Welcome to our new blogpost featuring the fascinating slug animal! Slugs, also known as gastropods, are a unique group of animals that belong to the mollusk family. In this post, we will explore the history, facts, size, habitat, and classification of these intriguing creatures.
Slugs have a long history on Earth, with their origins traced back to over 500 million years ago. These animals have evolved and adapted to various environments, making them one of the most successful groups of animals on our planet. Despite their humble appearance, slugs play vital roles in ecosystems as both decomposers and prey for other animals.
In terms of size, slugs come in different shapes and lengths. While the average slug measures about 1 to 2 inches in length, some species can grow up to 10 inches! They have a slimy body that enables them to move effortlessly across different surfaces. Slugs are found in a wide range of habitats, from gardens and forests to deserts and even underwater environments.
When it comes to classification, slugs are part of the mollusk phylum, specifically the Gastropoda class. Within this class, there are over 60,000 known species of slugs, showcasing their incredible diversity. These animals can be found worldwide, except in extreme cold regions such as Antarctica.
As we delve deeper into the world of slug animals in future posts, we hope to bring you more exciting information about these peculiar creatures. Stay tuned for more interesting facts about their behaviors, unique adaptations, and the roles they play in our ecosystem.
History of Slug’s
Slugs are fascinating creatures that have been roaming the Earth for millions of years. These slimy animals, also known as gastropods, belong to the same classification as snails. However, unlike their shelled relatives, slugs don’t have a protective outer covering.
The history of slugs goes back to the time when dinosaurs ruled the planet. Fossil records show evidence of slug-like creatures that lived in the oceans around 500 million years ago. As time passed, slugs adapted to various environments and eventually found their way onto land. Today, slugs can be found in almost every corner of the world, from damp forests to urban gardens.
One of the reasons why slugs have been so successful is their ability to survive in different conditions. They are capable of eating a wide range of plants, including vegetables and fruits, which can make them a nuisance in gardens and farms. However, slugs also play an essential role in the ecosystem as decomposers, feeding on dead plant material and enriching the soil with their waste.
Despite their humble appearance, slugs have many interesting characteristics. They move by secreting a slime that helps them glide along surfaces, leaving behind a unique trail. Some species of slugs can even regenerate lost body parts, such as their tentacles. Others use chemical signals to communicate and find potential mates.
In conclusion, slugs have a long history on Earth, dating back millions of years. Their adaptability and unique traits have made them successful in various environments. While they may not always be welcomed in our gardens, slugs are an integral part of the natural world, playing important roles as both pests and vital contributors to the ecosystem.
Importance of Slug
Slugs are small animals that may not seem very important at first glance, but they actually play a significant role in our environment. One reason why slugs are important is because they help break down decaying matter. When plants and animals die, they start to decompose, and slugs play a crucial part in this process by consuming the decaying matter. By doing so, they contribute to the nutrient cycle, helping to release important nutrients back into the soil.
Another reason why slugs are important is because they serve as a food source for other animals. Many creatures such as birds, frogs, and hedgehogs rely on slugs as a part of their diet. Without slugs, these animals would struggle to find enough food to survive. Additionally, slugs also help control the population of certain pests. They eat insects and pests that can damage crops, which is beneficial for farmers and gardeners.
Lastly, slugs are also an important indicator of environmental health. Since they have a high level of sensitivity to environmental changes, their presence or absence can provide valuable information about the health of a particular ecosystem. Monitoring slug populations can help scientists better understand the impact of pollution or habitat destruction on an area.
In conclusion, slugs may be small creatures, but they have a big impact on our environment. They contribute to the decomposition process, serve as a food source for other animals, help control pests, and provide valuable information about our ecosystems. Recognizing the importance of slugs can help us appreciate the role they play in maintaining a balanced and healthy environment.
