish in the sky. It’s like a rusty rock floating in space. Even though it’s the next-door planet, it’s pretty different from Earth. Mars is cold, and the air is skinny, so we can’t breathe like Earth.
Scientists are super curious about Mars, and they’ve sent cool robots and rovers to explore it. These machines take pictures, dig into the ground, and study the planet to learn more about it. Maybe someday, astronauts will visit Mars and tell us more about this mysterious neighbour in our cosmic family.
3. Mars is a Cold, Desert World

Mars is a cold, desert world, like a freezing, red Sahara Desert in space. It’s nothing like our cosy Earth. Imagine the coldest winter day you’ve ever felt, and Mars is even colder! The temperatures can drop way below freezing, and there’s no warm and toasty blanket of air to keep you comfy.
Also, Mars is super dry. You know how deserts on Earth have lots of sand and not much water? Well, Mars is even drier! There’s hardly any water, and you can’t find lakes, rivers, or oceans.
But, even though Mars might seem like a tough place, scientists are curious about it. They send cool robots and rovers to explore and learn more. And guess what? They plan to send astronauts to visit one day, but they’ll need warm spacesuits and special gear to survive on Mars’ cold and desert-like surface. So, while Mars is a bit chilly and dry, it’s a fascinating planet full of mysteries waiting to be uncovered!
4. Mars Has Two Moons
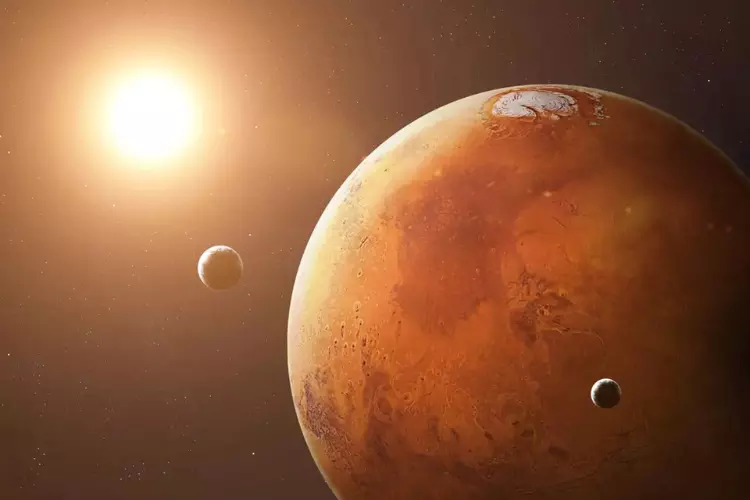

Did you know that Mars, the famous Red Planet, has not one but two moons? It’s true! Their names are Phobos and Deimos, quite different from our Moon.
Phobos is the larger of the two, but it’s still much smaller than Earth’s Moon. It’s like a tiny potato-shaped rock that orbits very close to Mars. Phobos is so close that it rises in the west and sets in the east, opposite to what we see with our Moon on Earth.
Deimos, on the other hand, is even smaller and farther away. It’s like a little speck in the Martian sky, moving slowly around the planet.
These two moons are mysterious because they are irregular in shape and much smaller than our Moon. Scientists think they might be captured asteroids and are fascinating objects for future missions to study. So, when you think of Mars, remember it has two tiny moons dancing around it in the vast space!
5. Mars has Water Ice in its Polar Ice Caps and Subsurface
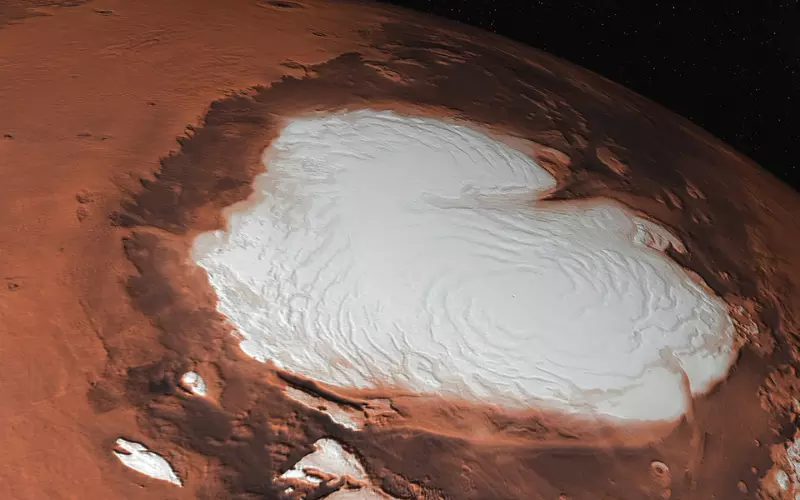