Amazing Facts About Slug’s
1. Slugs are soft-bodied animals that belong to the mollusk family.
2. They come in various colors, such as black, gray, brown, and even bright yellow.
3. Slugs have a slimy mucus coating on their bodies which helps them move and protects them from drying out.
4. These animals do not have a shell, unlike other mollusks like snails.
5. Slugs are found all around the world, except in very dry or extremely cold areas.
6. They prefer damp and dark habitats like gardens, forests, and meadows.
7. Slugs are nocturnal, which means they are most active during the night.
8. They move by gliding and sliding along a slimy trail they leave behind.
9. Slugs have a remarkable ability to regenerate, meaning they can regrow certain body parts if injured or cut.
10. They are herbivores and feed on a variety of plants, including flowers, leaves, vegetables, and fruits.
11. Slugs have a rasping mouthpart called a radula, which they use to scrape and consume plant material.
12. These animals are known for their slow and steady pace, as they have no legs and rely on their muscular foot for locomotion.
13. Slugs can reproduce both sexually and asexually, laying many small eggs in clusters or individually.
14. Some slug species are hermaphroditic, which means they possess both male and female reproductive organs.
15. Slugs play an essential role in ecosystems as decomposers, breaking down organic matter and cycling nutrients back into the soil.
Can we keep Slug as our Pet?
Keeping a slug as a pet can be a unique idea! Slugs are small creatures that can be found in gardens or other damp places. They have slimy bodies and move slowly, leaving behind a trail of slime. While slugs may seem intriguing to some, it is not a good idea to keep them as pets.
Firstly, slugs are best left in their natural habitats. They play an important role in our ecosystem by breaking down dead plants and other organic matter. This helps to keep our gardens and forests healthy. By taking them out of their natural environment, we disrupt the balance of nature and harm their population.
Secondly, slugs have specific needs that are hard to replicate in a home. They require a moist environment and a steady food source, such as decaying leaves or fruits. It can be challenging to maintain these conditions indoors, especially for a young student. Additionally, slugs are not very interactive pets. They do not play, respond to their owners, or perform tricks like other pets do. This can make it less enjoyable to keep them as pets.
In conclusion, it is best to admire slugs from a distance rather than keeping them as pets. They are fascinating creatures that have an important role in our environment. Let’s appreciate them in their natural habitat and do our part in preserving their existence.
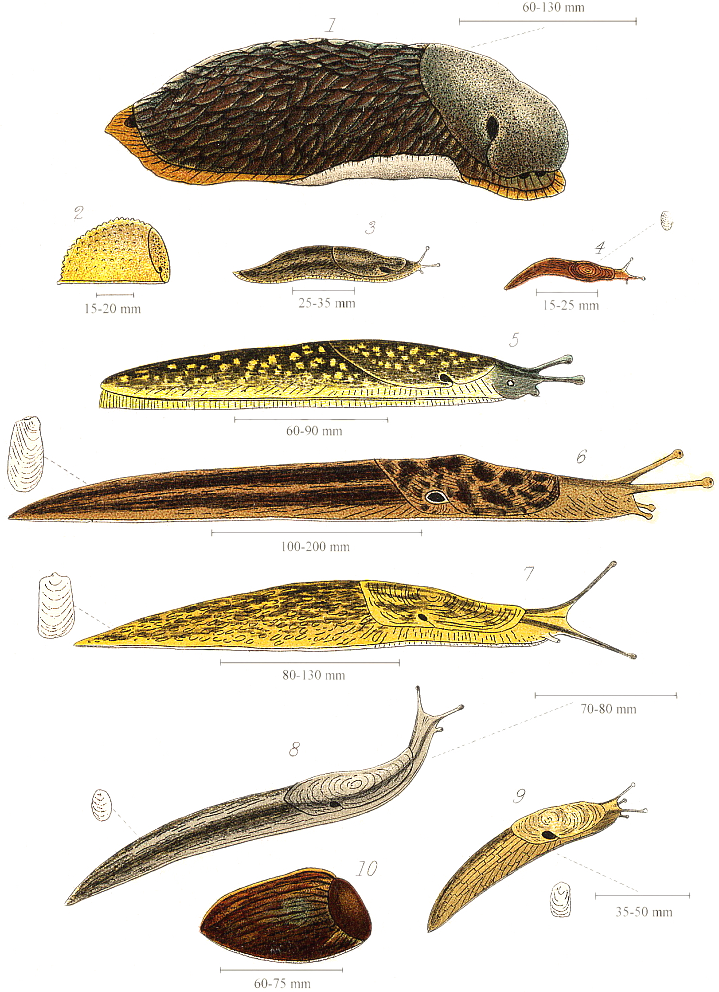
Size of Slug’s
A slug is a small and slimy animal that can be found in many places around the world. Despite being small, slugs can vary in size depending on the species. Some slugs are as small as a fingertip, measuring about 0.5 centimeters in length. They may be difficult to spot due to their tiny size and their ability to blend in with their surroundings.
Other slugs can grow to be much larger. Some species can reach up to 10 centimeters in length. That’s about the size of an adult’s thumb! These larger slugs are more visible and easier to spot because of their size. Slugs have soft and flexible bodies that allow them to easily slide across different surfaces and fit into small spaces.
The size of a slug can also depend on its age and environment. It takes time for a slug to grow from a tiny hatchling into a fully grown adult. During this time, they may shed their skin several times in order to accommodate their growing body. Slugs can be found in various habitats, such as gardens, forests, and even underwater. Their size and adaptability enable them to live in diverse environments.
Overall, slugs can come in different sizes, from tiny to quite large. Their size can depend on factors like species, age, and environment. Remember to keep an eye out when exploring nature, as you might spot these interesting creatures, regardless of their size!
Habitat of Slug’s
Slugs, a type of small animal, can be found in many different habitats across the world. Their homes can vary depending on the species of slug and the climate they live in. However, slugs are generally found in damp and moist environments.
One common habitat for slugs is in gardens. Slugs are often seen in flower beds, vegetable patches, and other parts of gardens. The damp soil and vegetation provide them with plenty of food and the moisture they need to survive. However, if these areas become too dry, slugs may seek out other places to live.
Another habitat for slugs is in forests or wooded areas. These environments offer the moisture and shelter that slugs need. Slugs can often be found under fallen leaves, rocks, or logs, where they are protected from drying out and from predators. They may also climb up plants or trees to feed on leaves or decaying organic matter.
Lastly, slugs can also be found near bodies of water such as ponds or streams. They are attracted to these areas because of the high humidity levels and the availability of water. Slugs in water habitats may live in the mud or hide in vegetation near the water’s edge.
In summary, slugs inhabit various environments, including garden beds, forests, and near bodies of water. They thrive in damp and moist habitats, where they can find food and shelter. Whether in gardens, forests, or by water, slugs adapt to their surroundings and play a unique role in their ecosystems.
Classification of Slug’s
Slugs are an interesting type of animal that belong to the mollusk group. Mollusks are creatures that have soft bodies and often live in water. However, slugs are unique because they can also be found on land.
When we look at the classification of slugs, we can see that they belong to the class Gastropoda. This means that they are related to other animals like snails and sea slugs. Within the class Gastropoda, slugs are further divided into different families, such as Arionidae or Limacidae. Each family has its own specific characteristics and features that distinguish them from one another.
Slugs are known for their slimy bodies and lack of a protective shell, which is different from their relatives, snails. They move by gliding along a trail of slime that they produce themselves. Slugs are also typically herbivores, which means they feed on plants. However, some slugs can also be scavengers and eat decaying plant matter or even other slugs.
In conclusion, slugs are fascinating animals that are classified as gastropods. They have soft bodies and can be found both on land and in water. Slugs play an important role in the ecosystem as herbivores or scavengers, depending on their species. Although they may not be the most popular animals, understanding their classification can help us appreciate the diversity of life on our planet.
Different Types of Slug’s
1. Leopard Slug:
– It is one of the largest slug species with distinctive leopard-like spots on its body.
– They are common in gardens and parks, and feed on decaying plant matter.
– Leopard slugs are hermaphrodites, meaning they have both male and female reproductive organs.
2. Banana Slug:
– Found in the forests of North America, banana slugs are known for their bright yellow color.
– They have a slimy trail that helps them move and protect from predators.
– Banana slugs are important decomposers, breaking down dead plants and returning nutrients to the soil.
3. Garden Slug:
– Garden slugs are one of the most common types found in outdoor spaces.