Did you know that Mars has ice? Yes, it’s true! Like on Earth, Mars has its kind of ice, but it’s not the kind you put in your drink. Mars has water ice, which is like frozen water.
This ice is mainly found in the polar ice caps of Mars, which are like the planet’s frozen tips. Think of them as Mars’ ice cream cones, but instead of ice cream, they’re filled with ice made of water. There’s also ice hiding under the ground, below the surface.
Having water ice on Mars is a big deal because it could be super helpful for future astronauts who want to visit or live there. They can melt the ice to get water and use it for other things. So, while Mars might seem like a dry, desert-like place, it does have a little bit of ice hidden away, waiting for explorers to discover and use.
6. Mars Is About Half the Size of Earth
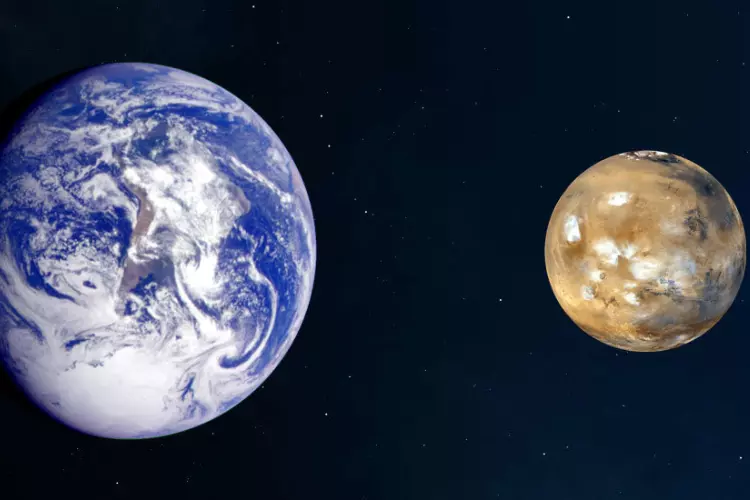

Mars is like Earth’s little sibling up in the sky. It’s about half the size of our home planet. If Earth were a big pizza, Mars would be like a smaller, personal-sized pizza.
Because it’s smaller, Mars has some differences. It has weaker gravity, so things would feel lighter there. If you jumped on Mars, you could jump much higher than on Earth.
But there’s a downside, too. Mars doesn’t have a thick blanket of air like Earth, so you can’t breathe there without a spacesuit. It’s also cold, and the landscapes are like a desert with many reddish-brown rocks and dust.
Even though Mars is smaller and quite different, scientists are curious about it. They’ve sent robots and rovers to explore its surface and learn more about this little neighbour in our solar system. Who knows, someday, people will visit Mars, too!
7. You Would Weigh Less on Mars than You Do on Earth

Here’s a remarkable fact: if you were to stand on Mars, you would weigh less than you do on Earth. That’s because Mars is smaller and has less gravity. You see, gravity is what keeps us grounded on Earth.
It’s like an invisible force that pulls everything towards the ground. On Mars, the force of gravity is weaker than on our home planet. It’s about one-third as vital. So, if you weigh 90 pounds on Earth, you’d only weigh around 30 pounds on Mars. Imagine feeling lighter and being able to jump higher! But wait to pack your bags.
While it might be fun to weigh less, living on Mars is challenging because it has a thin atmosphere, extreme temperatures, and no breathable air. So, for now, let’s enjoy Earth’s gravity and keep dreaming about space adventures!
8. Mars May Have Once Been Habitable

Did you know that Mars, our neighbouring planet, might have been a bit like Earth in the past? Scientists think that a long time ago, Mars had conditions that could have supported life. It had water, necessary for living things, and a thicker atmosphere that could have kept the planet warmer.
Imagine Mars as a possible home for Martian creatures, like Earth’s animals and plants. But something changed over time. Mars lost its thick atmosphere and most of its water, becoming the cold, dry planet we see today.
Scientists are like space detectives, trying to learn more about Mars’ history. They send rovers and spacecraft to explore and find clues. By studying Mars, we might discover if life existed or if it could in the future. So, while Mars isn’t habitable now, it’s a big space mystery waiting to be solved!
9. There is Evidence of Ancient Life on Mars