– They can cause damage to crops and plants by feeding on leaves and vegetables.
– These slugs prefer moist environments, especially during rainy seasons.
4. Ghost Slug:
– The ghost slug is an unusual species that is almost transparent and lacks pigmentation.
– They are typically found in damp areas such as under logs or stones.
– Ghost slugs feed on fungi and decomposing matter, helping to break down organic material in their habitat.
5. Tawny Garden Slug:
– Tawny garden slugs are among the most common slug species worldwide.
– They have a slimy mucus coating that provides protection and helps them move smoothly.
– These slugs predominantly feed on decaying organic matter, but can also cause damage to crops and garden plants.
6. Great Grey Slug:
– Great grey slugs are native to Europe and are known for their large size.
– They possess a slime layer that helps protect them from predators and provides moisture.
– These slugs can eat a wide variety of plant materials and are considered both pests and decomposers.
7. Spanish Slug:
– The Spanish slug is an invasive species that has spread across Europe.
– They are larger and more aggressive than many other slug species, causing significant damage to crops and gardens.
– Spanish slugs are known for their voracious appetite and ability to quickly reproduce.
8. Black Slug:
– Black slugs are commonly found in gardens, forests, and other outdoor habitats.
– They have a dark black color and are usually slimy to touch.
– These slugs feed on dead plant matter, mushrooms, and other decaying organic material.
9. Ashy Grey Slug:
– The ashy grey slug has a pale grey color with a slightly wrinkled appearance.
– They are commonly found in gardens and fields, feeding on decaying vegetation.
– Ashy grey slugs play a crucial role in the ecosystem by helping to break down plant matter and recycling nutrients.
10. Greenhouse Slug:
– Greenhouse slugs are adapted to living in warm and humid environments, making them common pests in greenhouses.
– They can cause significant damage to crops, feeding on leaves, stems, and fruits.
– These slugs are often attracted to the moisture and shelter provided by greenhouse structures.
Geographical Presence of Slug
The slug is a type of animal that can be found in many different parts of the world. It is often found in regions with cool, moist climates, such as forests, gardens, and even in our own backyard. Slugs like to hide in damp places during the day and come out at night to feed on plants and decaying matter.
While slugs can be found in many regions, there are some places where they are not found. Slugs do not usually live in very hot and dry regions, like deserts, because they need moisture to survive. They also prefer to stay away from places with very cold temperatures, like snowy mountains, as it is harder for them to move and find food in those conditions.
In summary, slugs can be found in regions with cool, moist climates, but not in very hot deserts or cold snowy mountains. These slimy creatures play an important role in recycling organic matter and are often considered pests in gardens. So next time you notice a slug in your garden, remember that it is a fascinating animal that is well-suited to its habitat.
Diet of Slug’s
The diet of a slug consists mainly of plants and leaves. These slimy creatures enjoy munching on various types of vegetation. They like to feed on leaves of different shapes, sizes, and colors. Slugs are not picky eaters and will devour almost any plant they come across. They can even eat decaying matter and fungi found in the soil, as well as flowers and vegetables in gardens.
When it comes to feeding, slugs use their radula, which is like a rough tongue, to rip apart the leaves they eat. They have a special saliva that helps them break down the plant material as it enters their digestive system. Slugs are slow eaters and take their time to consume their food. They can be found grazing on foliage during the nighttime, as they are more active in the dark. Sometimes, you may notice slimy trails left behind by slugs, indicating their presence during their feeding journey.
Gardens and other green spaces can be great places for slugs to find food. However, they can also become pests, as they may eat crops that are meant for people to eat. Some gardeners try different methods to protect their plants from slugs, like putting up barriers or using non-toxic repellents. Slugs play a small role in the ecosystem, as they help break down dead plant material and enrich the soil. So, next time you come across a slug, remember that it plays a part in the natural cycle of life!
Locomotion of Slug’s
Slugs are unique animals that move in a slow and fascinating way. They do not have legs like most animals do, but instead, they have a soft and slimy body. This helps them to move smoothly across different surfaces.
To understand how slugs move, imagine a wave flowing through their body. They use this wave-like motion to push themselves forward. The underside of a slug is covered in a slimy substance called mucus. It helps to reduce friction and allows them to glide without getting stuck. Slugs also have tiny muscles on the bottom of their body that contract and relax, helping them to move forward inch by inch.
This slow locomotion of slugs may not be as fast as other animals, but it allows them to explore their surroundings. They can crawl over rocks, leaves, and even up walls with their mucus. It’s quite interesting to observe how slugs gracefully slide along the ground, using their unique wave motion.
Social and Sexual Behaviour of Slug’s
Slugs, like many other creatures, engage in social and sexual behaviors that are important for their survival and repopulation. They may not look like they do much, but slugs have their own ways to interact and find mates.
In terms of social behavior, slugs communicate with each other by leaving behind a slimy trail. This trail contains chemicals that other slugs can detect. The chemicals tell them about the slug’s presence, whether it’s a potential mate or a competitor. In some cases, slugs even form groups, moving together to find food or to improve chances of reproduction. This way, they can benefit from each other’s company and increase their chances of survival.
When it comes to sexual behavior, slugs are hermaphrodites, which means they have both male and female reproductive organs. This allows them to reproduce with any other slug they encounter. During mating, slugs exchange sperm through a process called reciprocal fertilization. Each slug injects sperm into the other, enabling both to lay eggs afterward. This mutual exchange helps to ensure the survival of their species.
In summary, slugs engage in social behaviors to communicate with others, relying on their slimy trails to leave messages and establish connections. Additionally, their sexual behavior involves mutual exchange of sperm, enabling both partners to lay eggs. By understanding these aspects of slug behavior, we can appreciate the uniqueness of these slimy creatures and the fascinating ways they interact with their environment and each other.
Reproduction and Lifecycle of Slug’s
Slugs reproduce by laying eggs. The female slug produces up to 30 eggs at a time. She first finds a suitable spot in damp soil or decaying matter to lay her eggs. The eggs are very small and transparent and are laid in clusters. It takes about two to four weeks for the eggs to hatch.
Once the eggs hatch, baby slugs, called juveniles, emerge. They are very tiny and have a transparent body. Juvenile slugs go through a process called metamorphosis, where they go through different stages of development. As they grow, their bodies become less transparent and they start to develop the slimy mucus that slugs are known for. It takes several months for the juvenile slugs to reach maturity.
Once they reach maturity, adult slugs continue to grow until they are fully developed. They can live up to three years, depending on their species and environment. Adult slugs have both male and female reproductive organs, allowing them to reproduce with any other adult slug they encounter. This phenomenon is called hermaphroditism. During mating, two slugs exchange sperm to fertilize each other’s eggs. After mating, the slugs lay their eggs and the cycle begins again.
In summary, slugs begin their life cycle by laying eggs in suitable environments. The eggs hatch into tiny and transparent juveniles, which slowly grow into mature adult slugs. These adult slugs reproduce by exchanging sperm with another slug and then lay their own eggs to continue the life cycle.
Threats to Slug’s
There are many threats to the safety and survival of slugs. One major threat comes from humans and their activities. When people use pesticides in their gardens or on their crops, it can harm slugs. These chemicals are made to kill insects, but unfortunately, they can also harm other small creatures like slugs. So, when slugs come into contact with these toxic substances, it can make them very sick or even cause them to die.
Another threat that slugs face is from predators. Slugs are slow-moving creatures, so they can’t easily escape from animals that want to eat them. Some common predators of slugs include birds, frogs, and even some types of beetles. These animals see slugs as a tasty meal and will go after them whenever they can. This puts slugs at risk of being eaten and can greatly reduce their population in certain areas.
Lastly, habitat destruction is a big threat to slugs. When humans cut down trees or clear land for buildings or agriculture, it can destroy the places where slugs live. Slugs need cool and moist environments to survive, so when their homes are destroyed, they struggle to find suitable places to live. This can lead to a decline in slug populations and even cause some species to become endangered.
To protect slugs, it’s important for people to be mindful of their actions. Using natural alternatives to pesticides can help reduce the harm to slugs and other beneficial insects. Providing safe habitats for slugs in our gardens and green spaces can also make a big difference. By understanding these threats and taking steps to protect slugs, we can help ensure their survival in the future.