Guess what? Scientists have found some fascinating clues on Mars that suggest there might have been life there a long, long time ago!
Imagine you’re a space detective, and you’re looking for signs of life. These clever scientists used their space gadgets to study Martian rocks and soil. They found tiny things that looked like the ancient fossils on Earth.
These Martian fossils are super tiny and not like dinosaurs or big creatures. They’re more like microscopic hints that something living might have been on Mars billions of years ago. It’s like finding a puzzle piece and wondering what the whole picture looks like.
Now, scientists are excited and curious. They want to keep exploring Mars to learn more about its history and if it ever had living neighbours. It’s like reading a fascinating mystery book, but this one is happening on another planet!
10. There are Plans to Send Humans to Mars Soon

Exciting news, folks! There are big plans to send humans to Mars shortly. Imagine astronauts walking on the dusty red surface of the Martian planet, just like in your favourite space movies!
One of the big players in this cosmic adventure is NASA, the United States space agency. They plan to send a crewed mission to Mars, aiming for the 2030s. That might seem far away, but it’s just around the corner in space terms.
This mission will be a long road trip through space. Astronauts must prepare for a journey that takes many months to return to Mars. They’ll have to figure out how to survive on Mars, where the air is thin and the weather is wild.
So, while Mars still has a population of zero for now, please keep your eyes on the sky because soon, there might be real-life Martians taking their giant leap for humankind!
Let’s Know More About Mars
Why is Mars Often Called the “Red Planet”?

Mars is often called the “Red Planet” because of its reddish appearance in the night sky. This reddish colour comes from the rusty, iron-rich rocks and dust on its surface. Imagine a planet covered in many tiny, red-coloured particles, and that’s Mars!
The planet’s thin atmosphere also plays a part. It scatters sunlight differently than Earth’s thicker atmosphere, making Mars look even redder from a distance. Looking up at the night sky, we can easily spot Mars because of its distinctive red glow.
So, when people talk about the “Red Planet,” they describe Mars’ unique and captivating reddish colour, making it stand out among the other planets in our solar system.
What are the Names of Mars’ Two Moons?

Mars has two moons, and their names are Phobos and Deimos. Phobos is the larger of the two, and its name means “fear” in Greek mythology. Deimos is the smaller one named after the Greek word for “terror.” These names reflect these moons’ scary and swift nature, as they were named after the sons of the Greek god of war, Ares (equivalent to Mars in Roman mythology).
Unlike Earth’s moon, which is quite big and bright, Phobos and Deimos are much smaller and dimmer. They appear like tiny dots in the Martian sky. These moons have been a mystery for scientists, and they continue to study them to learn more about the Red Planet and its fascinating moons.
How do Scientists Study Mars from Earth?

Scientists use clever tools to study Mars from Earth because visiting Mars in person is tricky. Here’s how they do it:
- Telescopes: Think of these as giant, super-powered binoculars. They help scientists see Mars far away and study its surface and weather.
- Rovers: These are like robot explorers that we send to Mars. Rovers like Curiosity and Perseverance have cameras and instruments to analyze rocks, soil, and the atmosphere.
- Orbiters: These are like satellites around Mars. They take pictures and gather data from above, helping us map the planet’s surface and study its climate.
- Radio Signals: Scientists use big antennas on Earth to send signals to Mars. By studying how long it takes for signals to travel to and from Mars, they can learn about its atmosphere and weather.
- Mars Meteorites: Sometimes, pieces of Mars come to Earth as meteorites. Scientists study these rocks to learn more about Mars’s history.
So, even though Mars is far away, scientists have found clever ways to learn a lot about it without ever leaving our home planet.
What challenges would Living on Mars present for humans?