Conclusion
In the animal kingdom, slugs are fascinating creatures. They can be found in various habitats around the world, from rainforests to gardens. Slugs are soft-bodied animals with a muscular foot that helps them move and leave a trail of slime behind. This slime not only helps them glide smoothly, but also serves as a protection against predators.
Slugs come in different sizes and colors, ranging from small ones as tiny as a fingernail, to large ones as big as a banana. Despite their slow pace, these little creatures play an important role in the ecosystem. They are decomposers, feeding on decaying matter and helping to recycle nutrients back into the soil. In this way, they contribute to maintaining the balance of the environment.
Being a type of gastropod mollusk, slugs are classified under the same category as snails. However, unlike snails, slugs do not have a shell. Instead, they have a slimy, moist skin that helps them survive in damp environments. This adaptation allows them to live in a variety of places, from forests to deserts, as long as there is enough moisture to keep them hydrated.
Overall, slugs are remarkable animals with unique characteristics. From their slimy trails to their diverse habitats, they continue to captivate both scientists and nature enthusiasts. By learning about slugs’ history, facts, size, habitat, and classification, we gain a deeper appreciation for the incredible diversity found in the animal kingdom.
Frequently Asked Questions about Slug’s (FAQ’s)
Q: What is a slug?
A: A slug is a type of mollusk, specifically a gastropod, that lacks a shell.
Q: How do slugs move?
A: Slugs move by gliding along a trail of mucus they produce.
Q: What do slugs eat?
A: Slugs are primarily herbivorous and feed on plants, leaves, fruits, and vegetables.
Q: Are all slugs harmful to plants?
A: While many slugs can be pests and cause damage to plants, not all slugs feed on plants exclusively.
Q: Do slugs have eyes?
A: Yes, slugs have rudimentary eyes located at the tips of their tentacles.
Q: Can slugs bite humans?
A: Slugs cannot bite humans because they do not possess jaws, teeth, or a venomous sting.
Q: Where are slugs commonly found?
A: Slugs are found in various habitats worldwide, including gardens, forests, and damp areas.
Q: How long do slugs live?
A: The lifespan of a slug differs among species but is generally around one to five years.
Q: Are slugs nocturnal?
A: Yes, most slugs are nocturnal creatures and are more active during the night.
Q: Can slugs swim?
A: Slugs are adept at swimming and can move through water by undulating their muscular foot.
Q: How do slugs reproduce?
A: Slugs are hermaphrodites, meaning they possess both male and female reproductive organs. They engage in mating activities to reproduce.
Q: Are slugs harmful to humans?
A: While slugs are generally harmless to humans, they can pose a threat if ingested raw or if their slime comes into contact with open wounds.
Q: Do slugs have any predators?
A: Yes, slugs have various predators, including birds, frogs, toads, snakes, beetles, and some insects.
Q: Can slugs live in dry environments?
A: Slugs are highly susceptible to drying out, so they generally prefer damp and humid environments.
Q: How do slugs protect themselves from predators?
A: Slugs rely on their mucus to deter predators, and some species can even produce a noxious or toxic secretion.
Q: Do slugs have any economic significance?
A: While slugs can be considered garden pests, they also play a role in ecosystems by decomposing organic matter and aiding in nutrient cycling.

Hi there, I’m Emily Buono, and I’m thrilled to introduce myself! Currently, I’m part of two fantastic places: I work as a VisEx at the New England Aquarium and as an RAS at MGH CCM.
I completed my education at the Mass General Research Institute and Stonehill College, which is located in Valatie Colony, New York, in the United States.
Now, here’s the exciting part: I absolutely adore animals! They captivate me, and I’m always eager to learn more about them. In fact, I write articles all about these incredible creatures.
In the past, I’ve worn many hats, such as being a biologist at the Maria Mitchell Association, a cashier, a floor organizer, and a visitor experience and research animal specialist.
My passion lies in exploring the world of animals and helping others understand them better. So, if you ever have questions about animals, feel free to reach out. I’m here to make animal info easy and fun to grasp!