Living on Mars would come with several significant challenges for humans:
- Harsh Environment: Mars has a thin atmosphere that lacks oxygen, making it impossible for humans to breathe without life support. It’s also icy, with temperatures often dropping far below freezing.
- Radiation: Mars lacks a protective magnetic field and thick atmosphere, so its surface is exposed to harmful radiation from space and the sun. Long-term exposure to this radiation can be dangerous to human health.
- Limited Resources: Water, food, and other essential resources are scarce on Mars. Humans must bring supplies from Earth or find ways to extract and recycle resources from the Martian environment.
- Gravity Differences: Mars has only about 38% of Earth’s gravity. Living in low gravity for extended periods could lead to health problems like muscle and bone loss.
- Transportation: Traveling to and from Mars is a long and risky journey. Any trip-related issues could be life-threatening, and supplies must be carefully planned.
- Extreme Weather: Mars experiences dust storms that can cover the entire planet and last for weeks. These storms could disrupt daily life and damage equipment.
Despite these challenges, scientists and engineers are working on solutions to make the human colonization of Mars a reality. Still, it will require careful planning and innovative technologies to ensure the safety and well-being of future Martian residents.
What are the Potential Benefits of Living on Mars?
Living on Mars could offer several potential benefits:
- Scientific Discovery: Mars is a fascinating planet with a unique history. Studying it up close could help us learn more about the solar system’s origins and evolution and the possibility of past or present life on Mars.
- Space Exploration: Establishing a human presence on Mars could be a stepping stone for further exploration of solar systems. It could be a base for missions to other celestial bodies, like asteroids or the moons of Jupiter and Saturn.
- Resource Utilization: Mars has resources like water ice, which could be turned into drinking water and used for growing plants and generating oxygen. These resources could support future colonies and reduce the need to transport supplies from Earth.
- Technological Innovation: Developing the technologies needed to survive on Mars could lead to advancements in areas like renewable energy, life support systems, and recycling, which could benefit life on Earth.
- Backup for Humanity: Having a presence on Mars could serve as a “backup” for humanity. In case of catastrophic events on Earth, a colony on Mars could ensure the survival of our species.
While many challenges exist to overcome, the potential benefits of living on Mars could be far-reaching and transformative for scientific understanding and space exploration’s future.
Conclusion
Mars doesn’t have any people living on it yet. It’s a quiet, empty place in space. But scientists and space experts are thinking about sending humans there in the future. Right now, we have robots and machines exploring Mars to learn more about it.
It’s exciting to think that one day, people might call Mars their home, but there are many challenges to overcome, like its thin air and frigid temperatures. So, for now, Mars is a planet waiting for its first human visitors, and we’ll have to keep watching and learning about it from afar.
FAQ’s
Can humans live on Mars?
Scientists plan for future Mars colonization but face challenges like harsh conditions and life support.
How much population can Mars hold?
Uncertain, but likely small due to limited resources and harsh environment.
How much is 1 Mars year?
About 1.88 Earth years.
Has any human been to Mars?
Humans have yet to visit Mars.
Is Mars hot or cold?
Mars is generally cold, averaging around -80°F (-62°C).
Has India landed on Mars?
Yes, with the Mars Orbiter Mission (Mangalyaan) in 2013.
Why is Mars red?
Due to iron oxide (rust) on its surface.
Is Mars older than Earth?
No, both formed around the same time, about 4.5 billion years ago.
How long is one day on Mars?
It takes about 24.6 hours, close to Earth’s day length.
Who went to Mars first?
No humans have visited Mars yet; only robotic missions have explored it.
Does India have a flag on the moon?
India’s lunar mission (Chandrayaan) did not carry a flag.
What is 1 hour on Mars?
Approximately 1.03 Earth hours.
Is Mars bigger than Earth?
No, Mars is smaller than Earth.
Is there any water on Mars?
There is frozen water on Mars, and there may be underground liquid water.

Hi there, I’m Emily Buono, and I’m thrilled to introduce myself! Currently, I’m part of two fantastic places: I work as a VisEx at the New England Aquarium and as an RAS at MGH CCM.
I completed my education at the Mass General Research Institute and Stonehill College, which is located in Valatie Colony, New York, in the United States.
Now, here’s the exciting part: I absolutely adore animals! They captivate me, and I’m always eager to learn more about them. In fact, I write articles all about these incredible creatures.
In the past, I’ve worn many hats, such as being a biologist at the Maria Mitchell Association, a cashier, a floor organizer, and a visitor experience and research animal specialist.
My passion lies in exploring the world of animals and helping others understand them better. So, if you ever have questions about animals, feel free to reach out. I’m here to make animal info easy and fun to grasp!












